

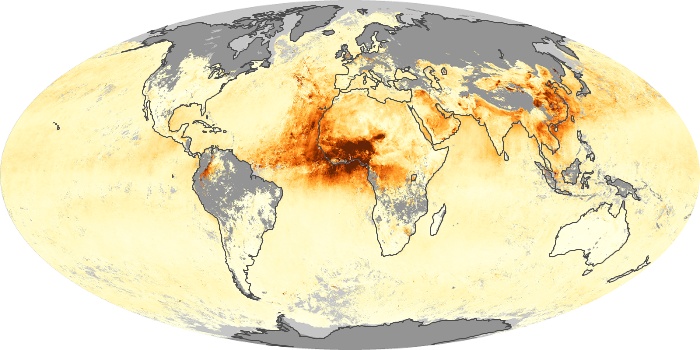
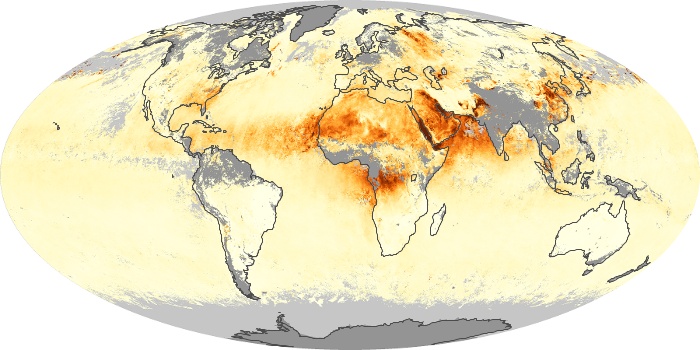
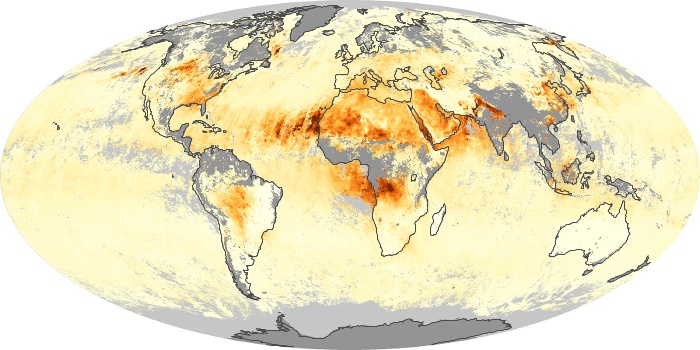
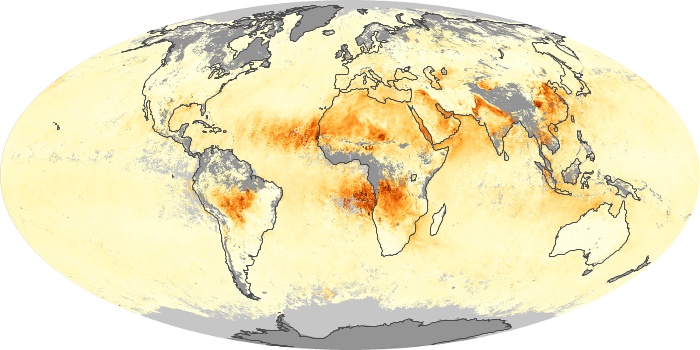
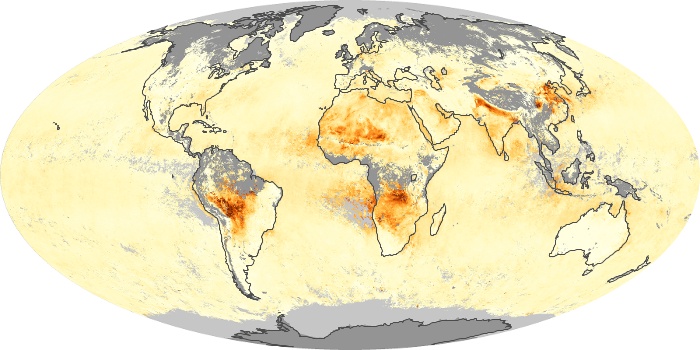
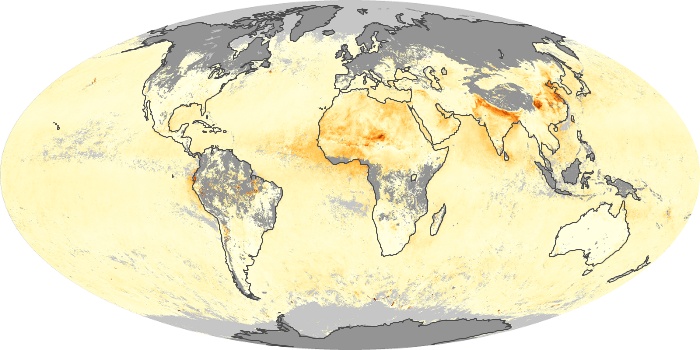
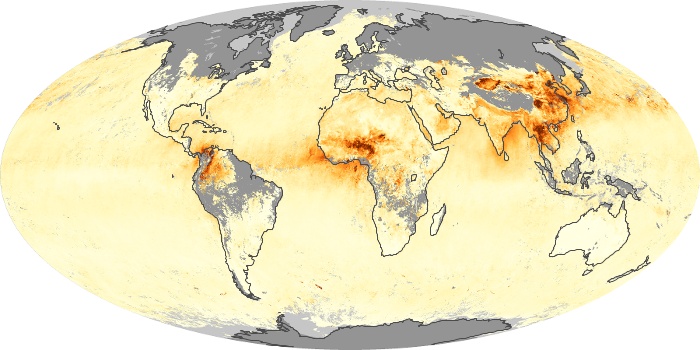
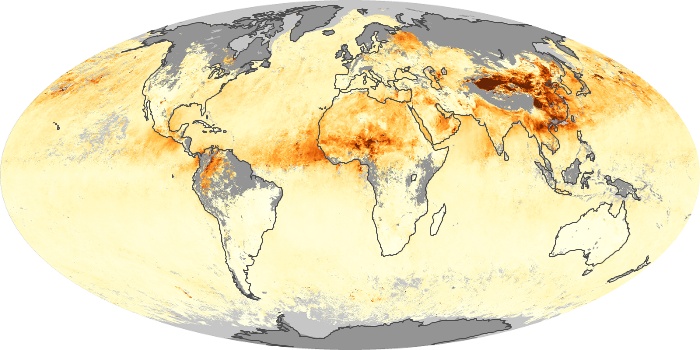
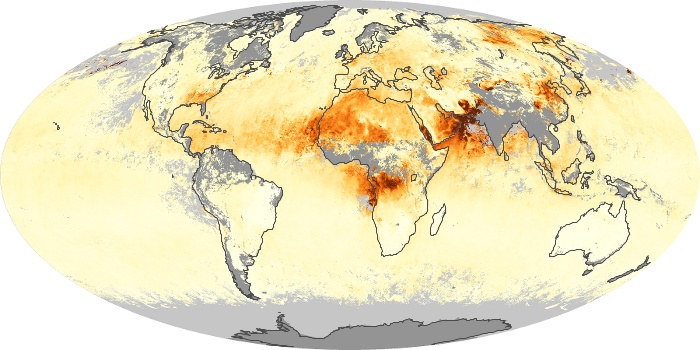
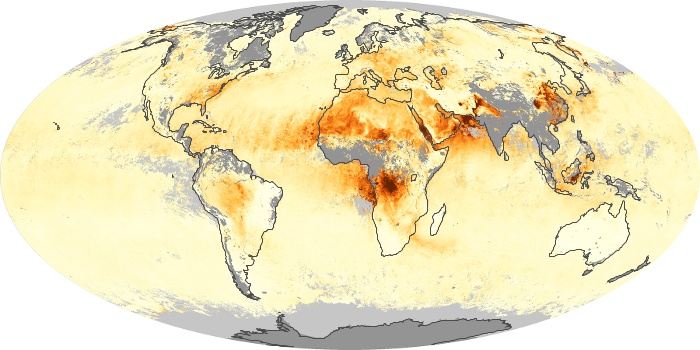
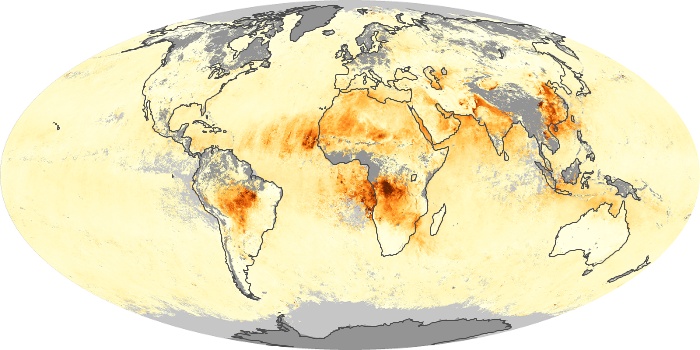
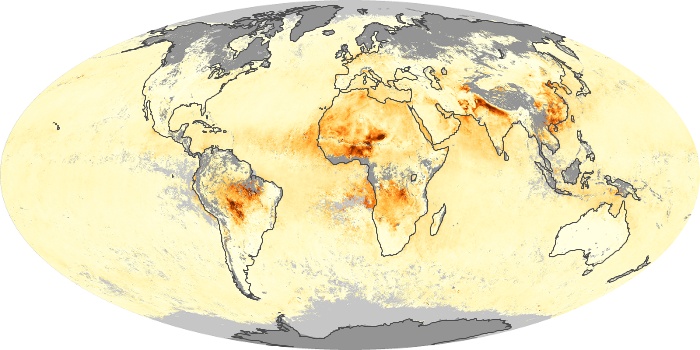
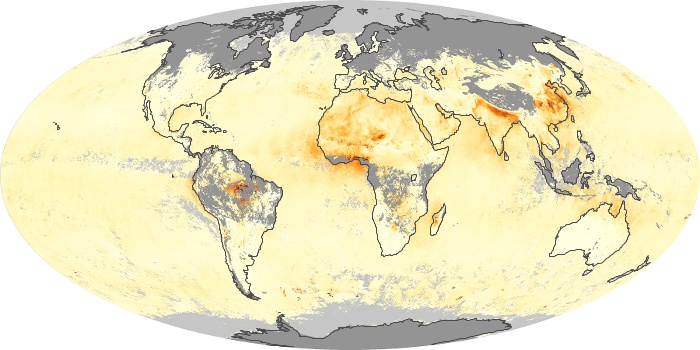
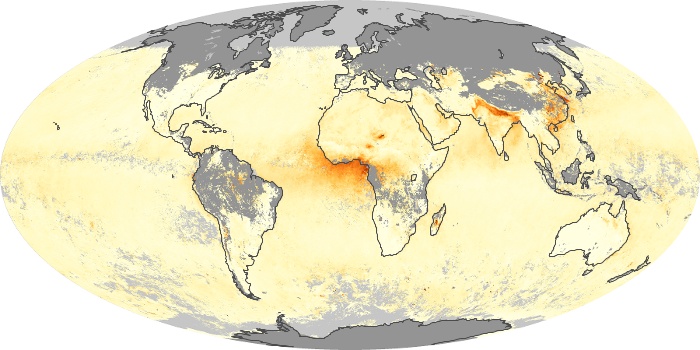
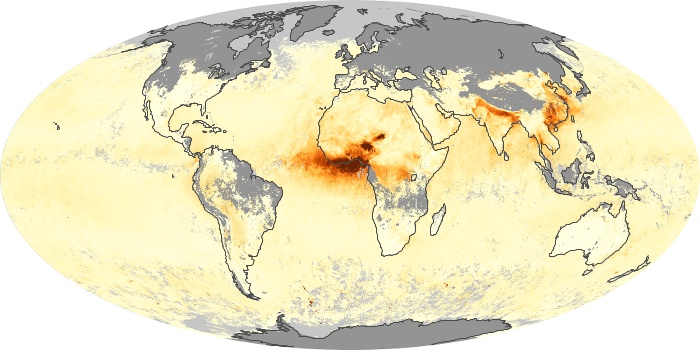
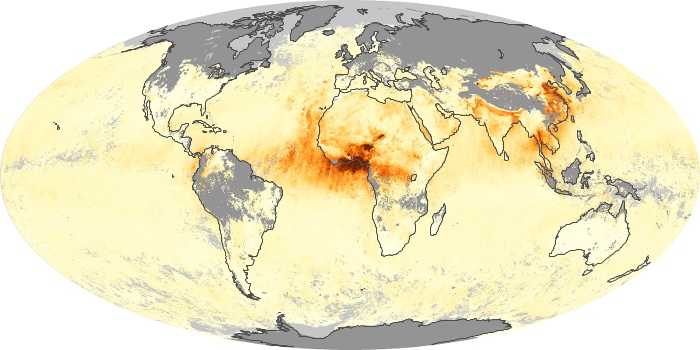
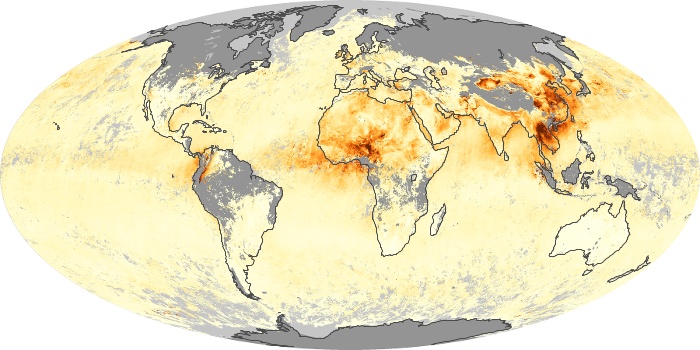
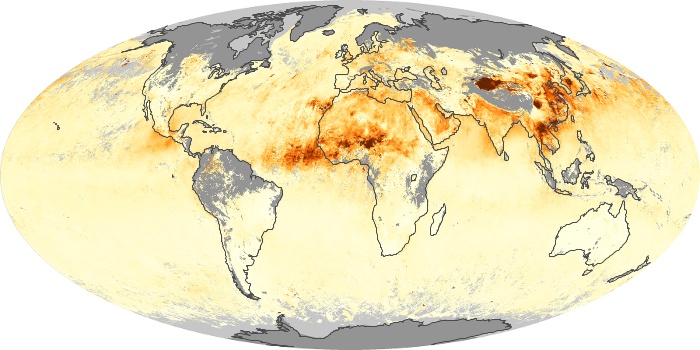
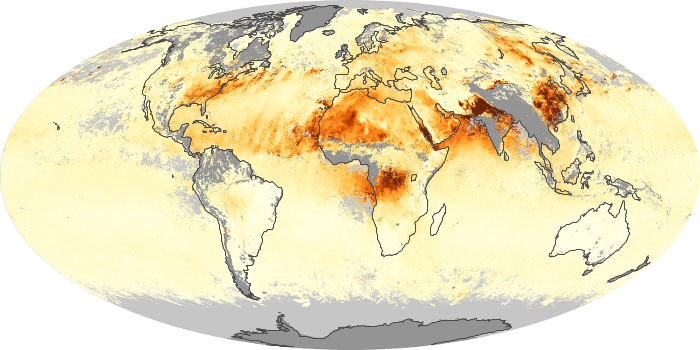
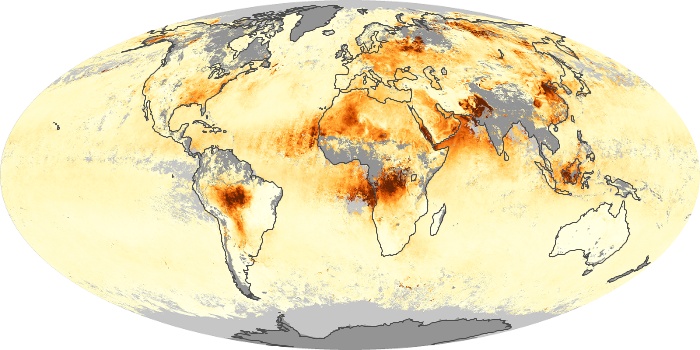
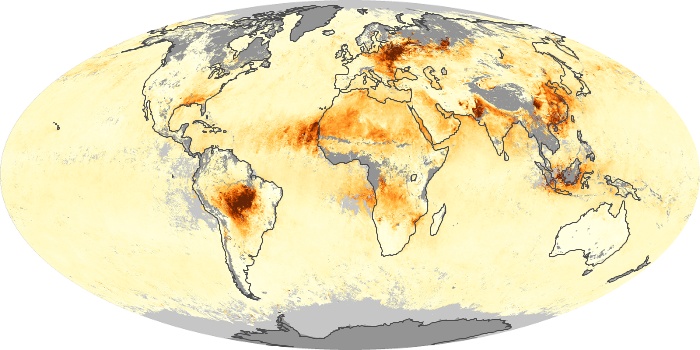
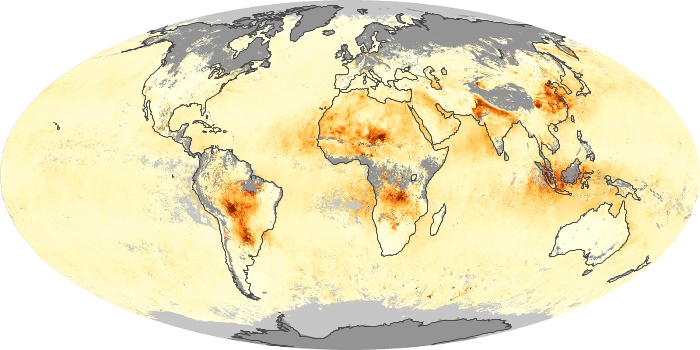
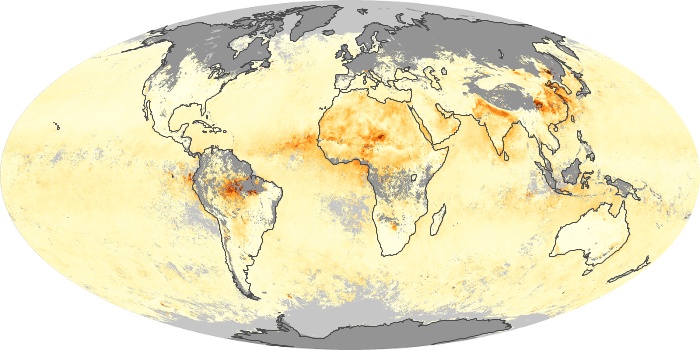
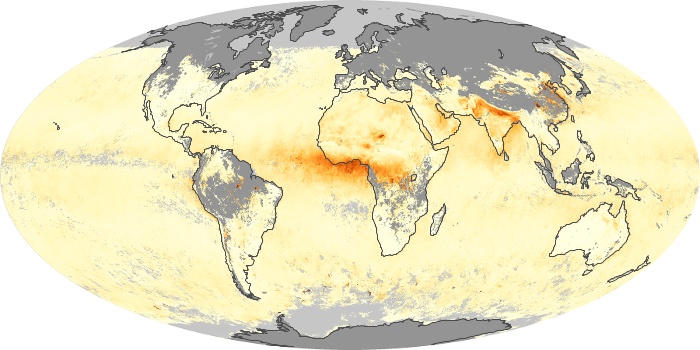
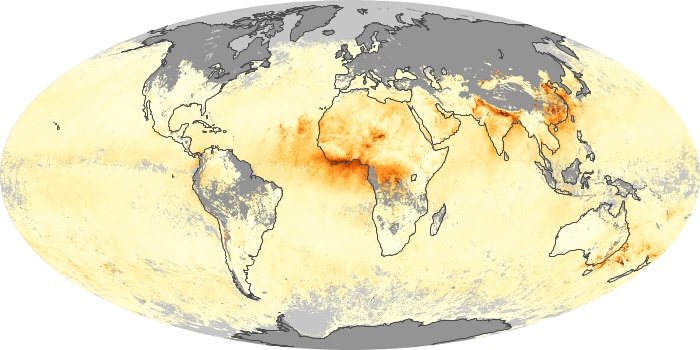
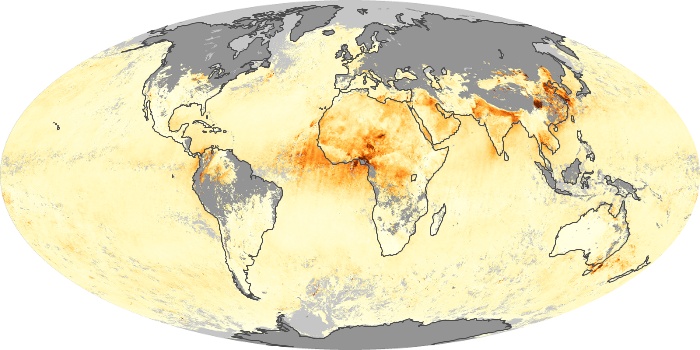
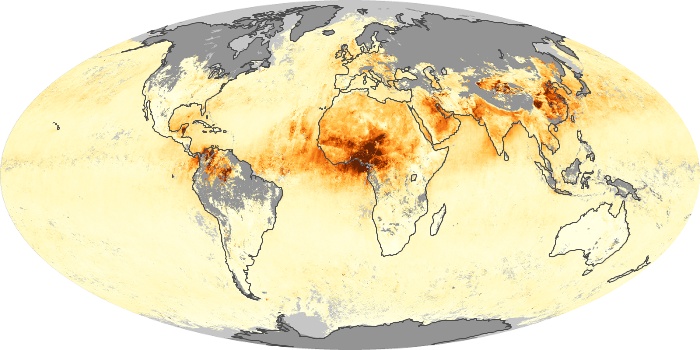
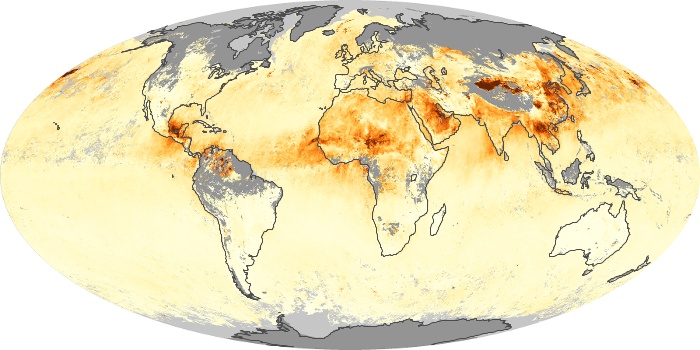
