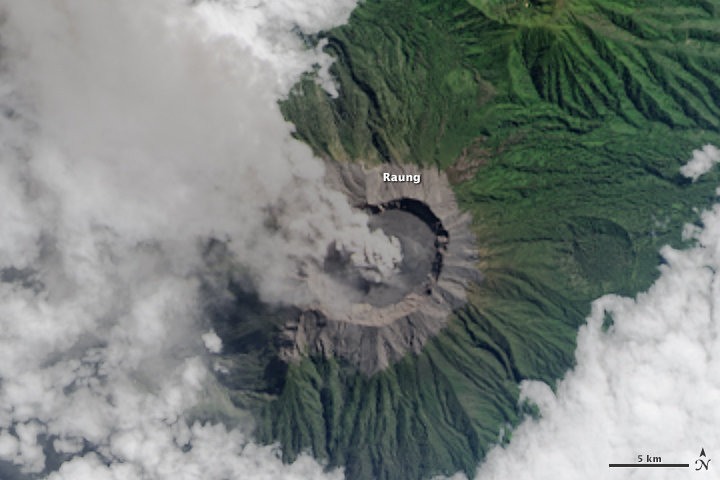
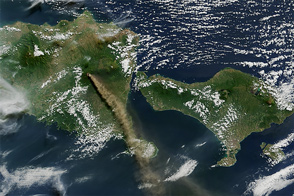
On July 27, 2015, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured a view of ash and volcanic gases drifting northwest from Mount Raung on the Indonesian island of Java. The lower image shows a closer view of the vocano’s caldera.
Mount Raung is a stratovolcano that has erupted at least 13 times in the past 25 years, according to records kept by the Smithsonian Global Volcanism program. The summit stands 3,332 meters (10,932 feet) above sea level and is capped by steep caldera that is 3 kilometers (2 miles) in diameter.
Raung’s latest eruption has been ongoing for about four weeks. The eruption has been characterized by strong lava flow and near-constant ash emissions. Ash has risen to altitudes ranging from 4 to 5 kilometers (2 to 3 miles) and has generally drifted 100 to 200 kilometers (62 to 124 miles). Shifting winds have prompted authorities to temporarily cancel flights and close airports several times in July. Ash emissions recently canceled 18 flights from Notohadinegoro Airport in East Java, according to The Jakarta Post.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Adam Voiland.
One of the most active volcanoes on the Indonesian island of Java spewed fresh ash and gases in early July 2015.