

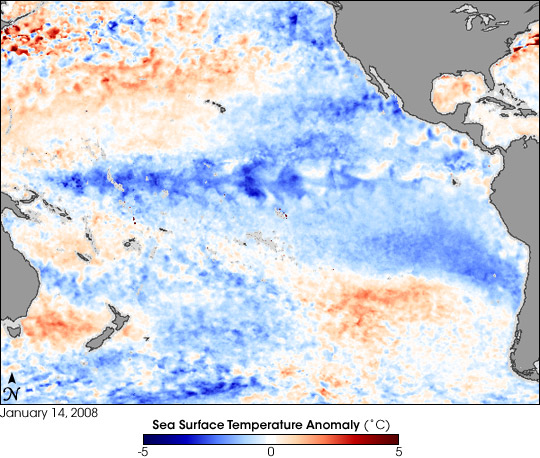
La Niña conditions often follow El Niño in the cycle known as the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). La Niña episodes are marked by stronger-than-normal easterly trade winds and below-normal sea surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. These changes in ocean temperature and atmospheric circulation have worldwide implications for weather patterns. La Niña conditions appeared in February 2007 and strengthened in October and November. La Niña conditions often peak in January, as they appeared to do in January 2008.
This image shows the temperature anomaly for the top millimeter of the Pacific Ocean’s surface—the skin temperature—on January 14, 2008, based on data from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR-E) flying on NASA’s Aqua satellite. In this image, January 14, 2008, temperatures are compared to the long-term average measured by a series of sensors that flew on NOAA Pathfinder satellites from 1985 to 1997. A strong band of blue (cool) water appears along the Equator, fanning out near North and South America. Patches of orange to red (warm) conditions appear north and south of this strong blue band. As of January 2008, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predicted that La Niña conditions would continue until spring, with a possible weakening in February 2008.
Cool ocean temperatures can impede cloud growth, leading to reduced rainfall from South America to Indonesia. In the continental United States, La Niña affects the jet stream, which in turn affects weather. Typical La Niña winter weather patterns include very cool, wet conditions in the Pacific Northwest, especially cold winter conditions on the Great Plains, and unusually dry conditions in the Southwest and Southeast. Because La Niña conditions can persist for years, such adverse weather conditions can continue. In short, continued La Niña conditions were expected to prolong the droughts in the American Southeast and Southwest.
Daily, 8-day, and monthly sea surface temperature anomaly images from AMSR-E are available from NASA Earth Observations (NEO).
You can download a 0.25-degree-resolution KMZ file of global sea surface temperature anomaly suitable for use with Google Earth.
NASA image by Jesse Allen, using AMSR-E data processed and provided by Chelle Gentemann and Frank Wentz, Remote Sensing Systems. Caption by Michon Scott.