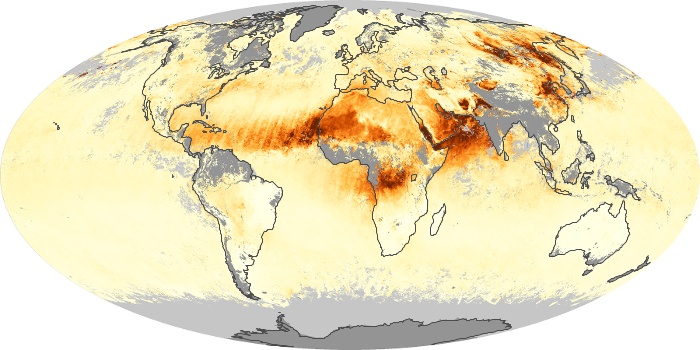
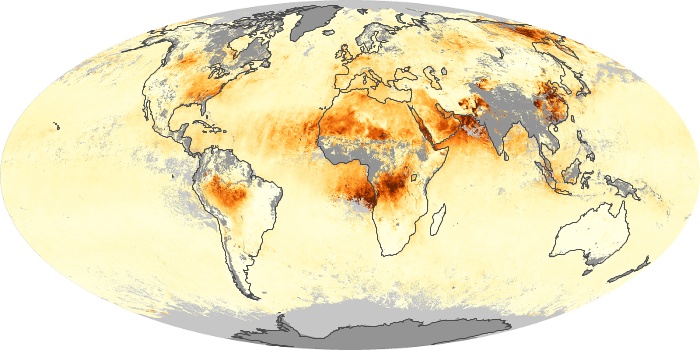
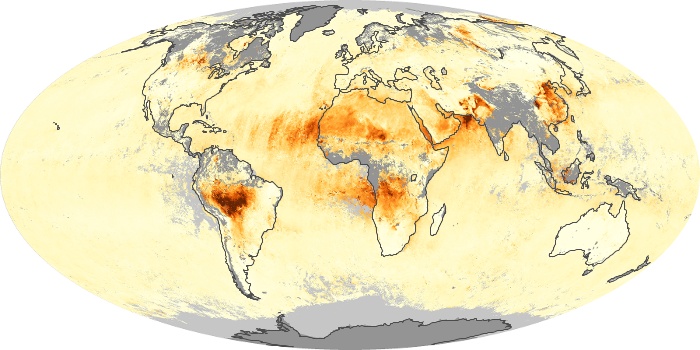
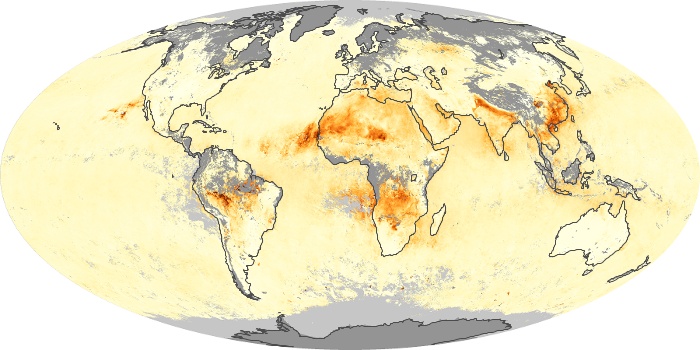
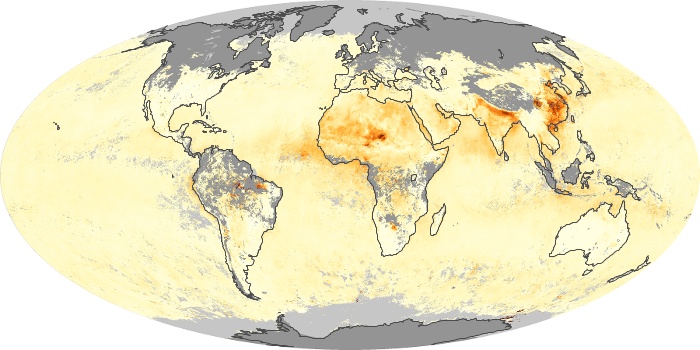
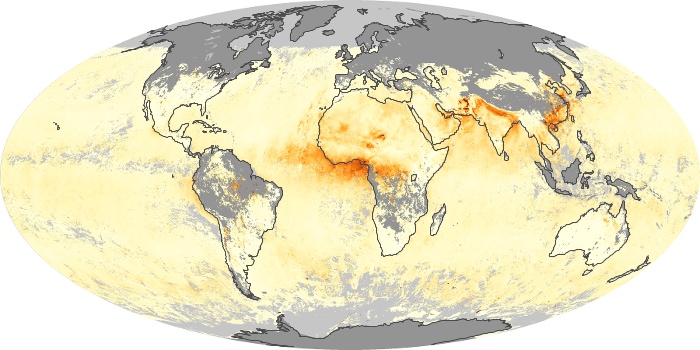
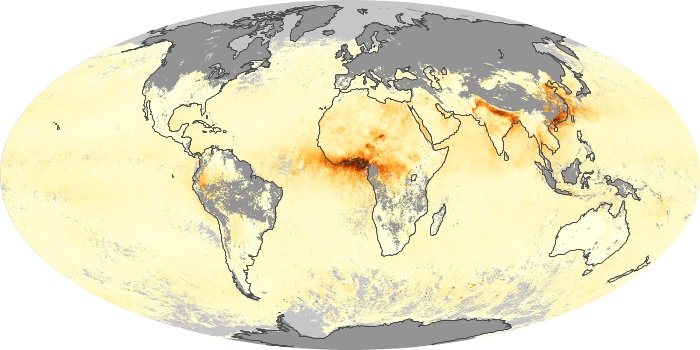
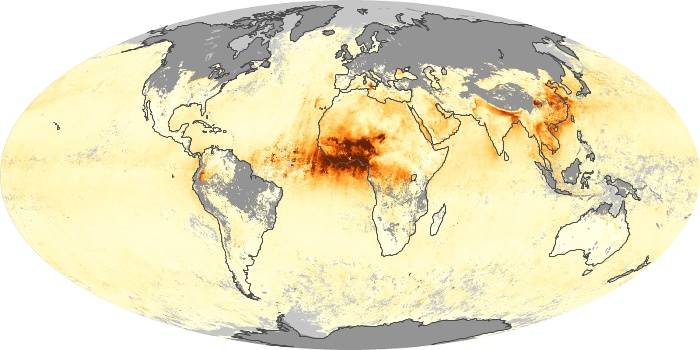
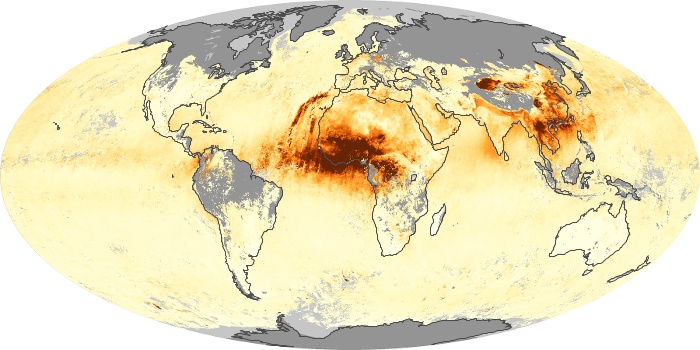
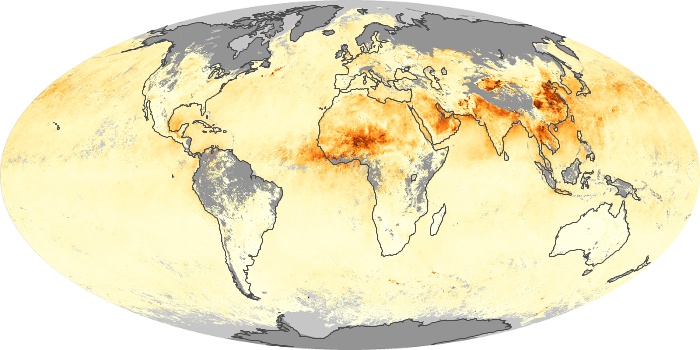
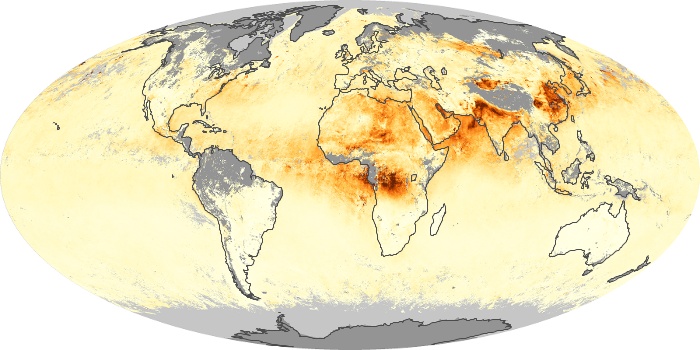
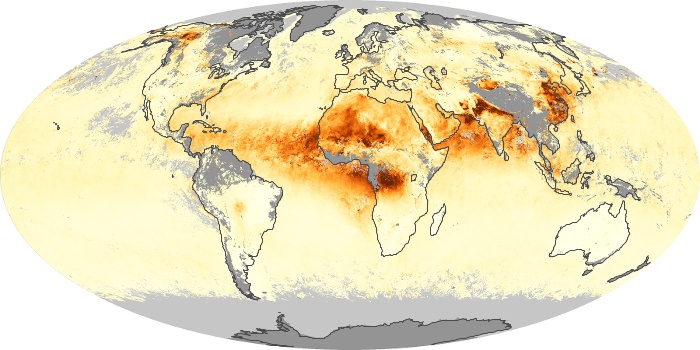
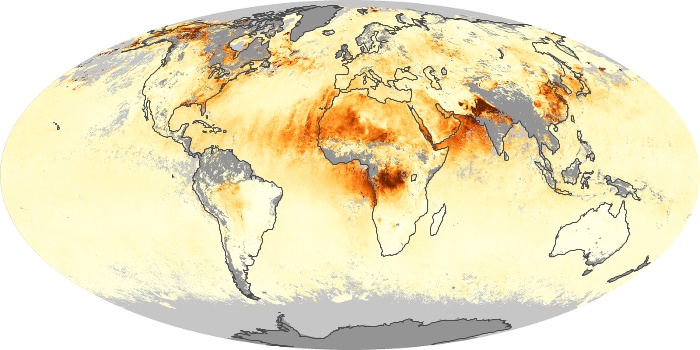
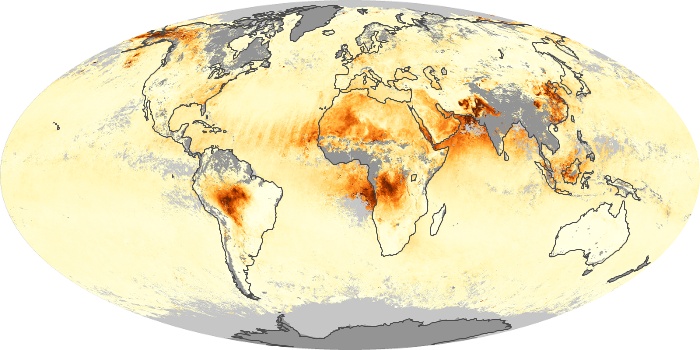
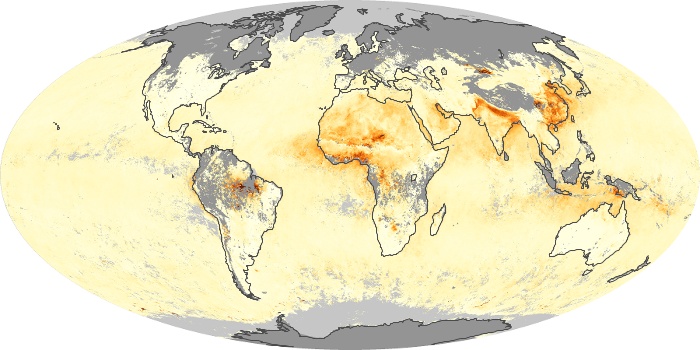
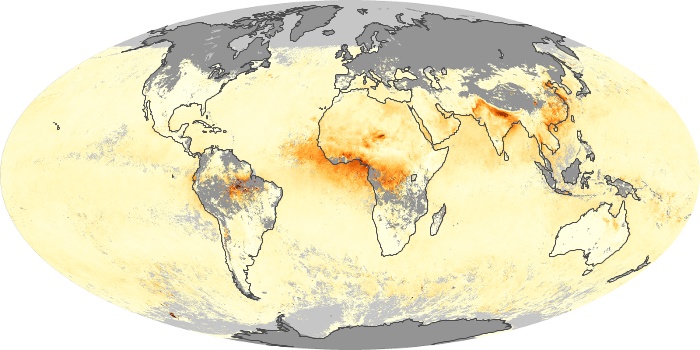
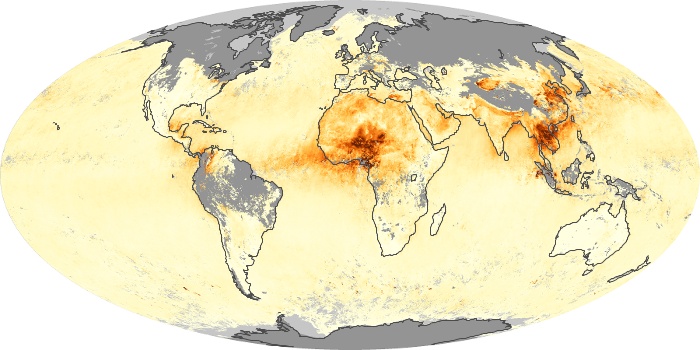
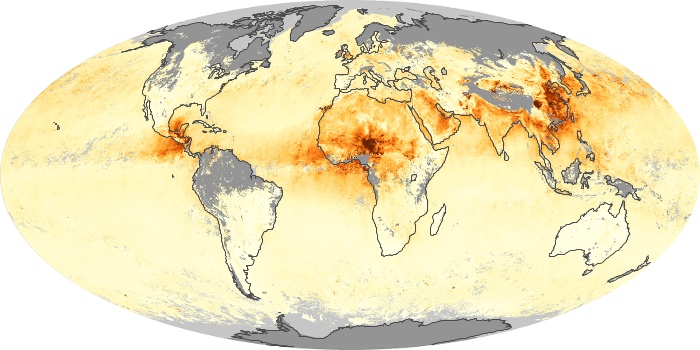
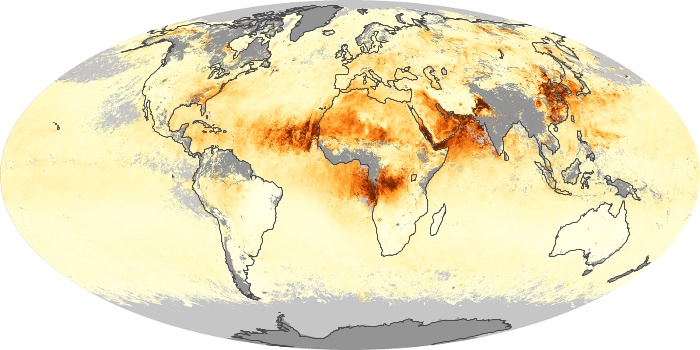
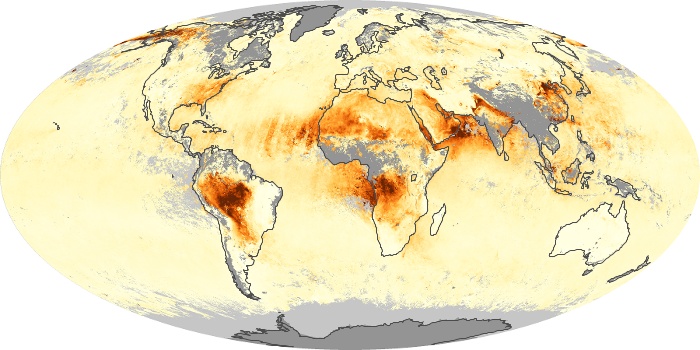

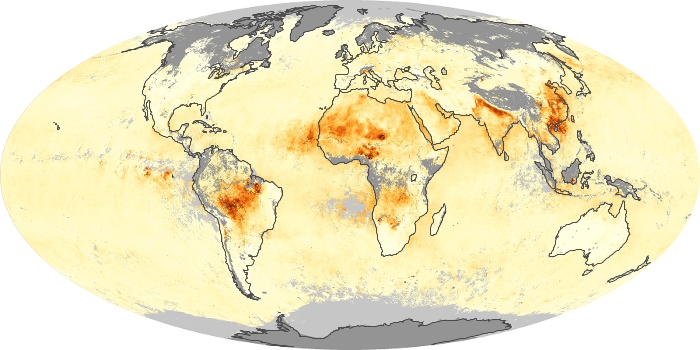
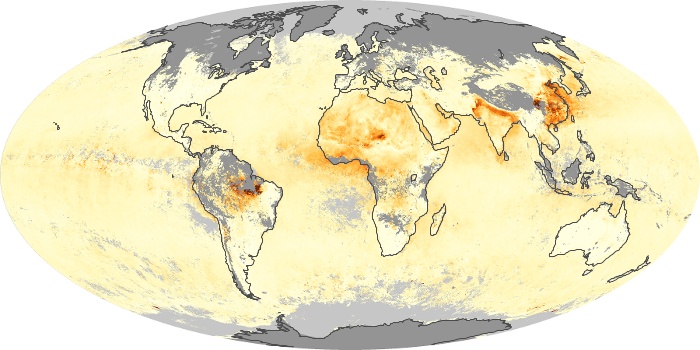
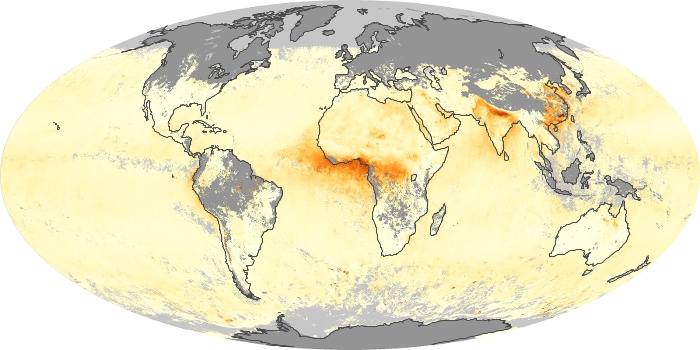
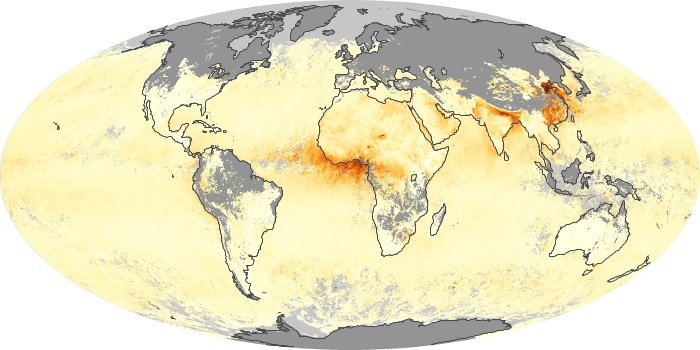
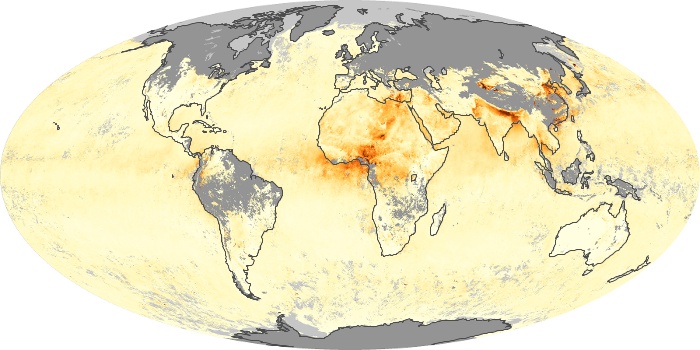
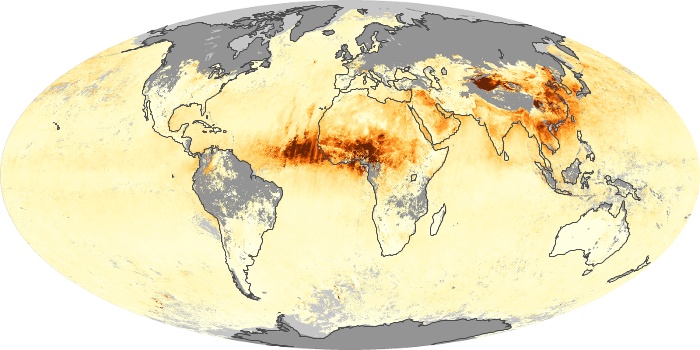
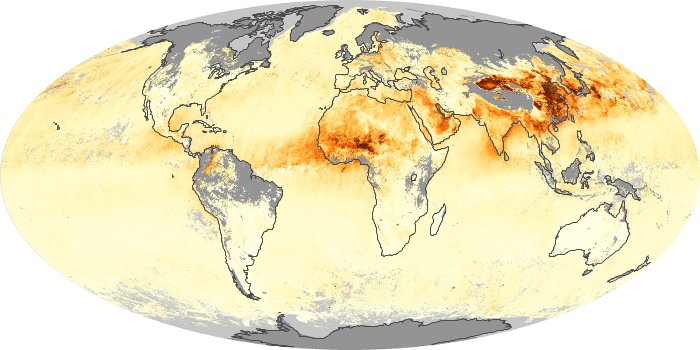
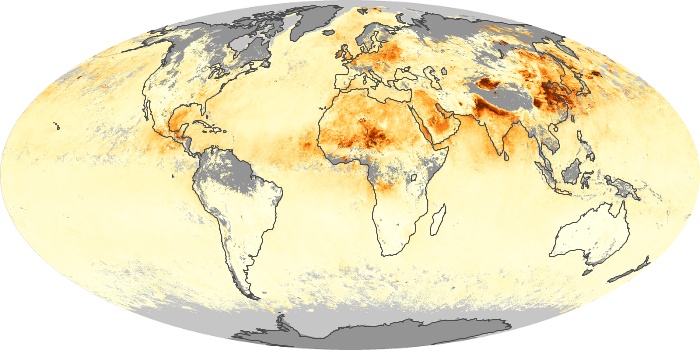
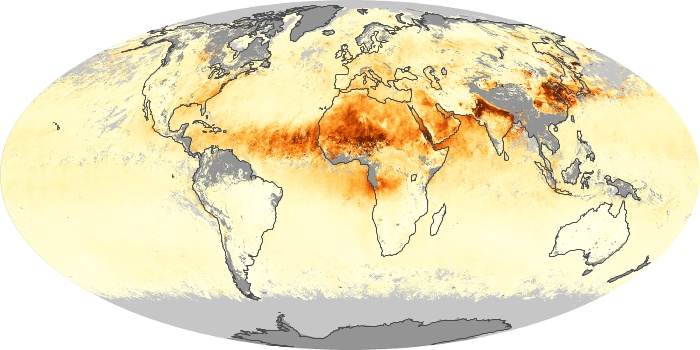
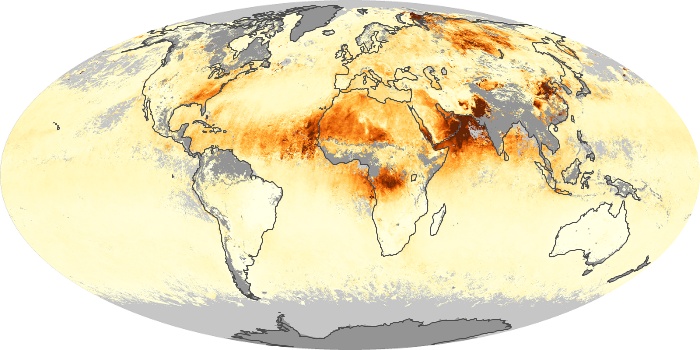
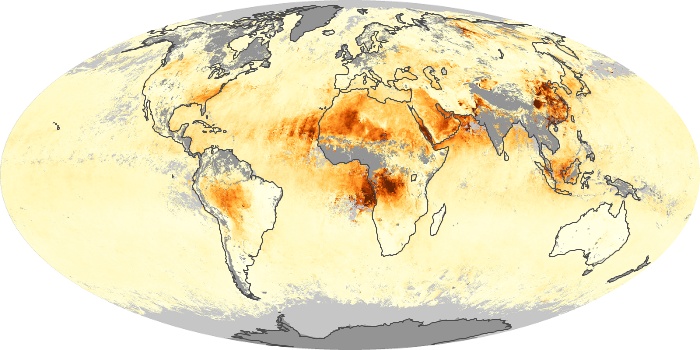
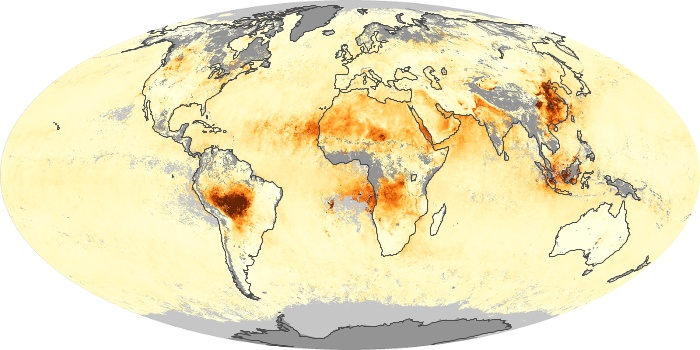
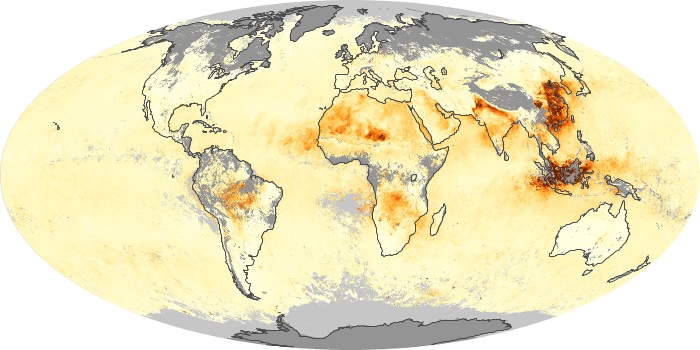
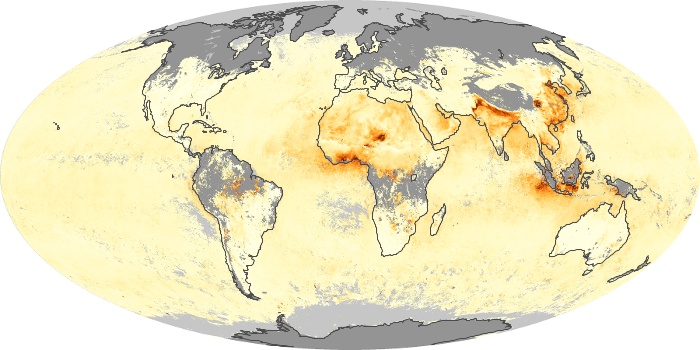
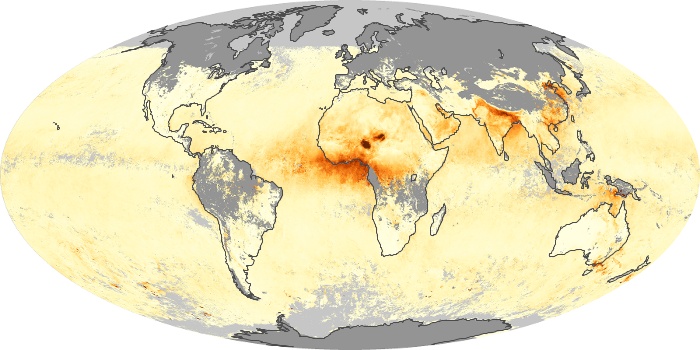
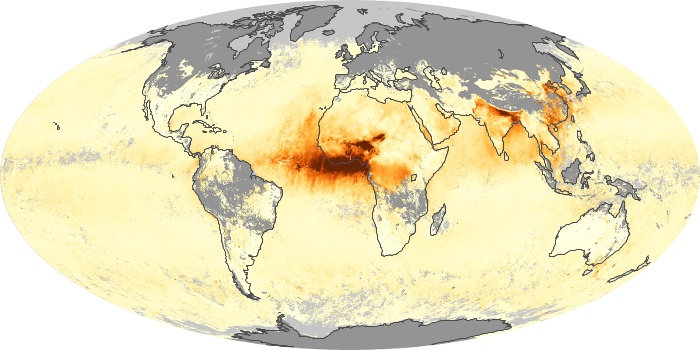
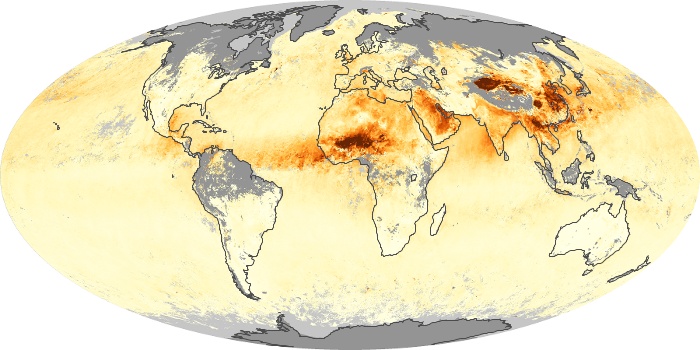
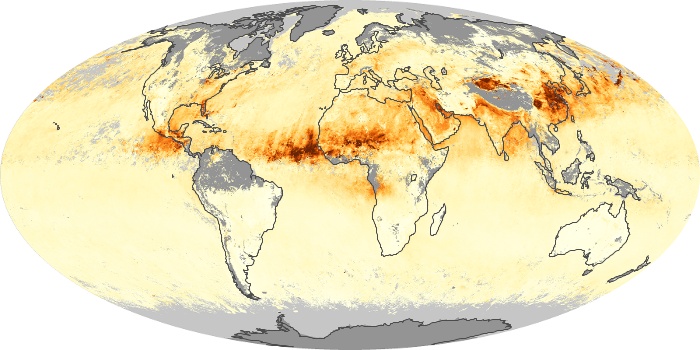
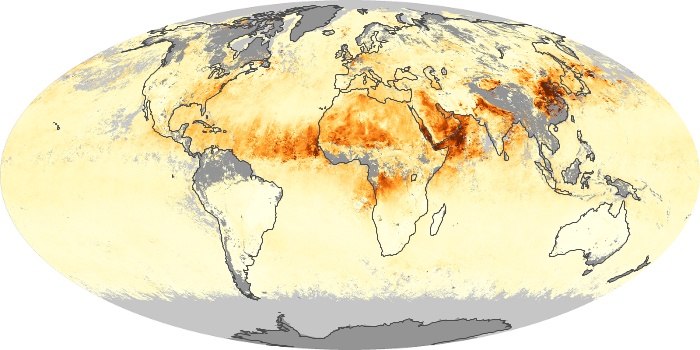
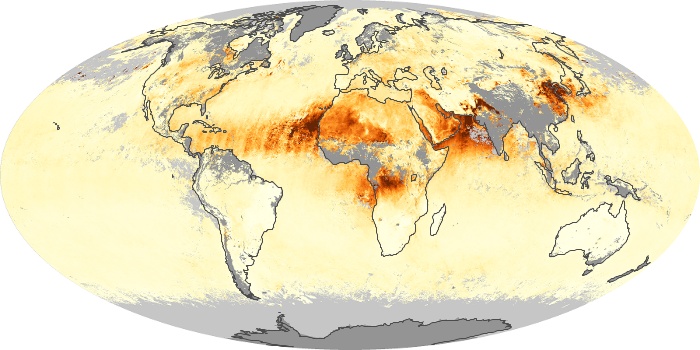
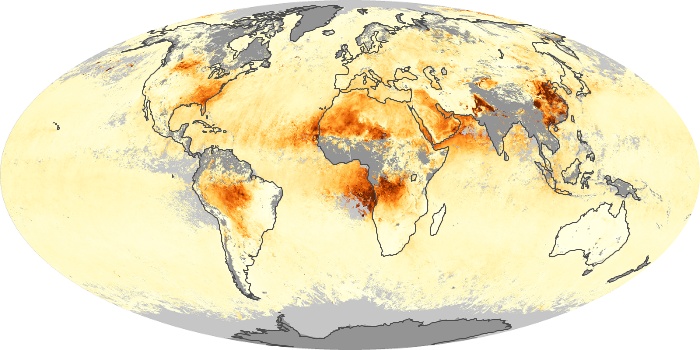
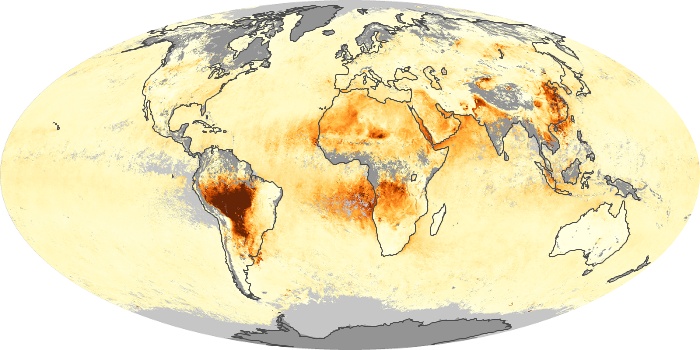
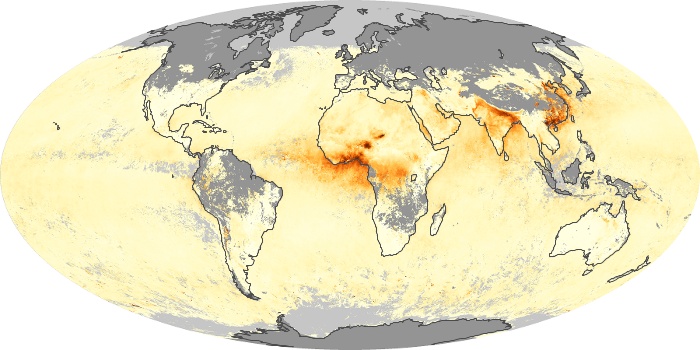
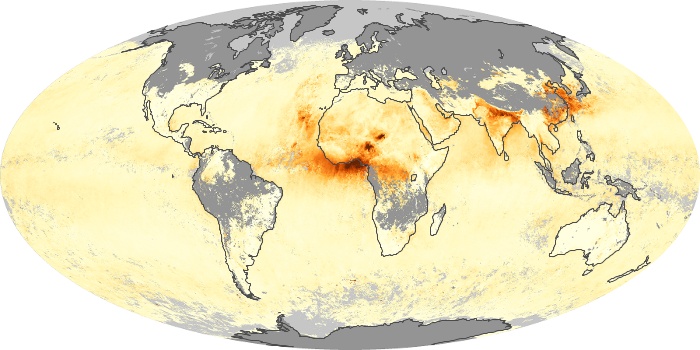
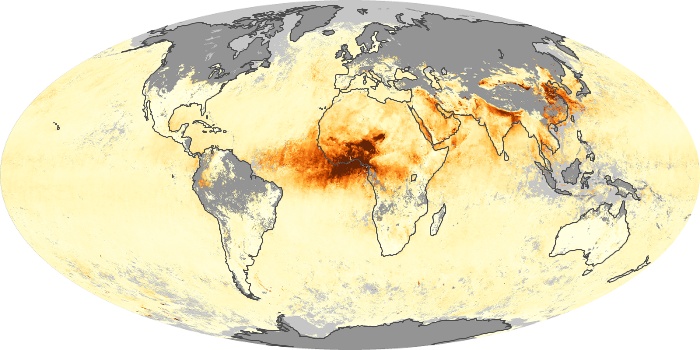
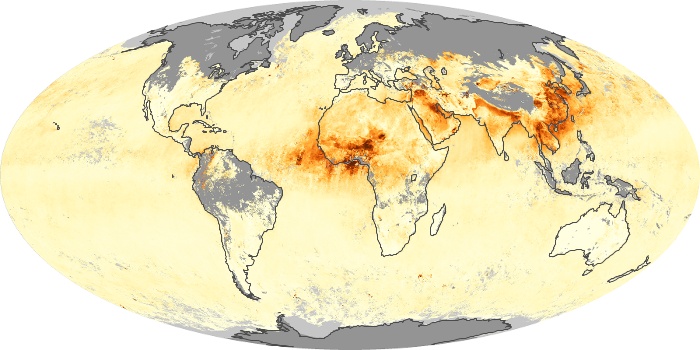
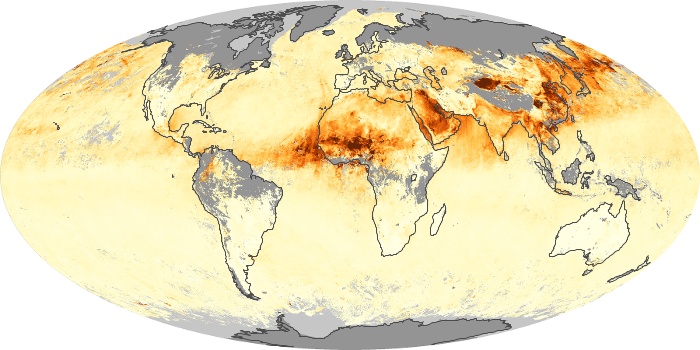
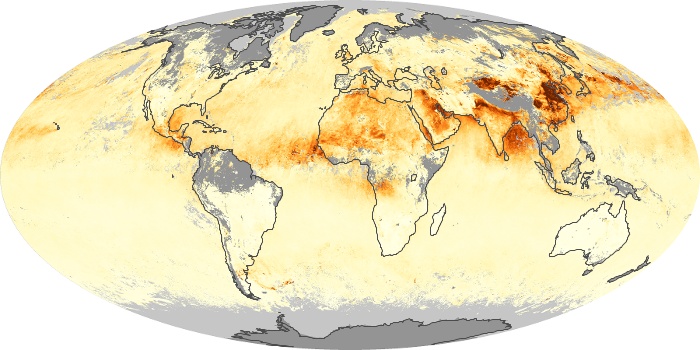
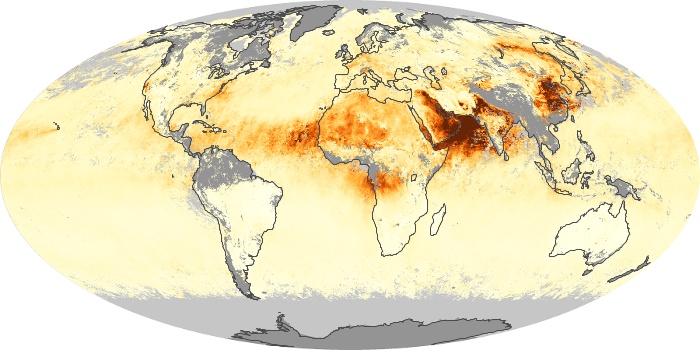
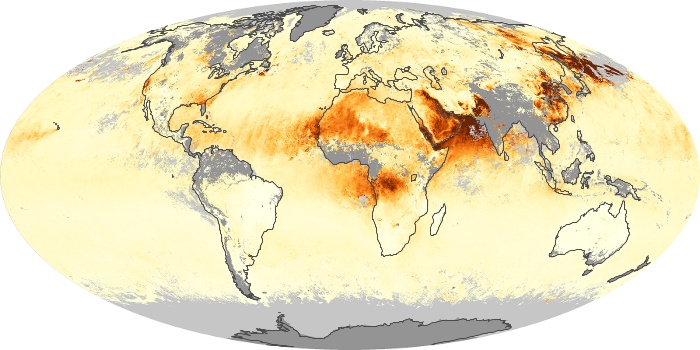
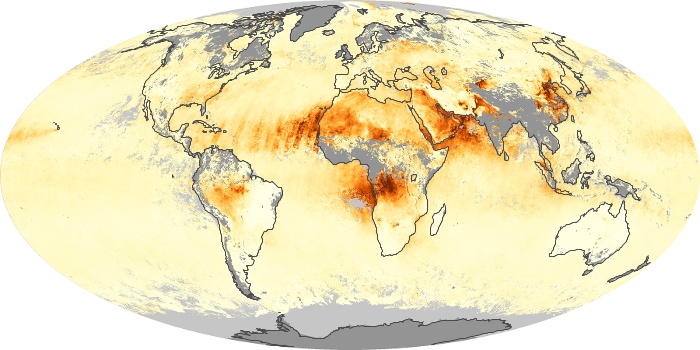
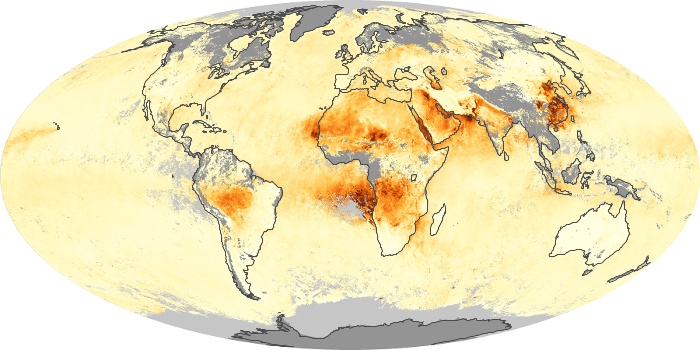
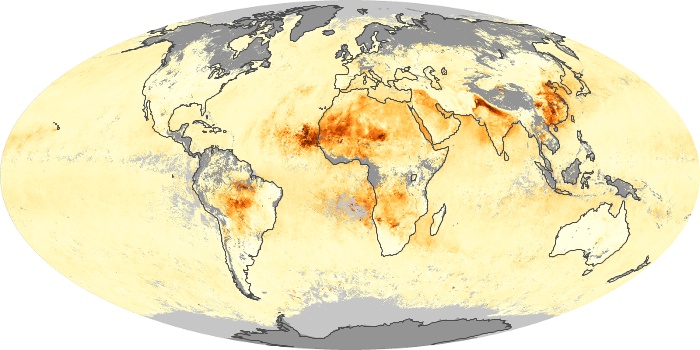
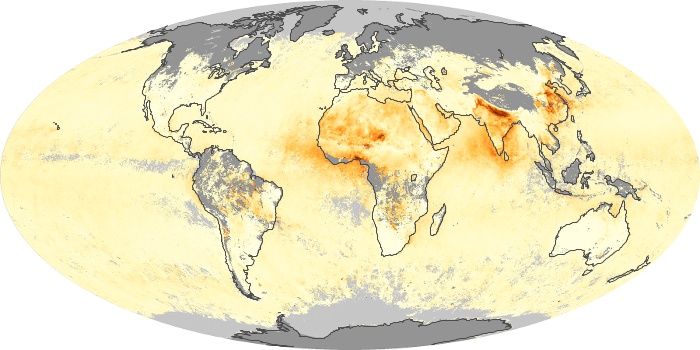
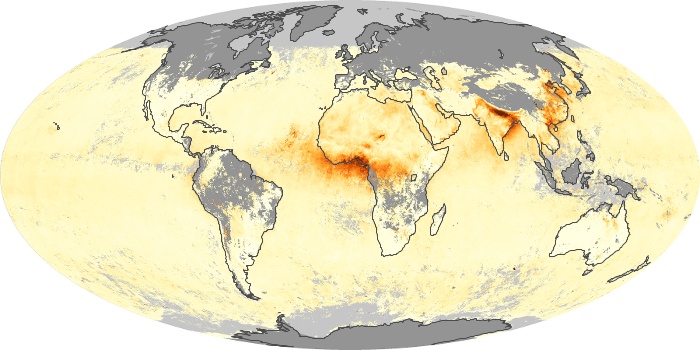
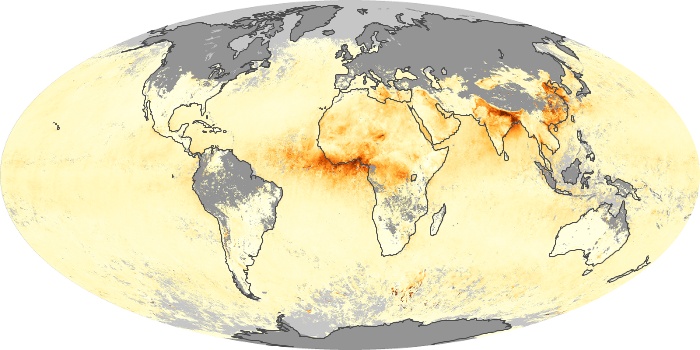
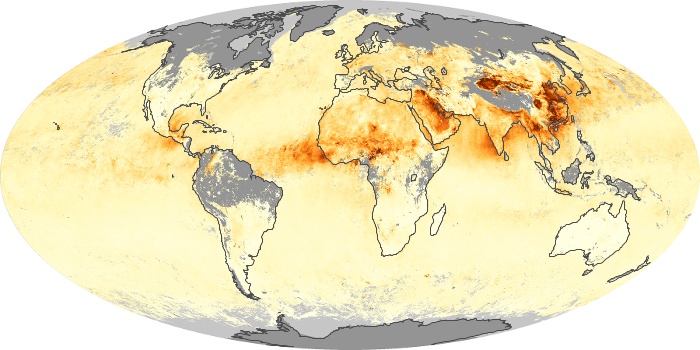
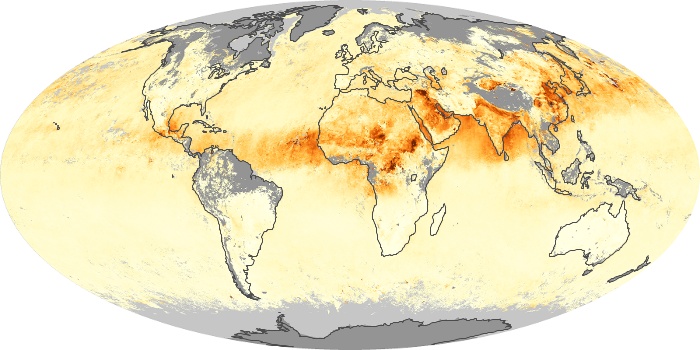
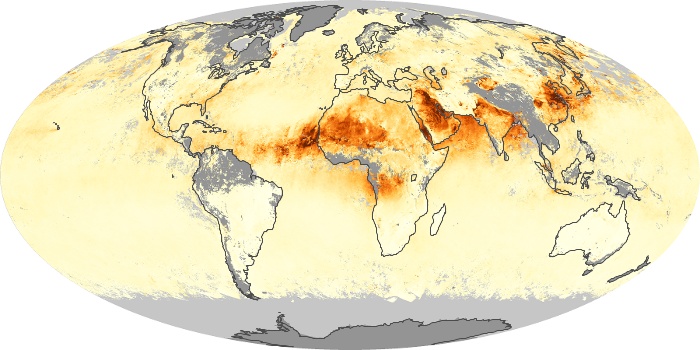
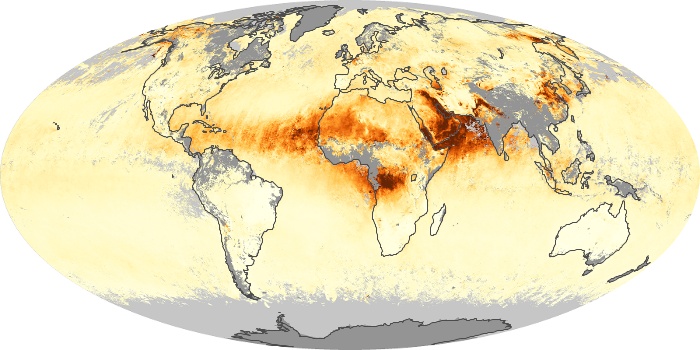
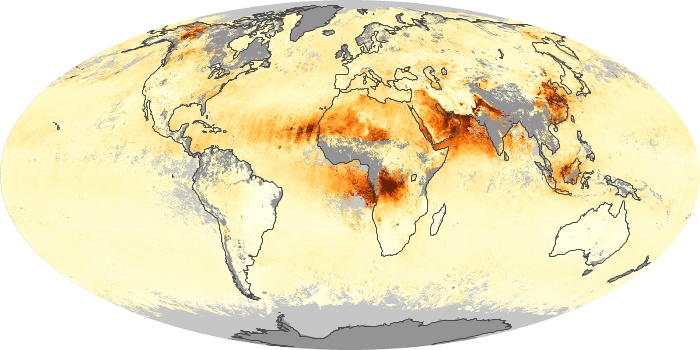
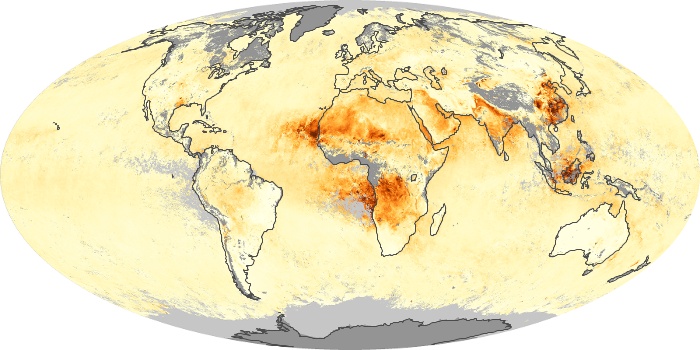
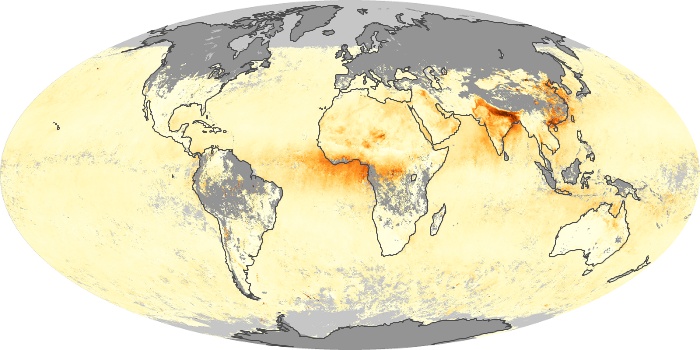
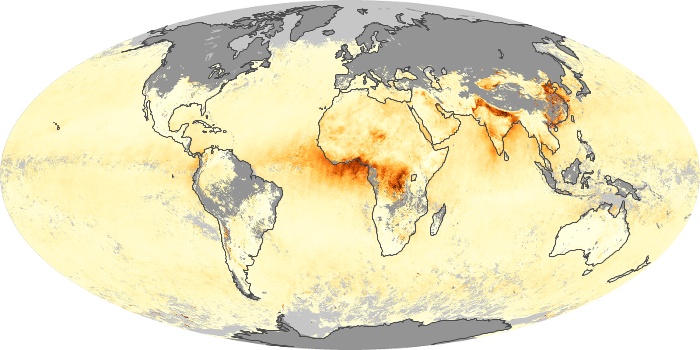
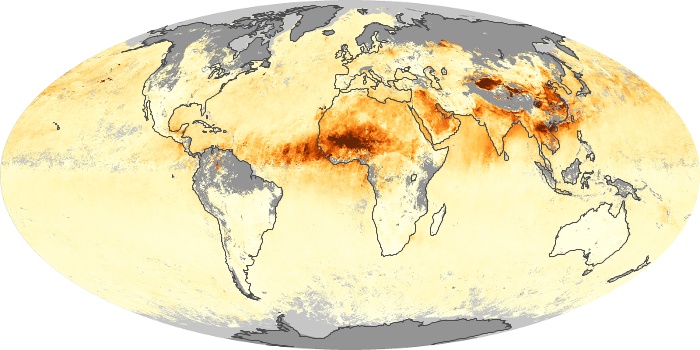
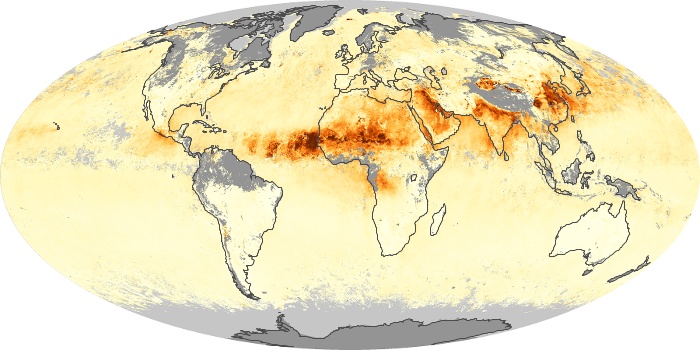
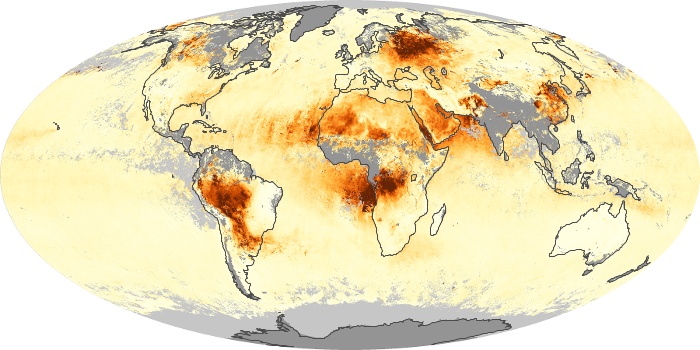
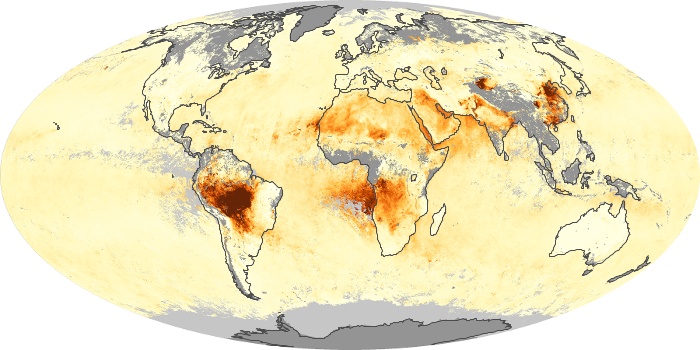
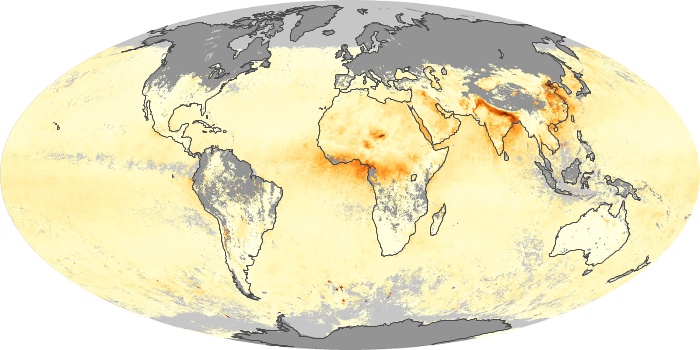
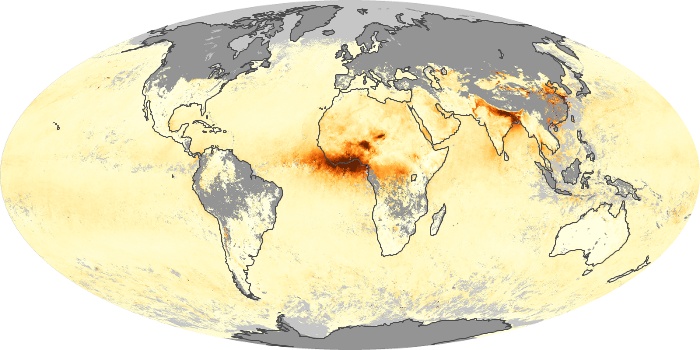
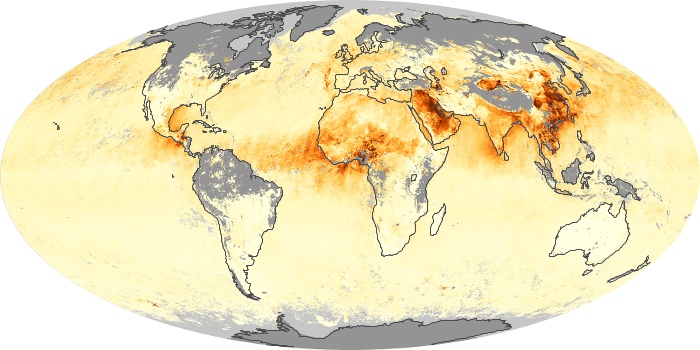
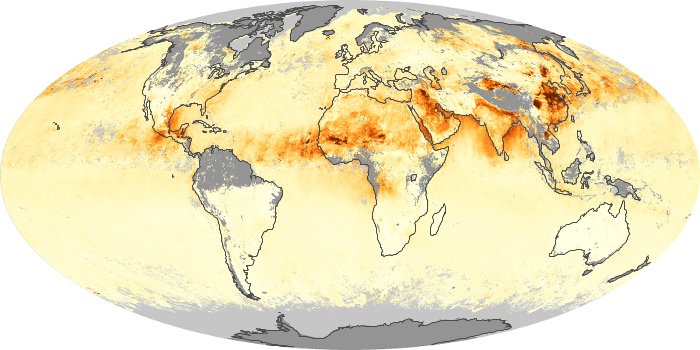
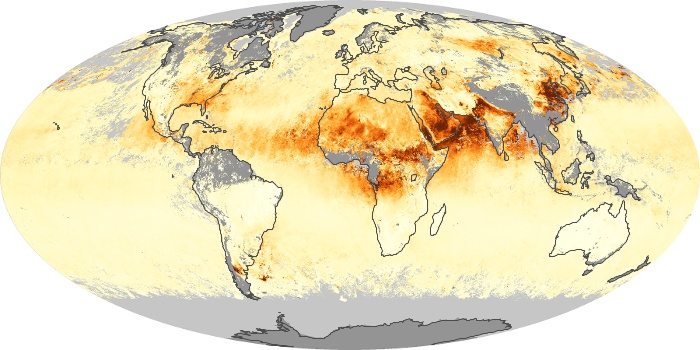
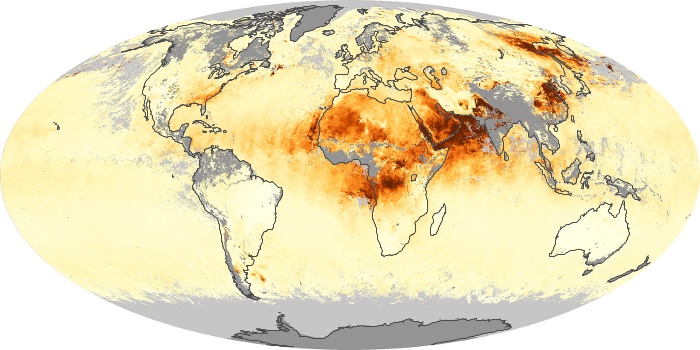
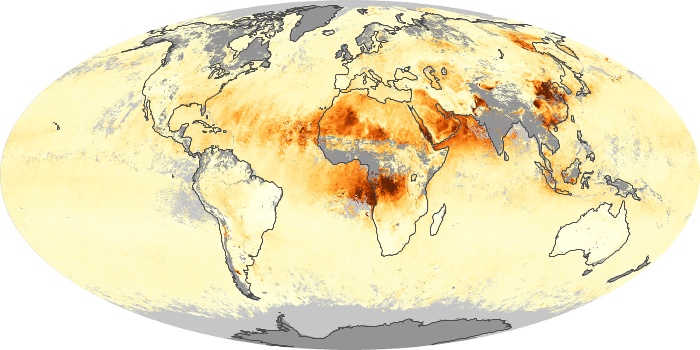
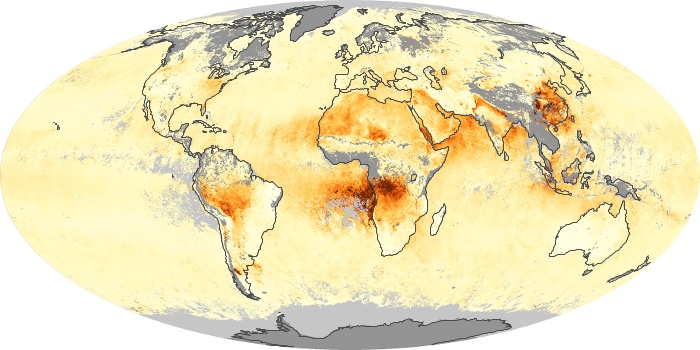
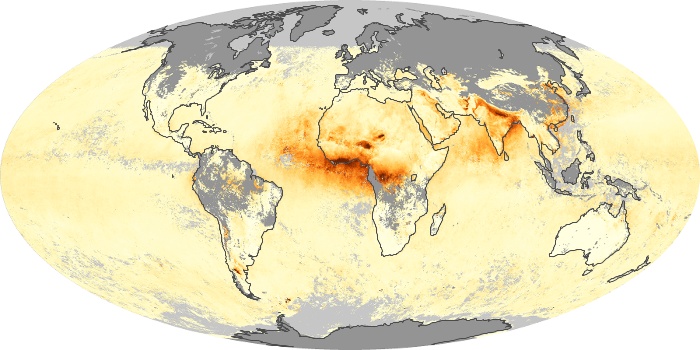
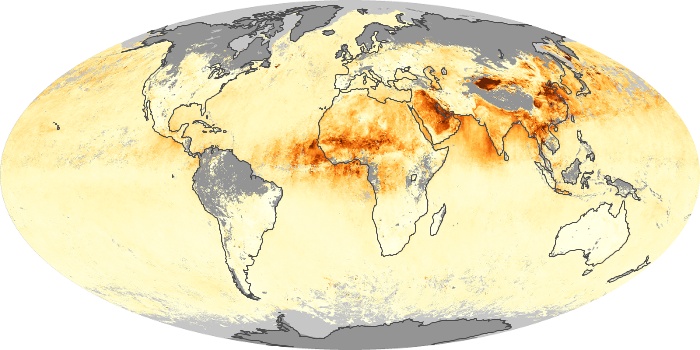
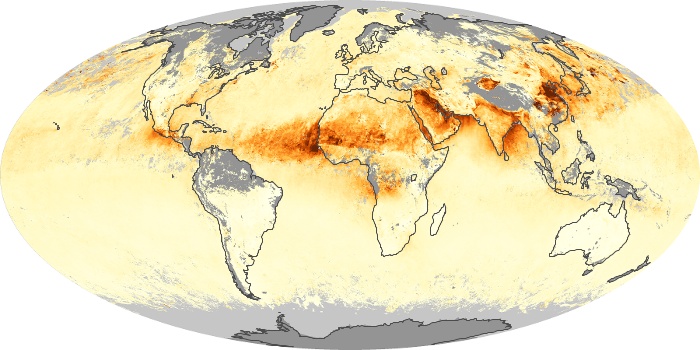
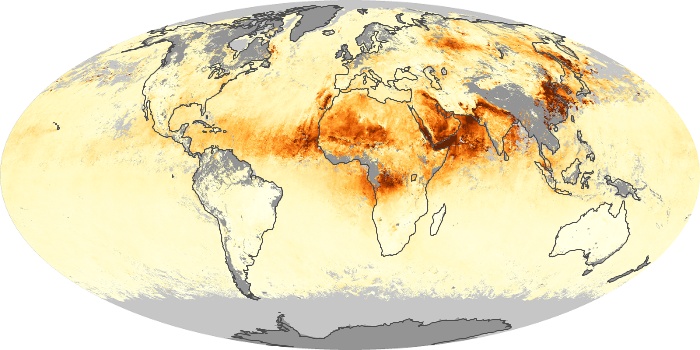
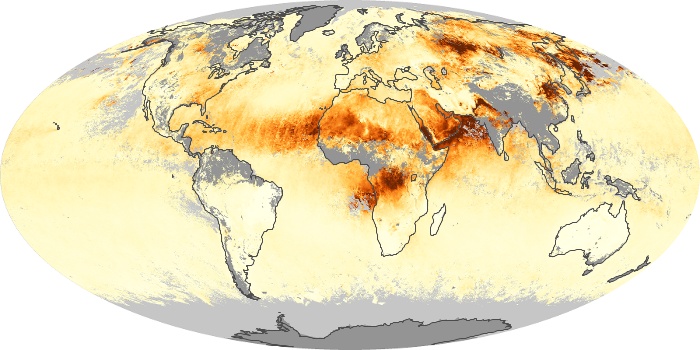
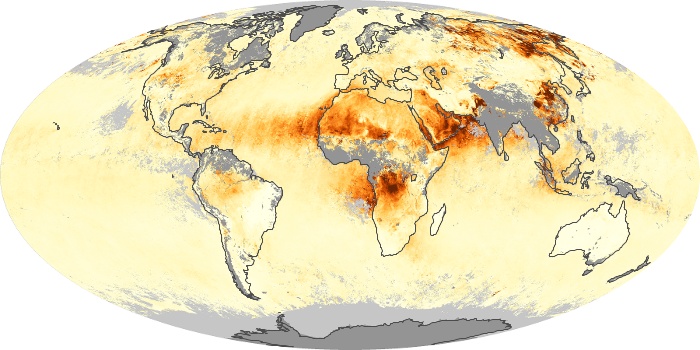
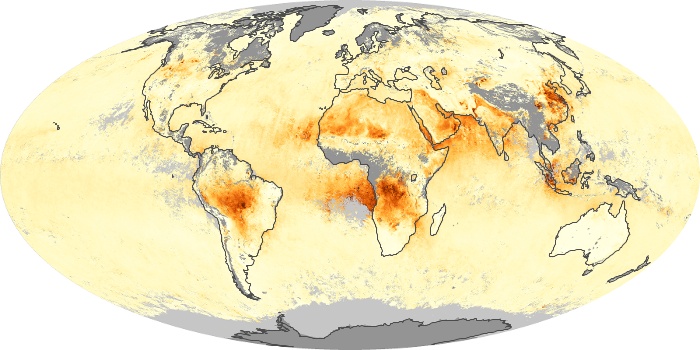
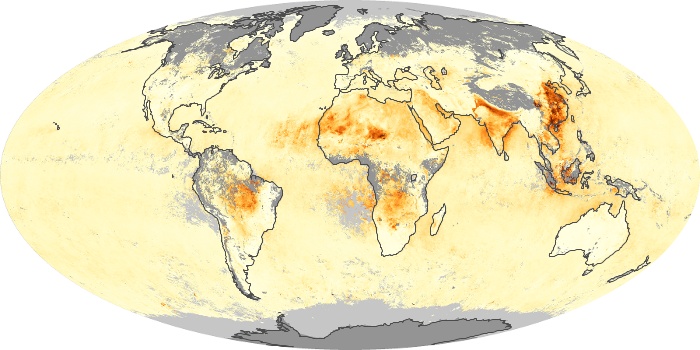
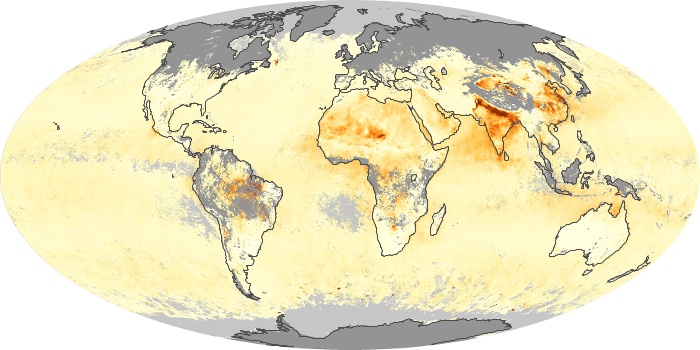
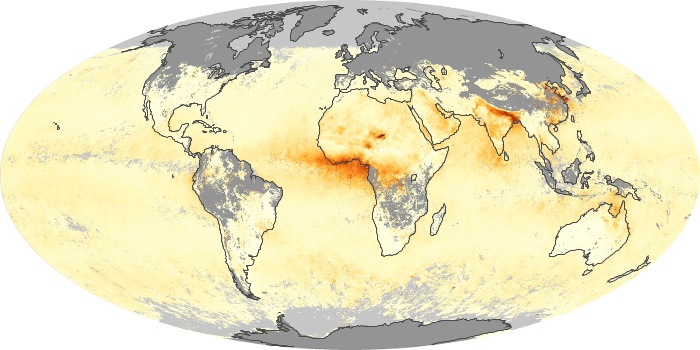
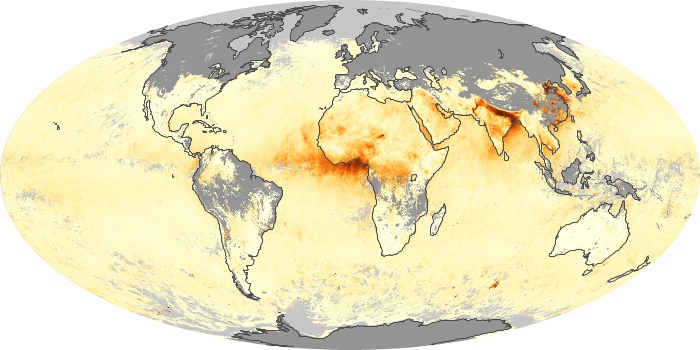
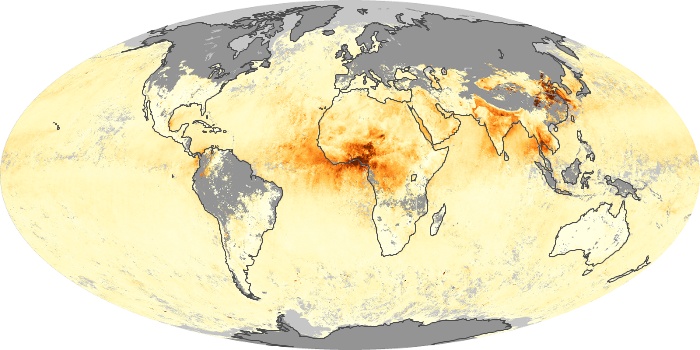
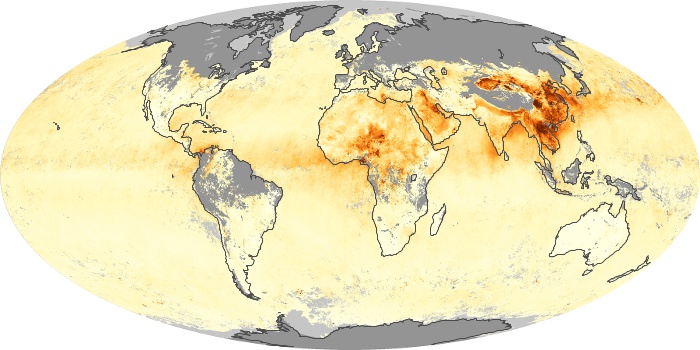
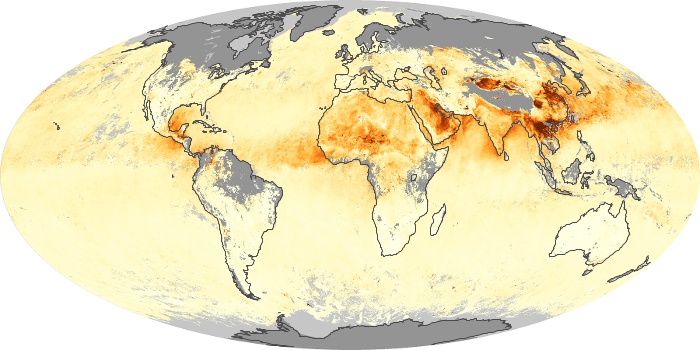
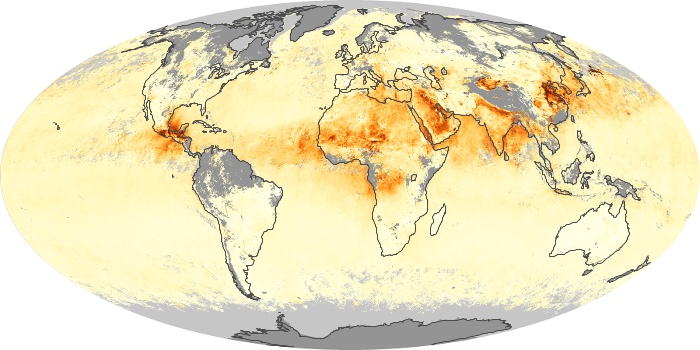
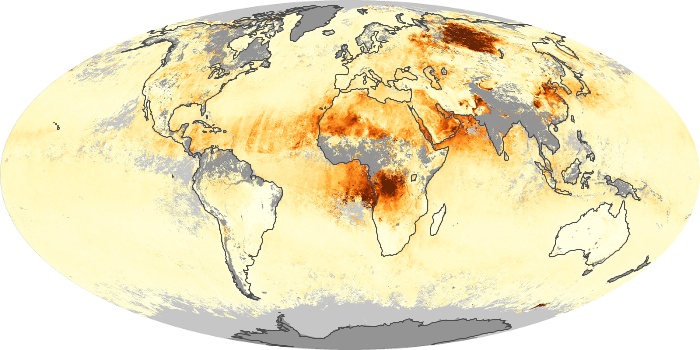
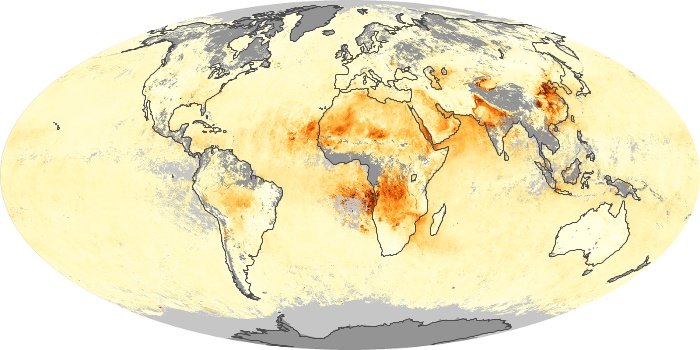
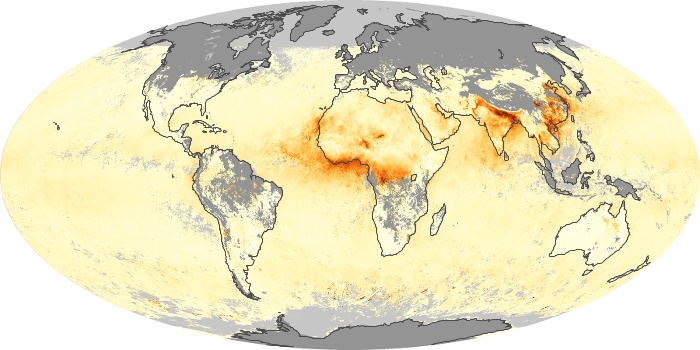
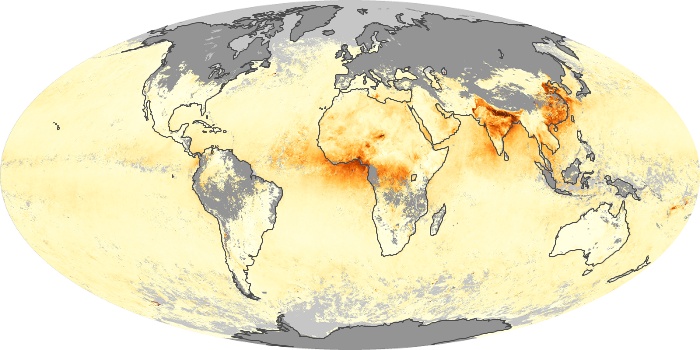
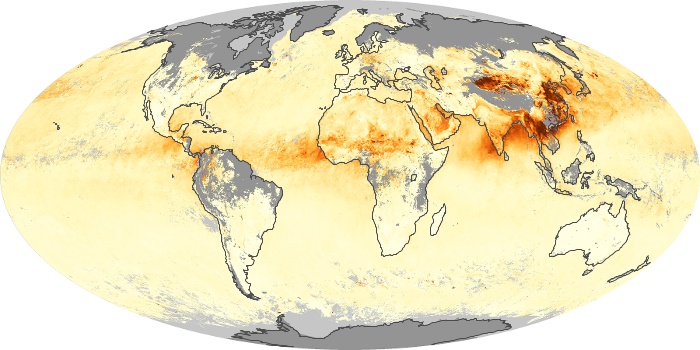
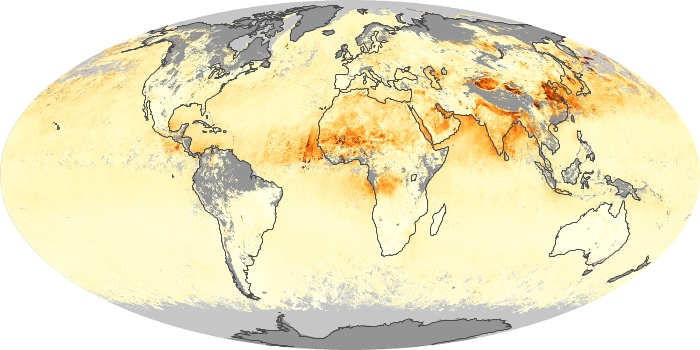
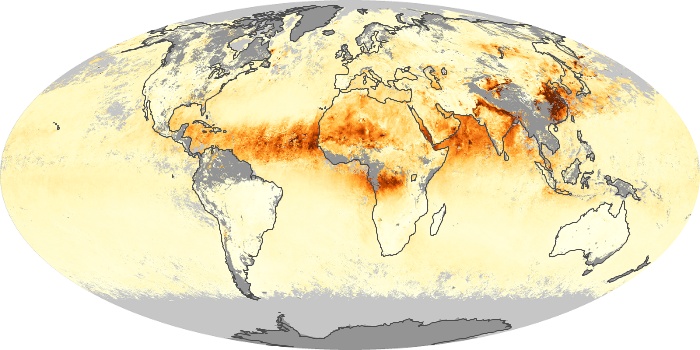
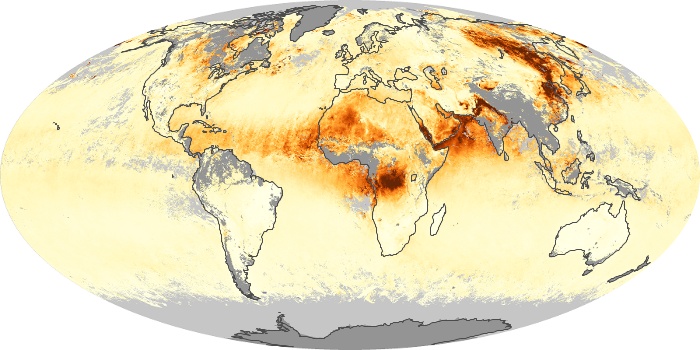
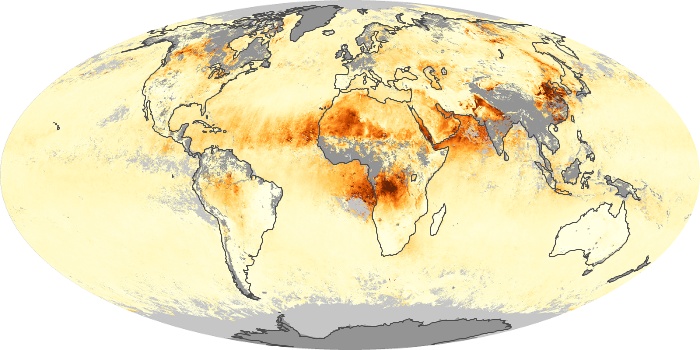
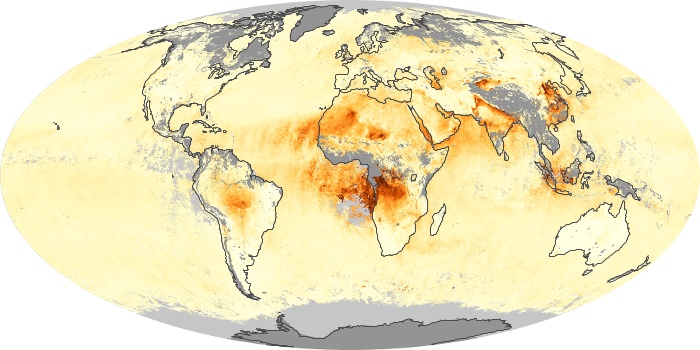
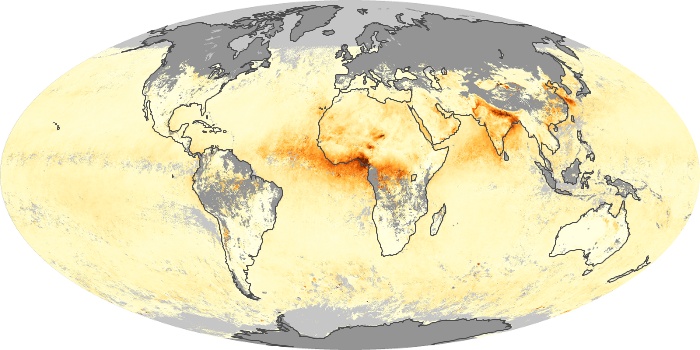
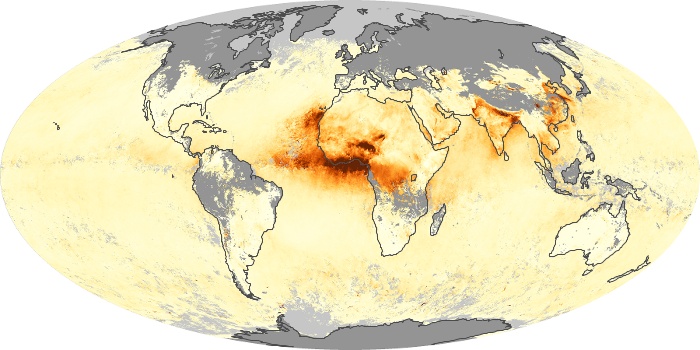
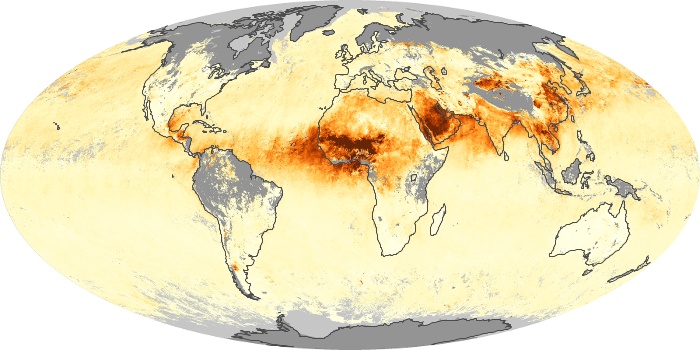
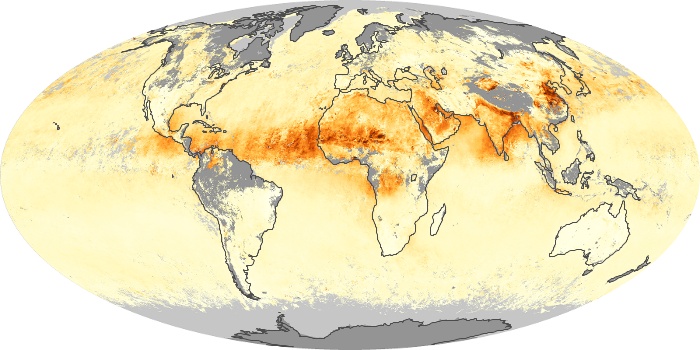
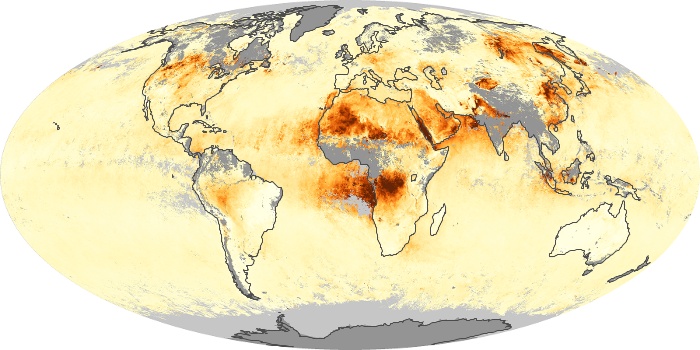
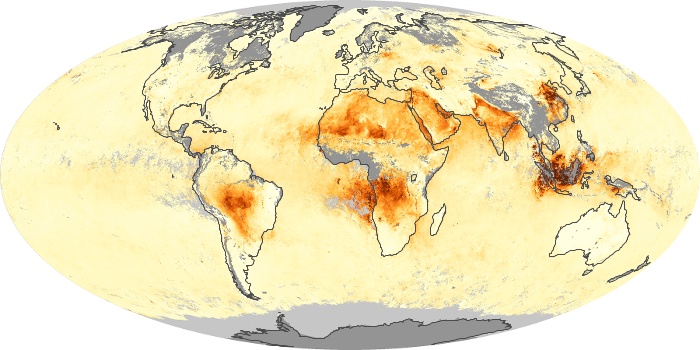
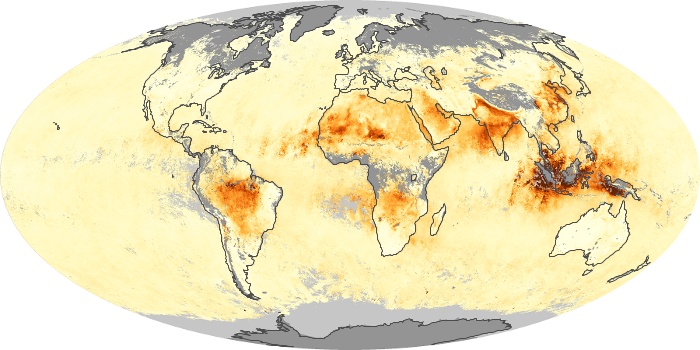
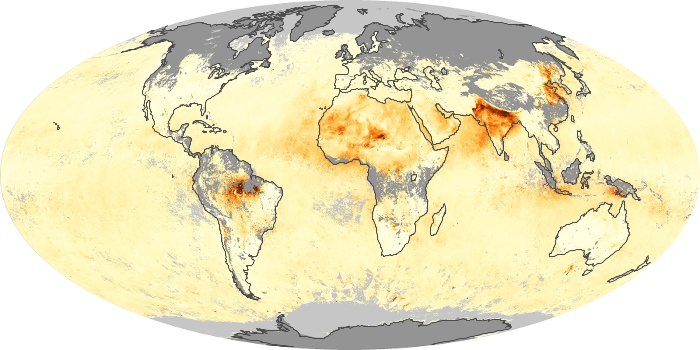
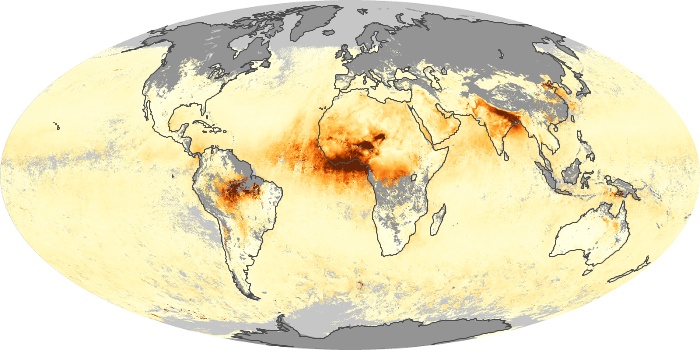
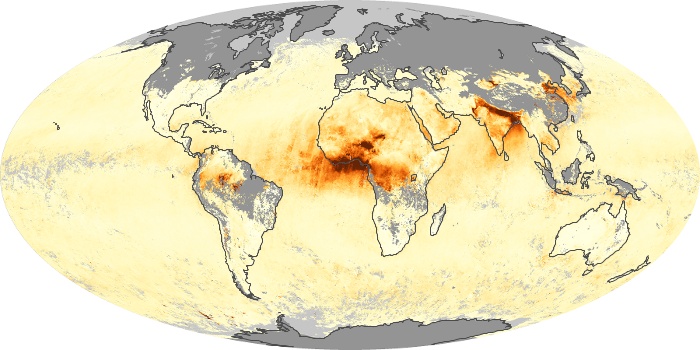
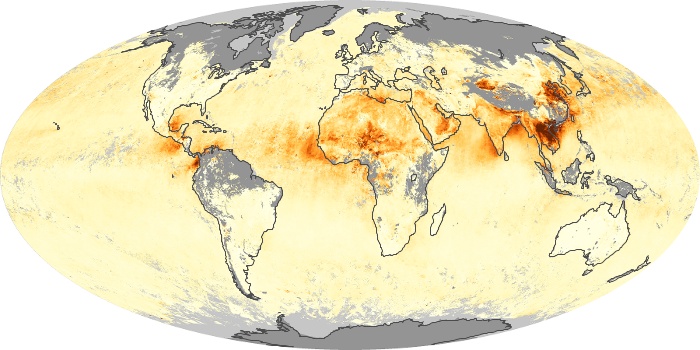
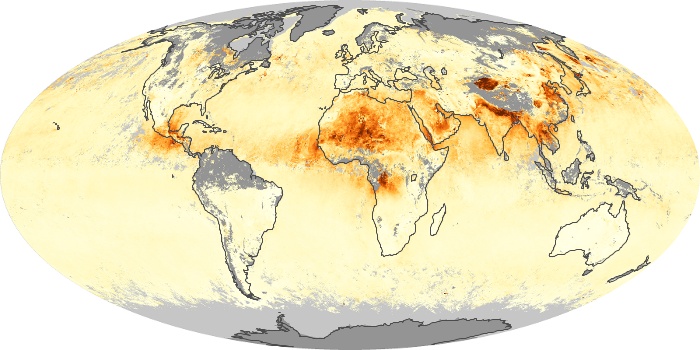
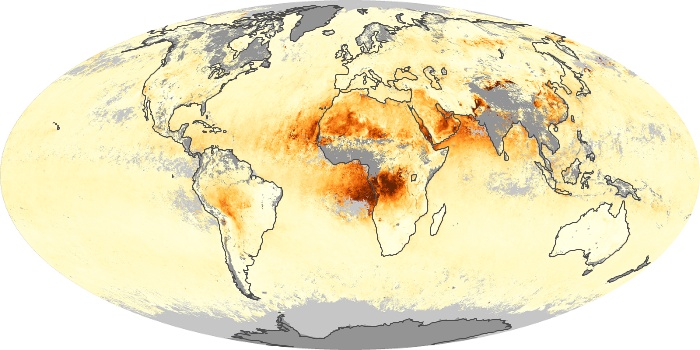
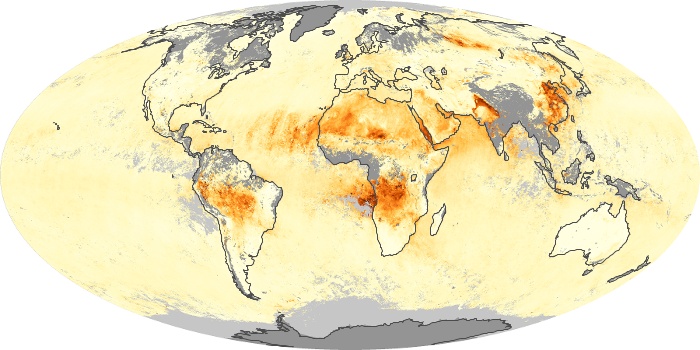
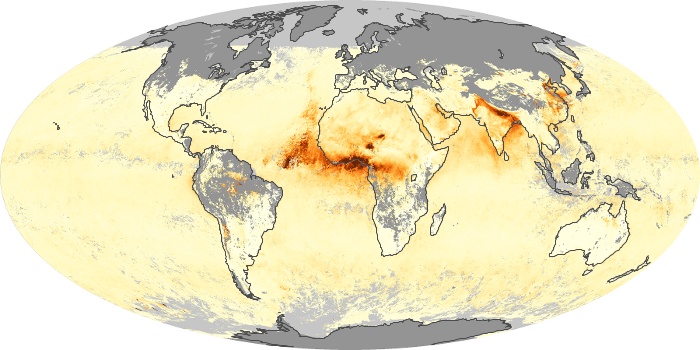
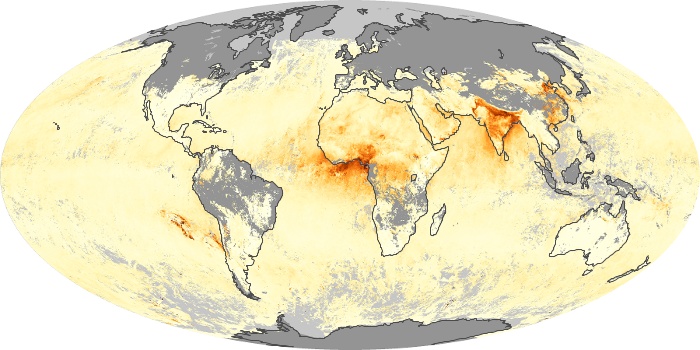
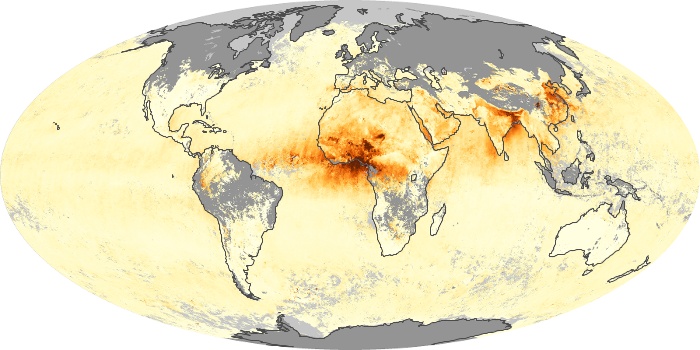
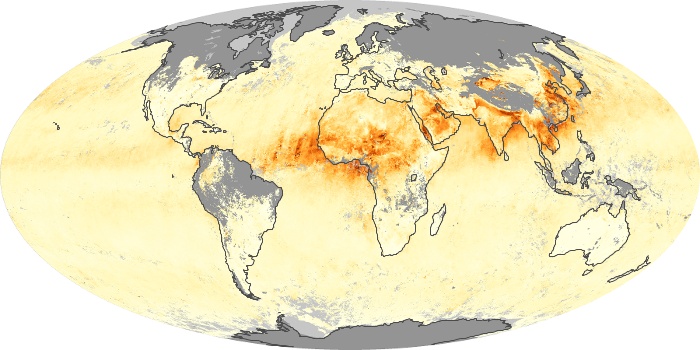
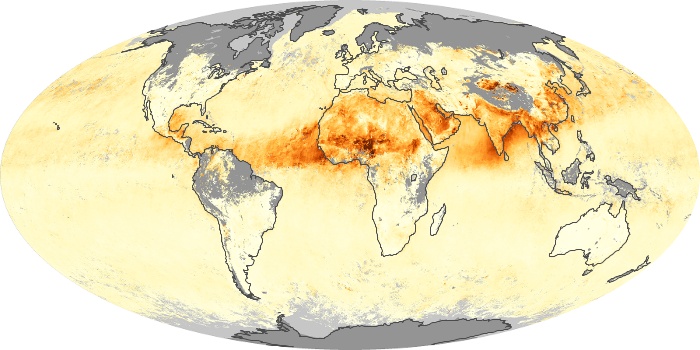
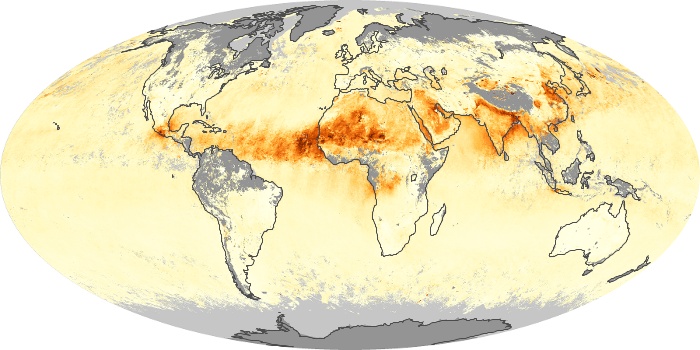
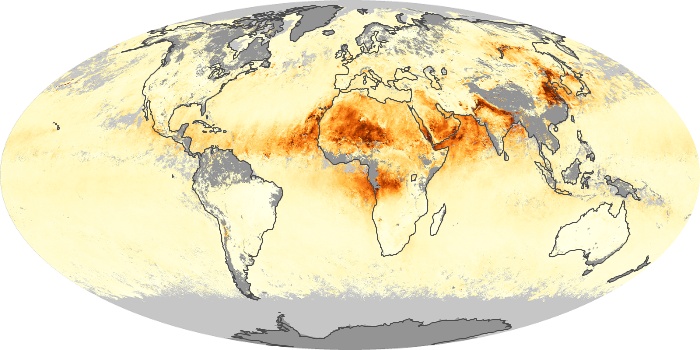
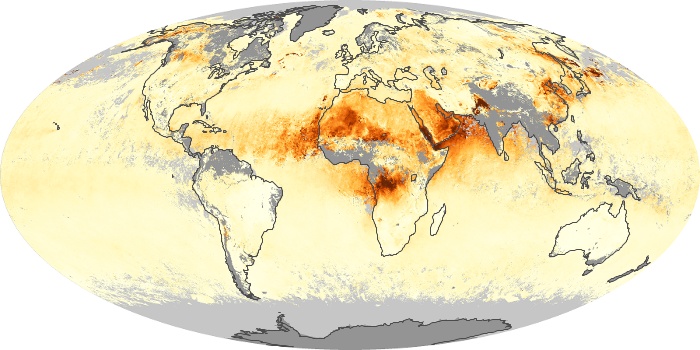
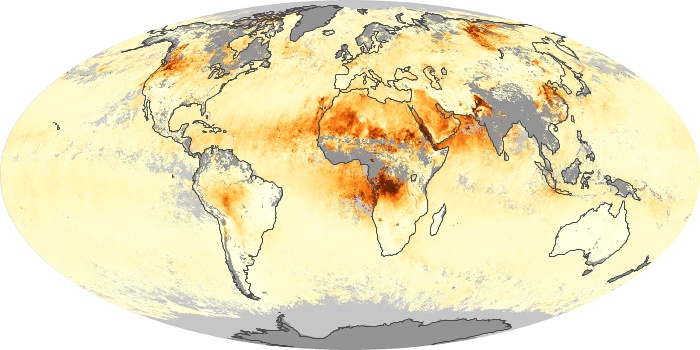
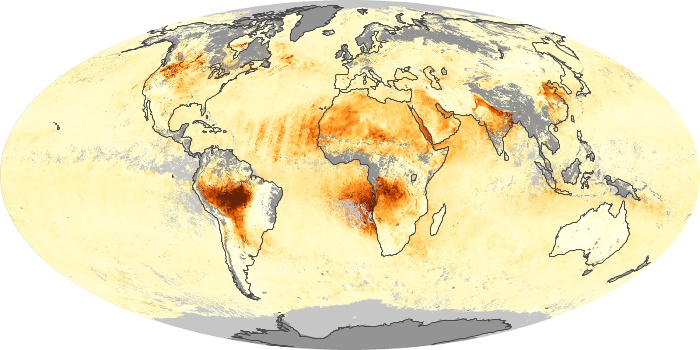
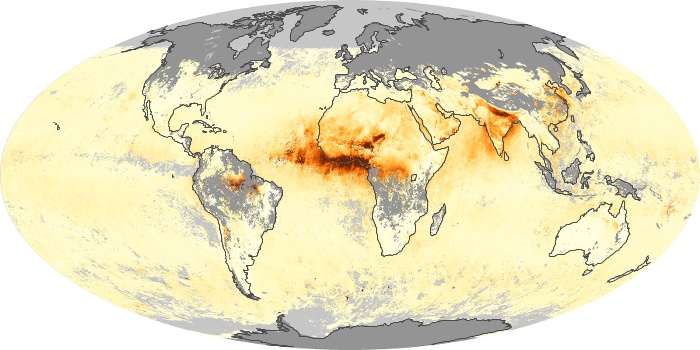
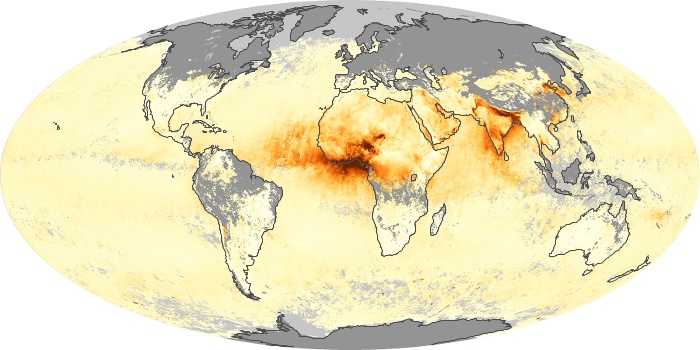
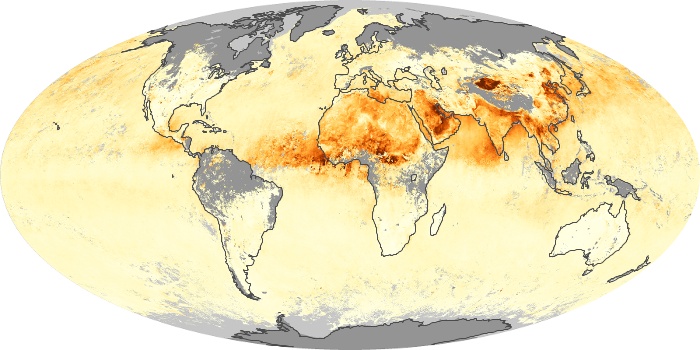
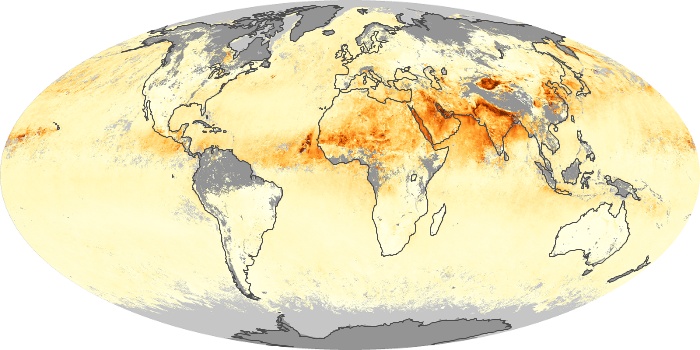
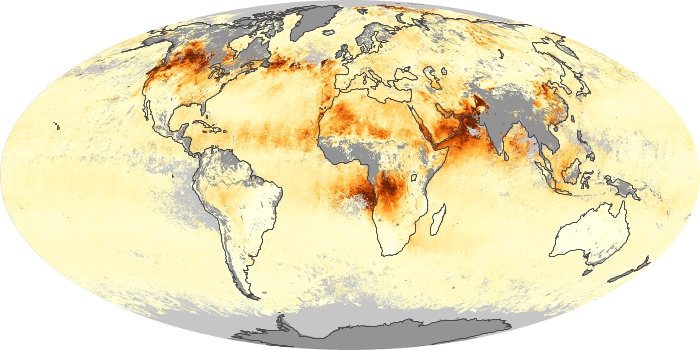
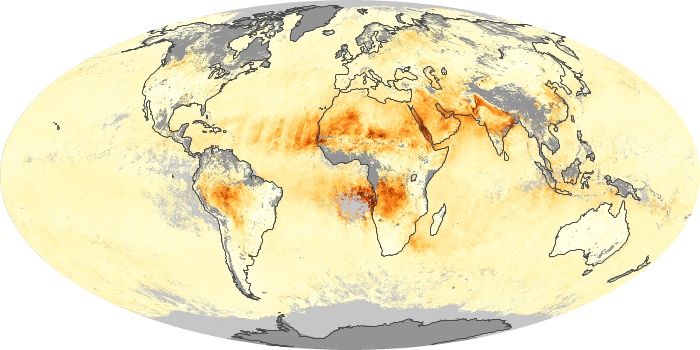

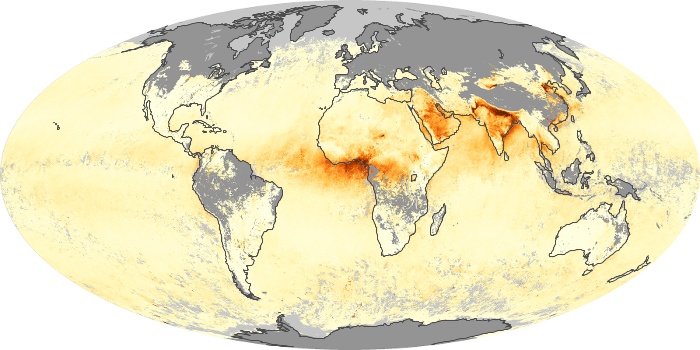
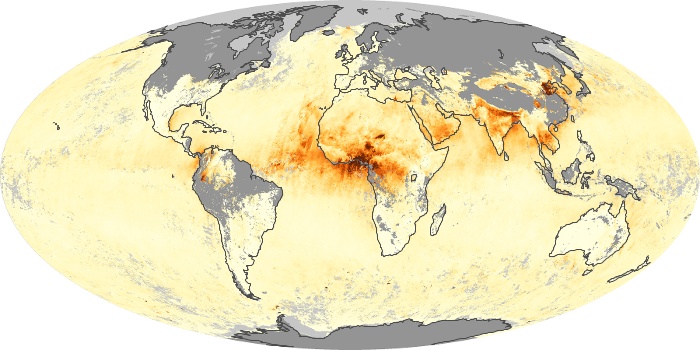
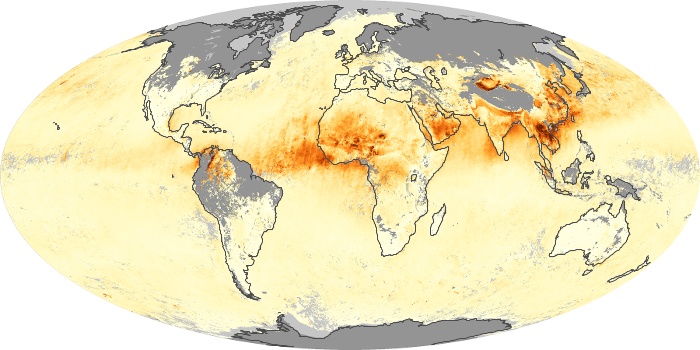
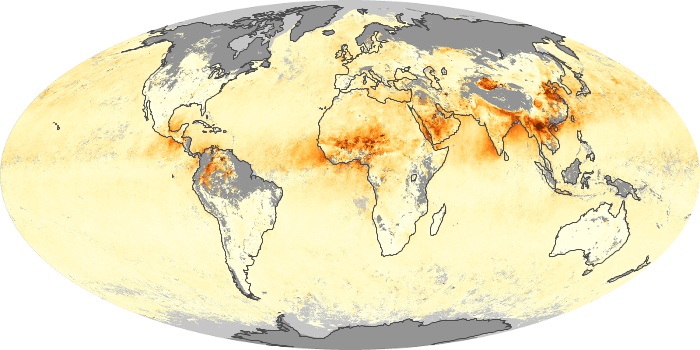
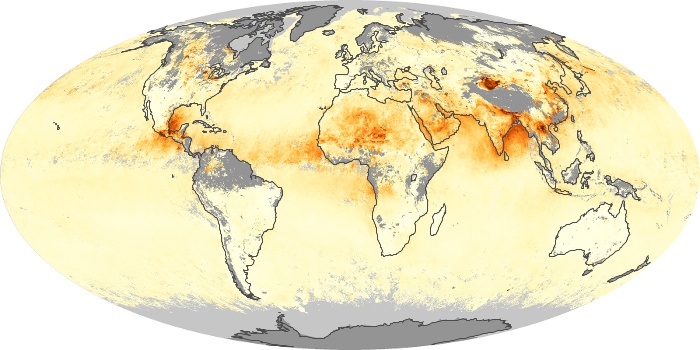
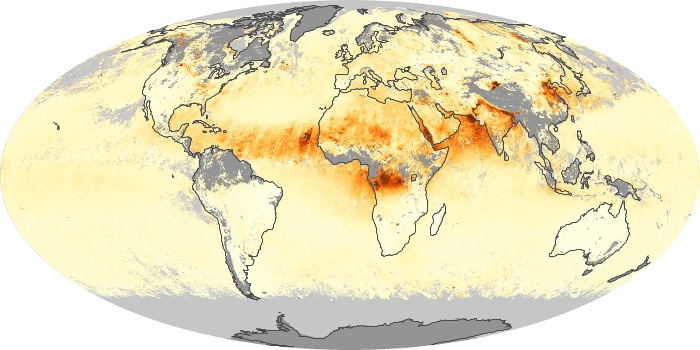
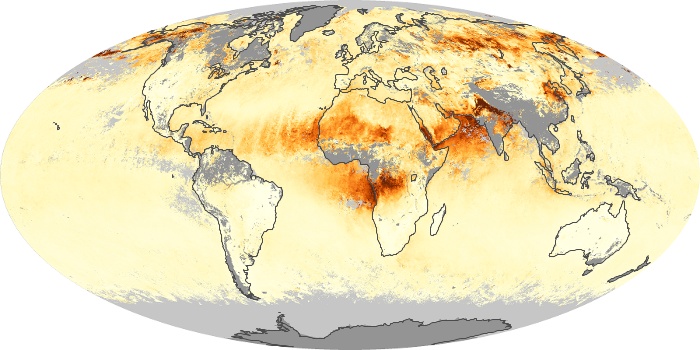
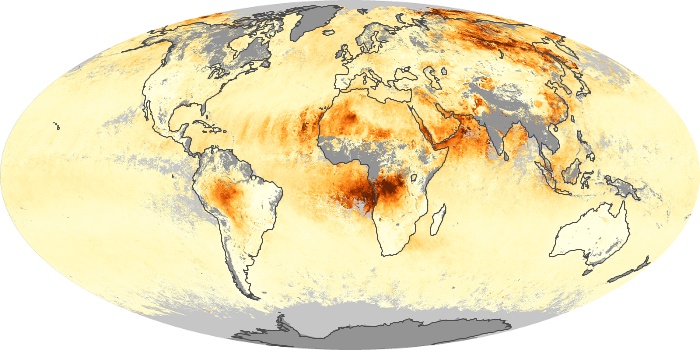
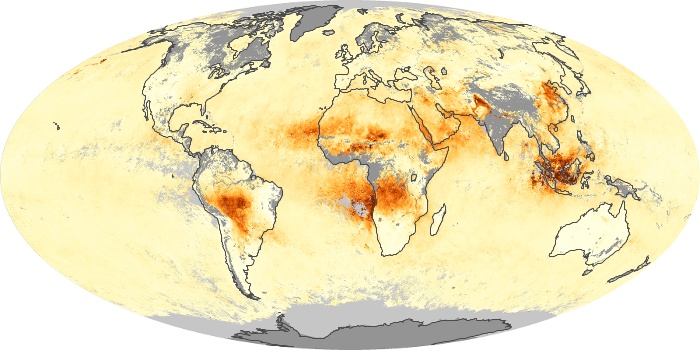

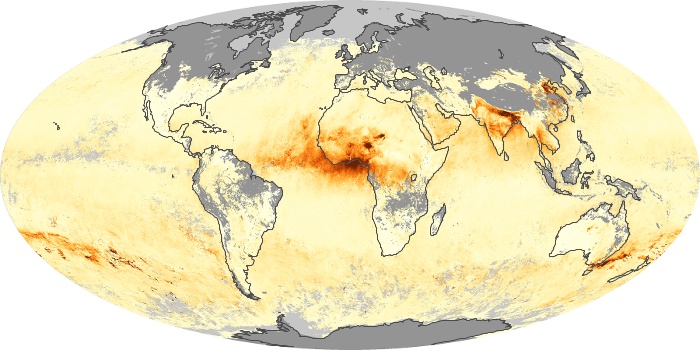
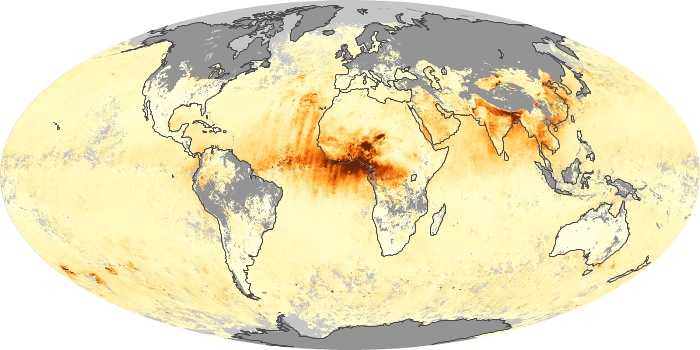
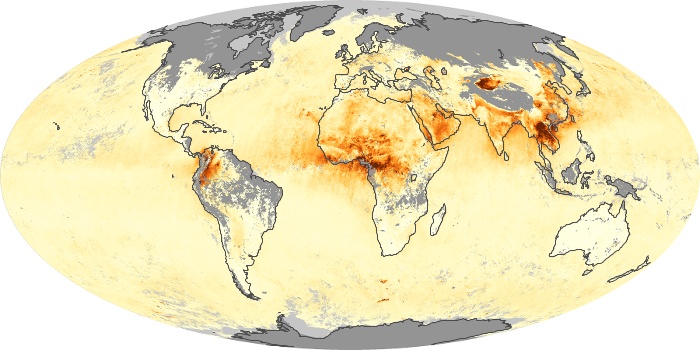
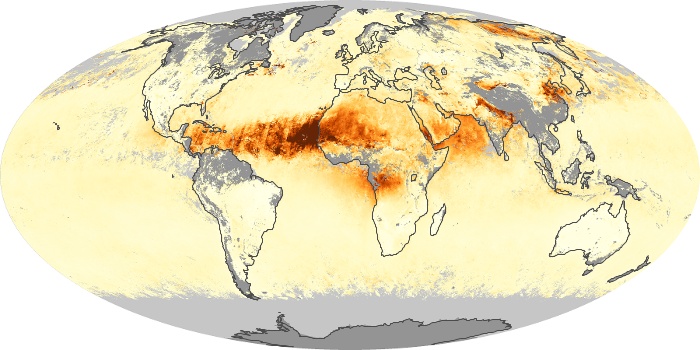
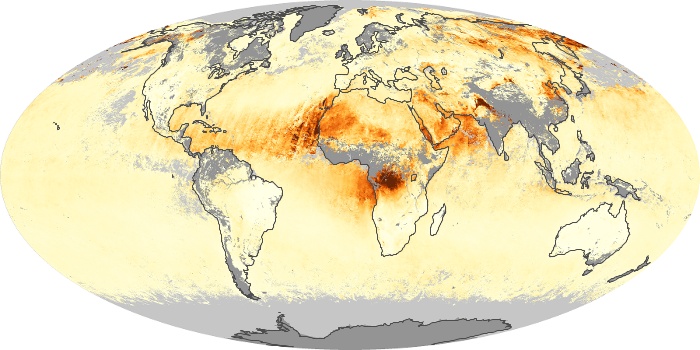
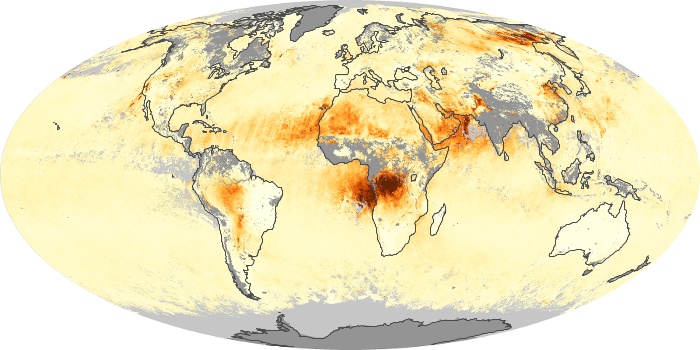
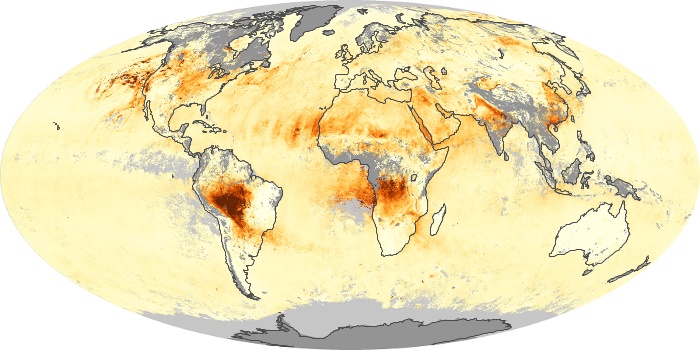
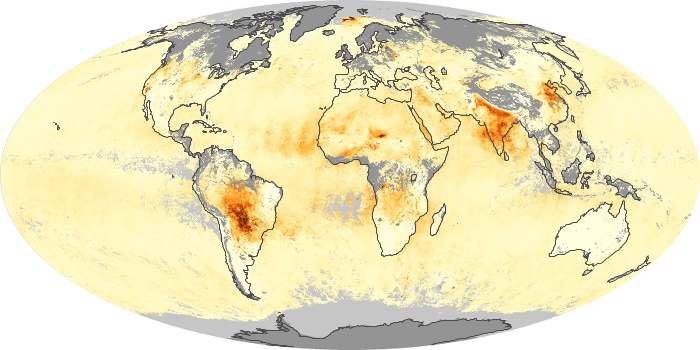
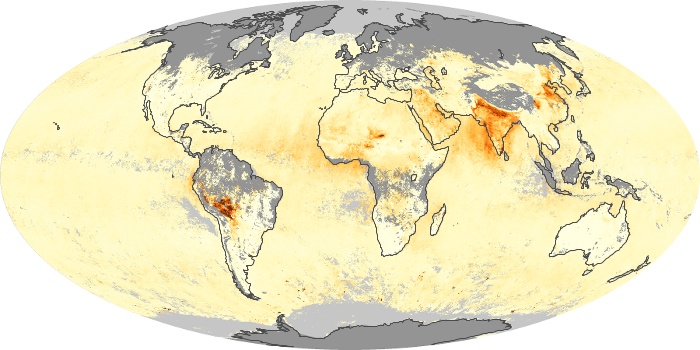
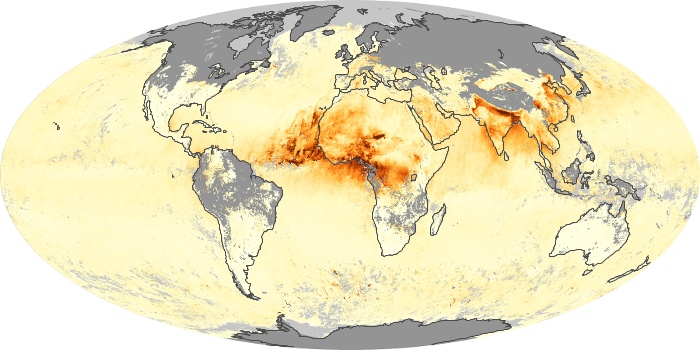
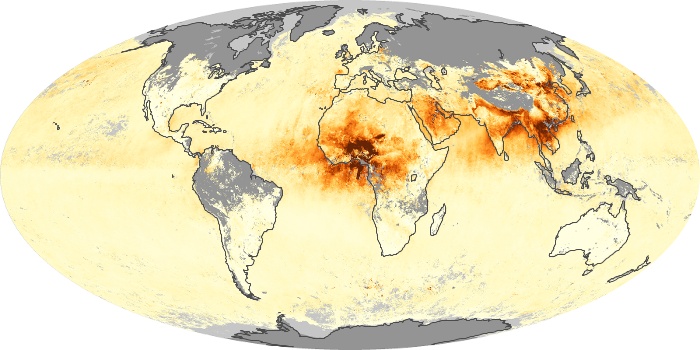

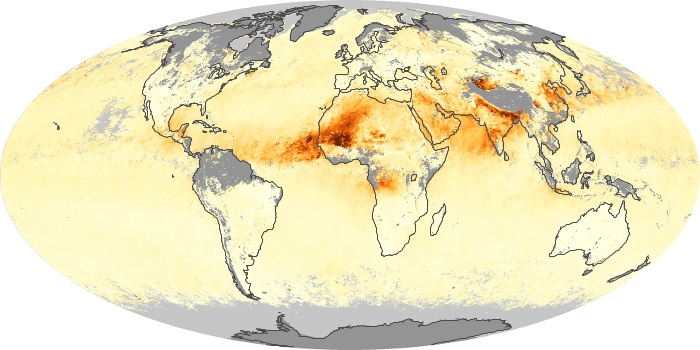
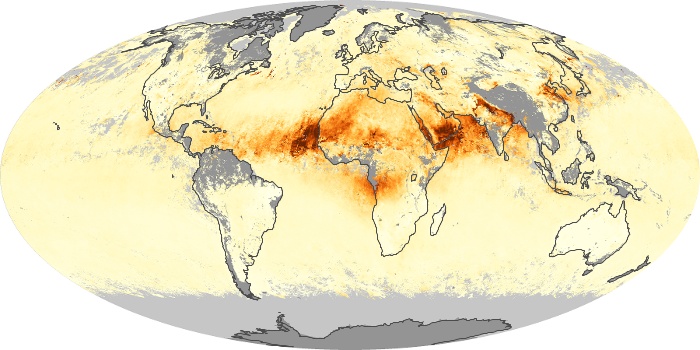
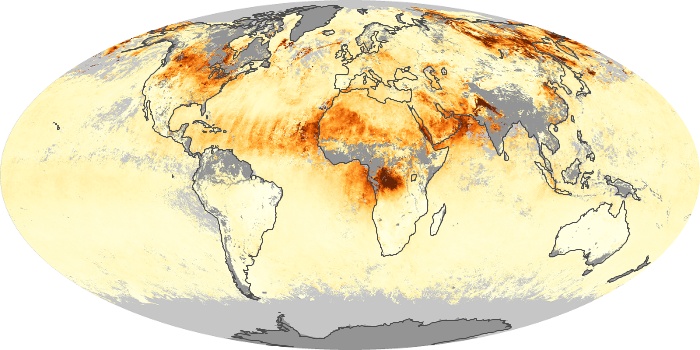
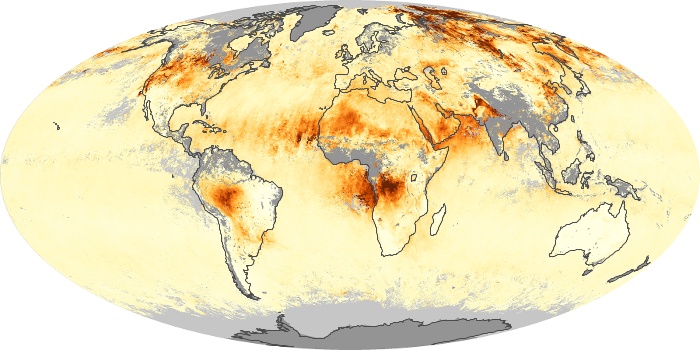
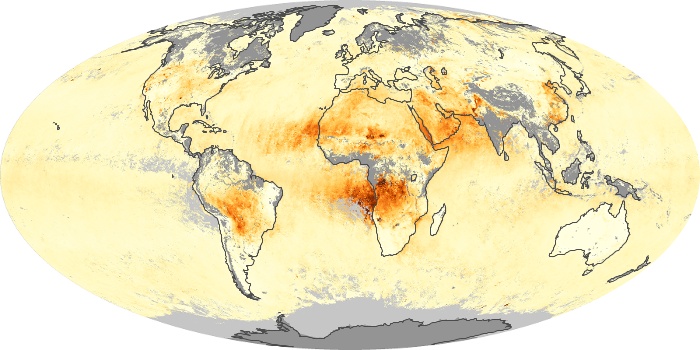
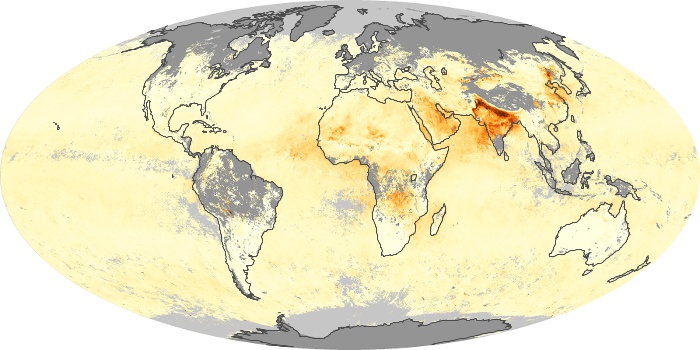
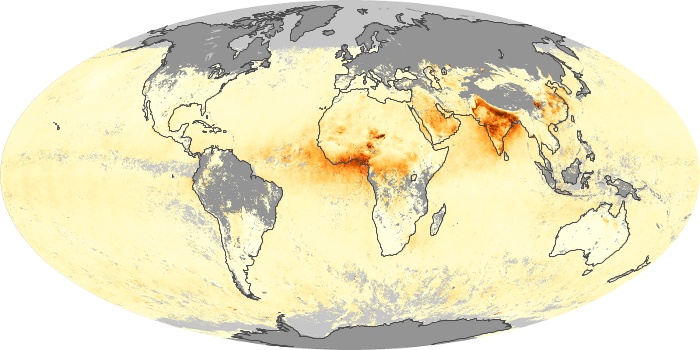
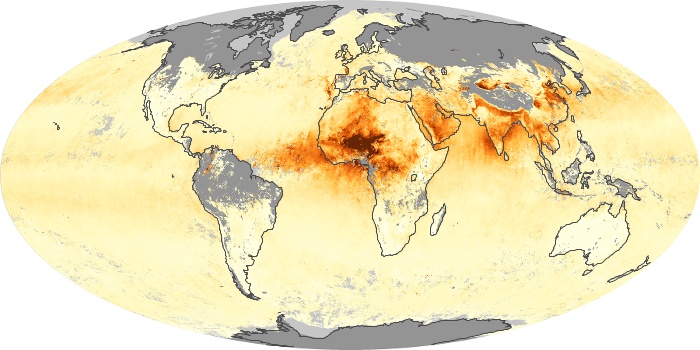
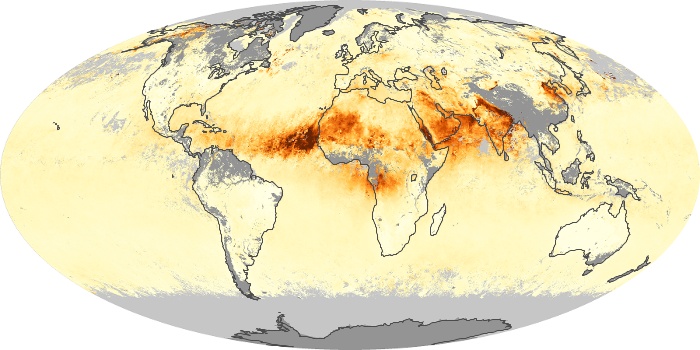
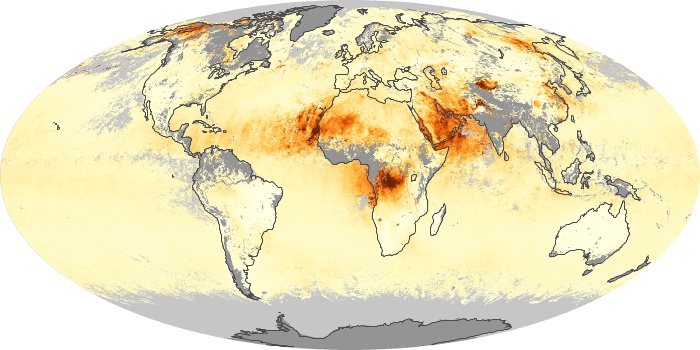
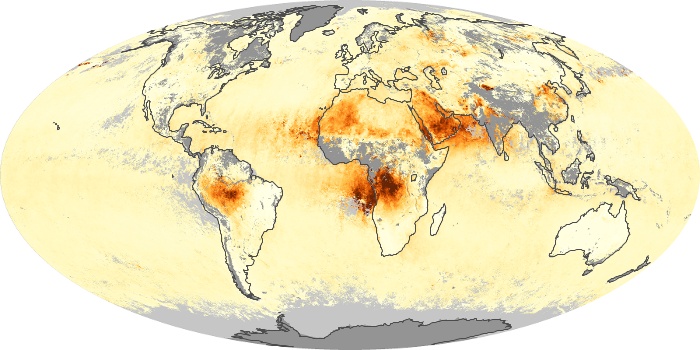

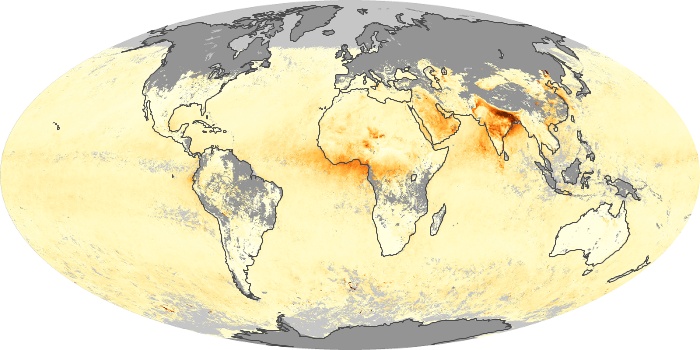
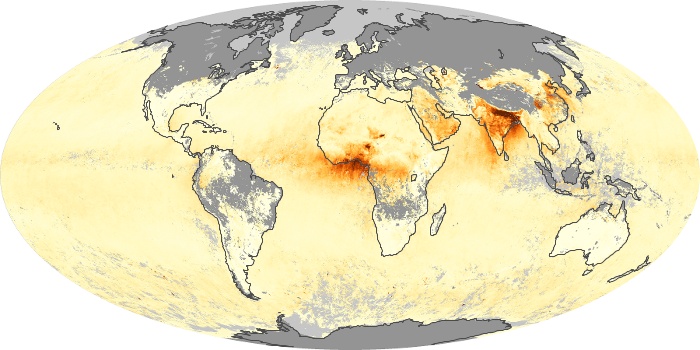
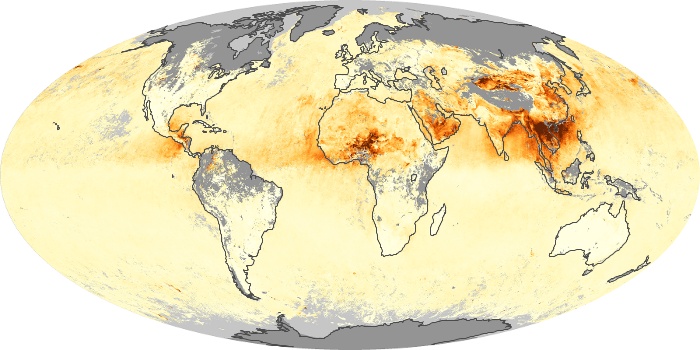
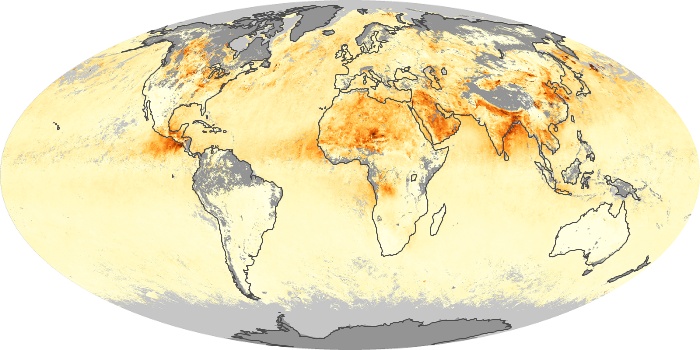
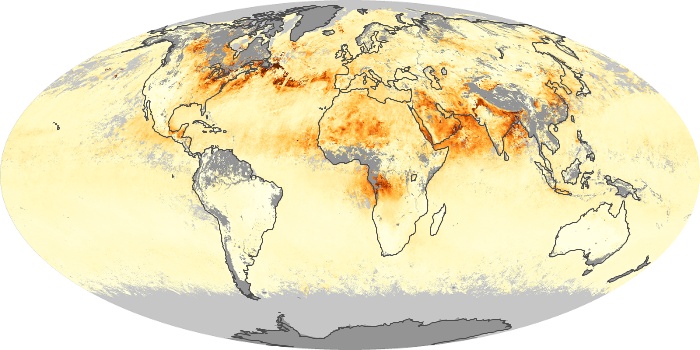
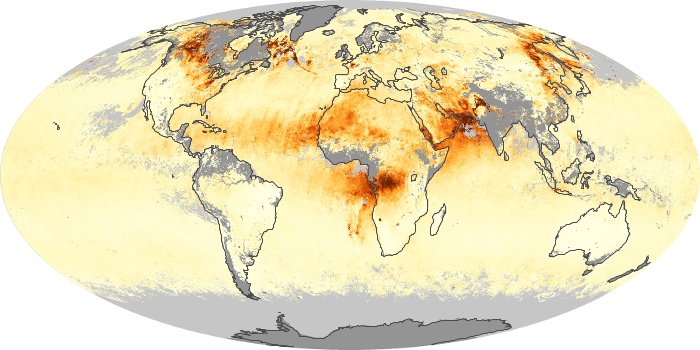
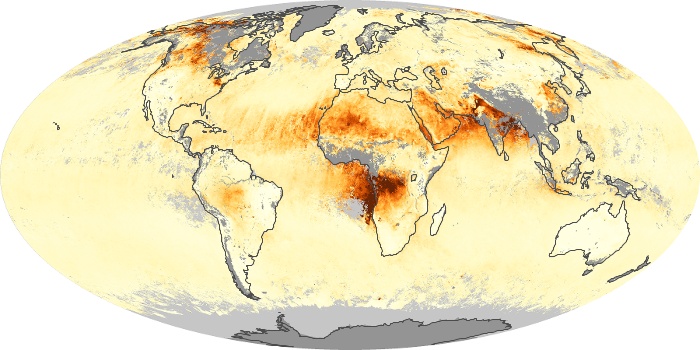
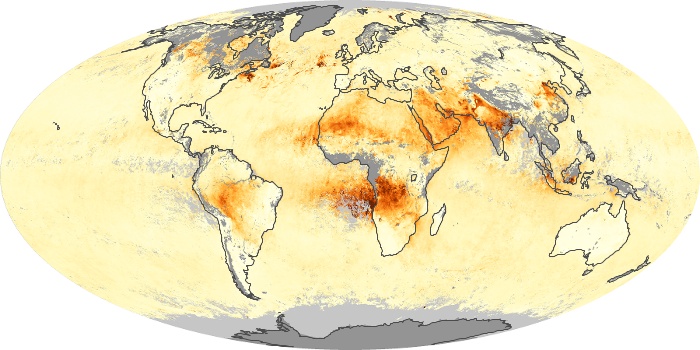
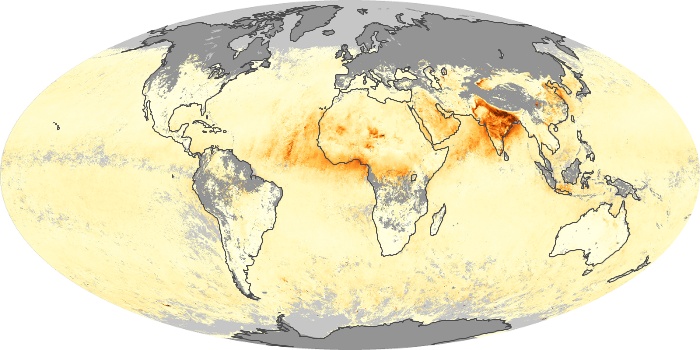
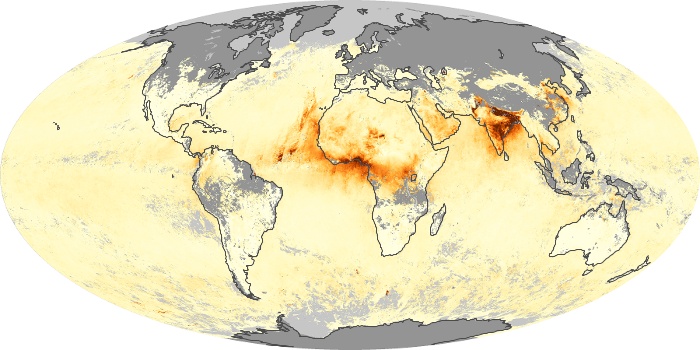
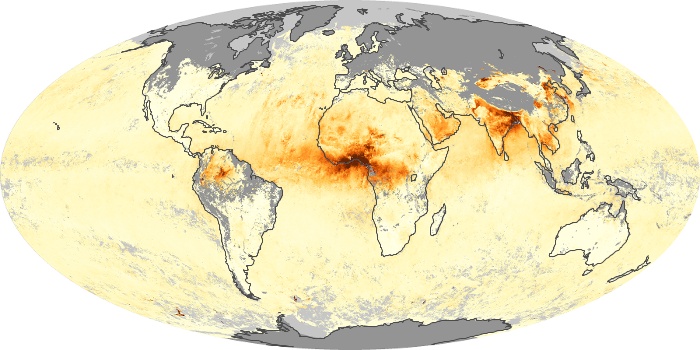
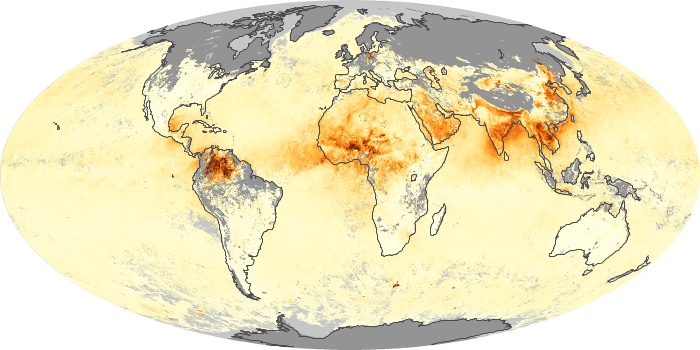
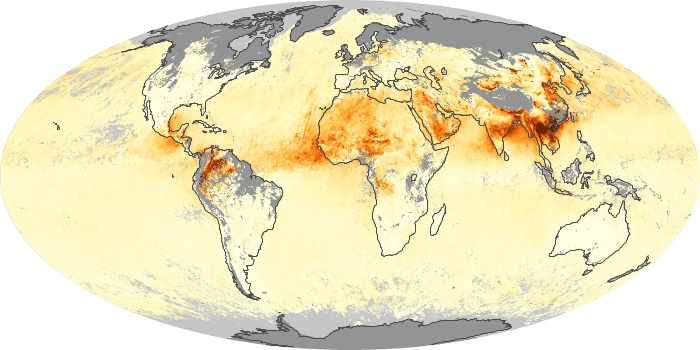
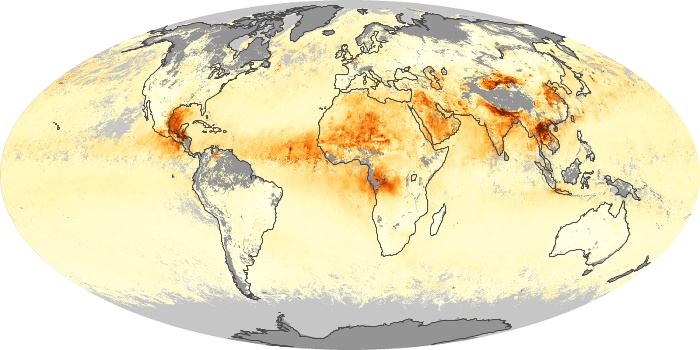
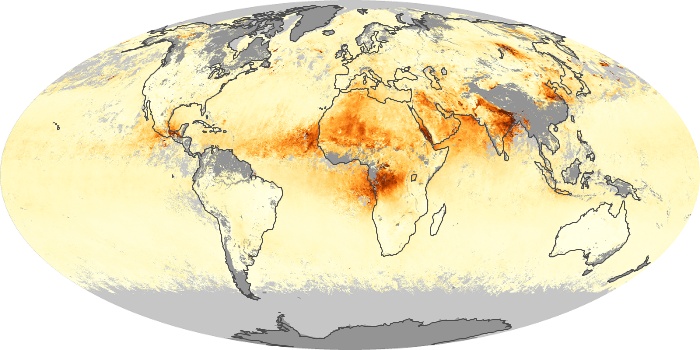
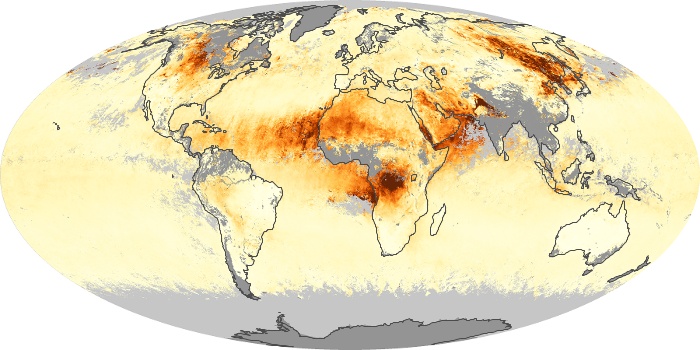
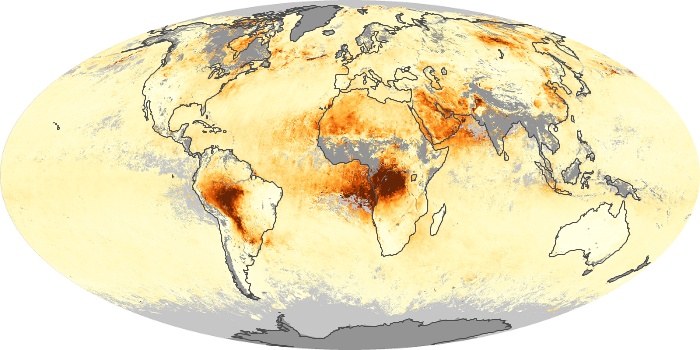
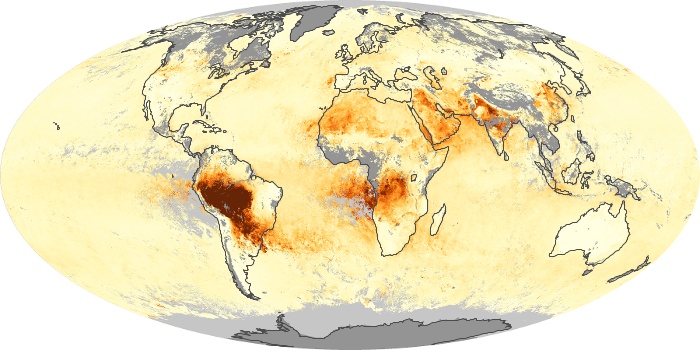
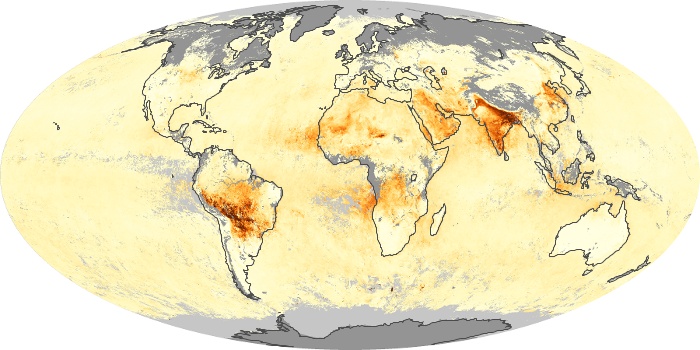


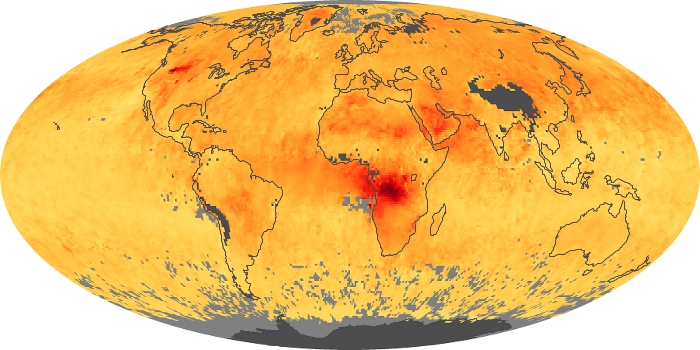
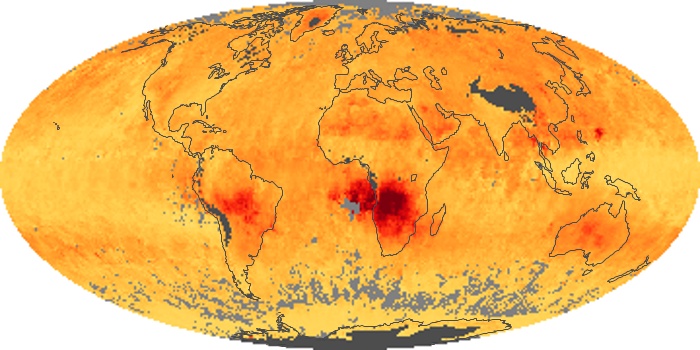
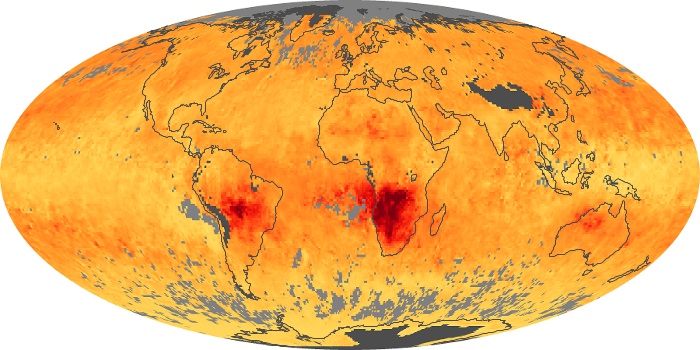
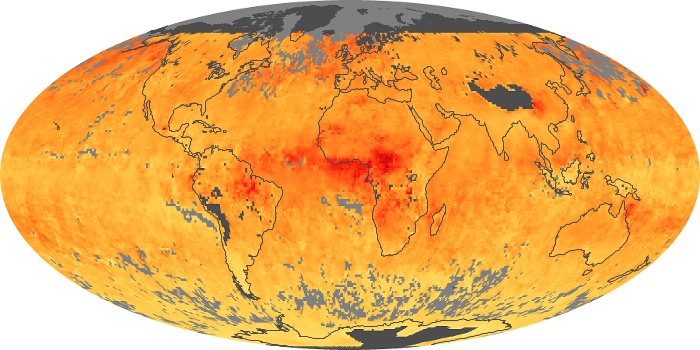
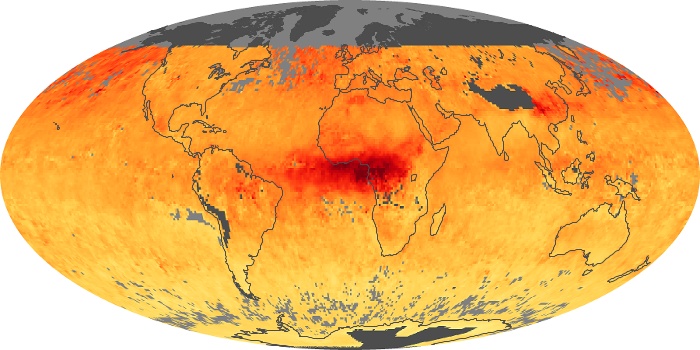
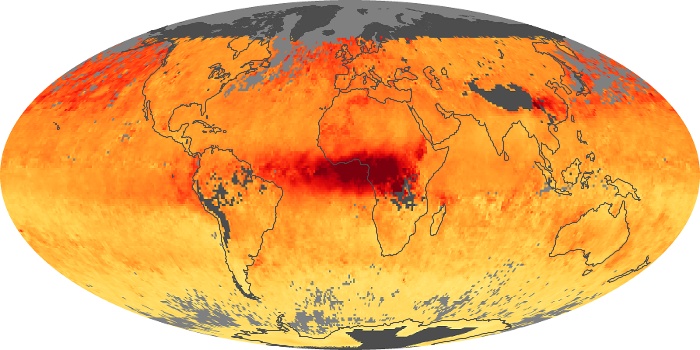
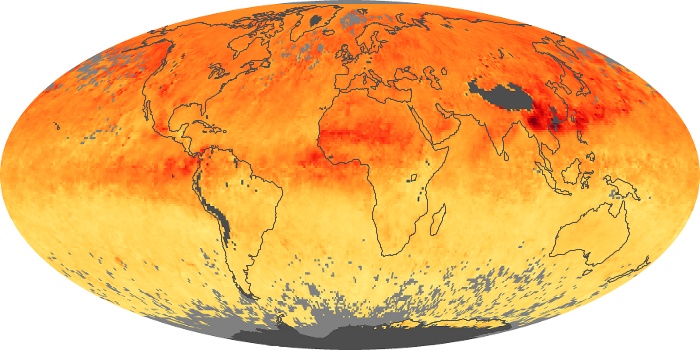


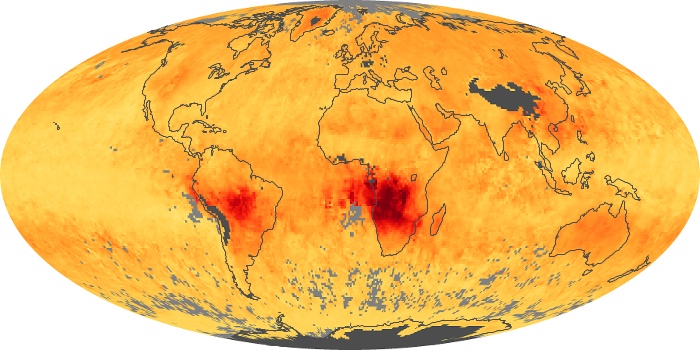
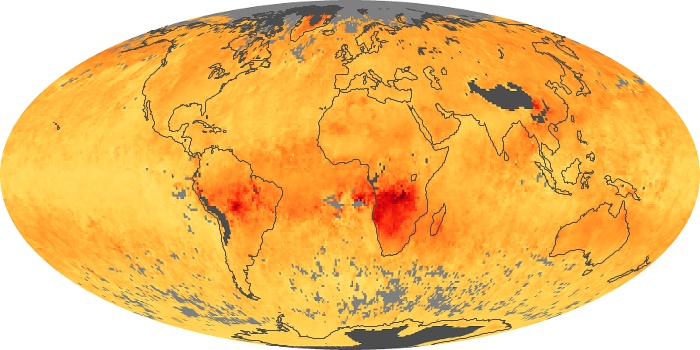
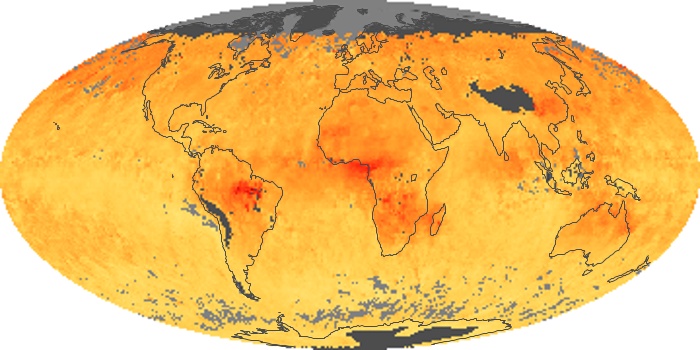
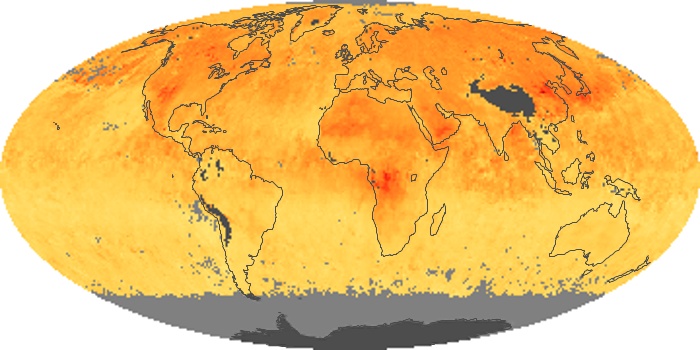
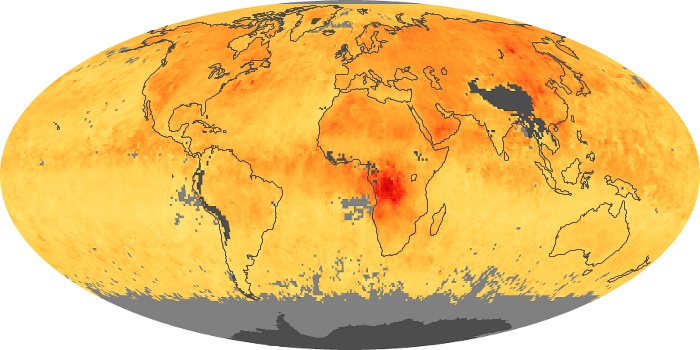
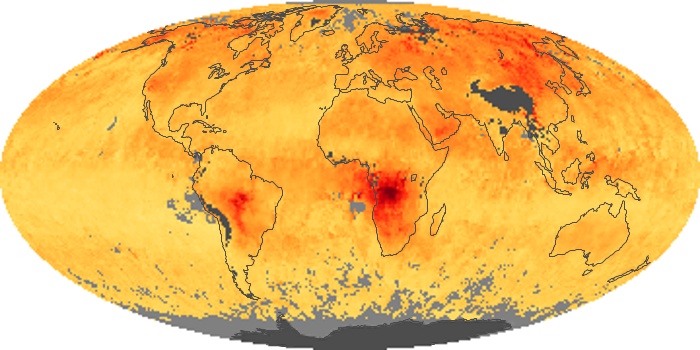
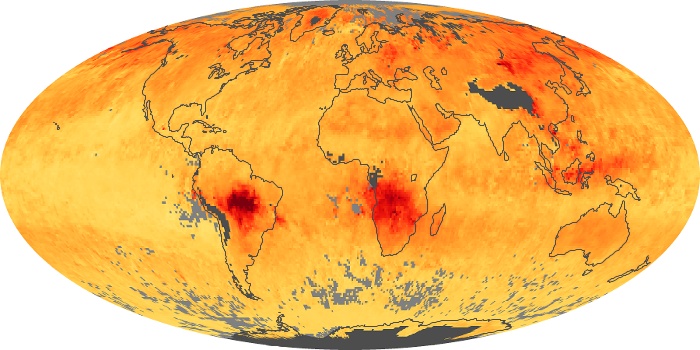
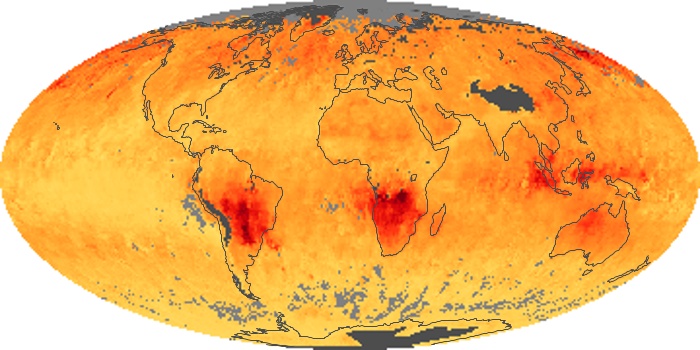
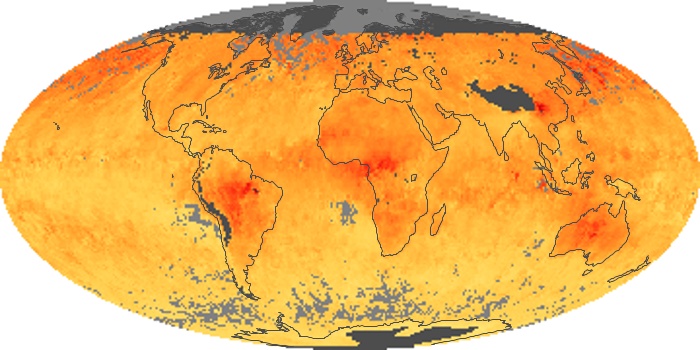
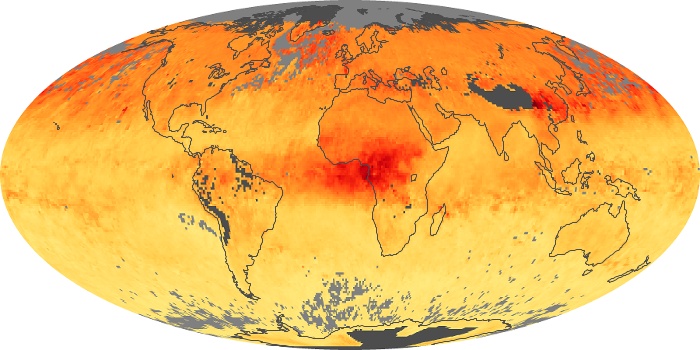
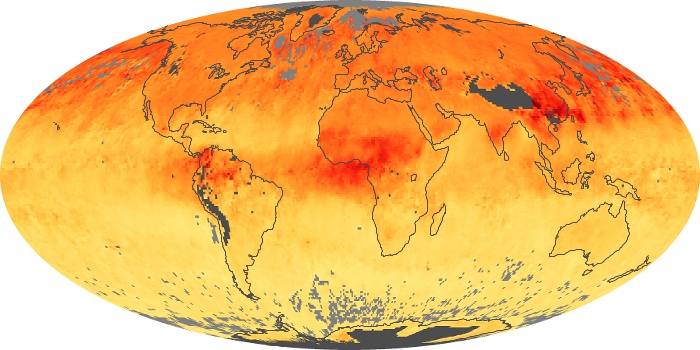
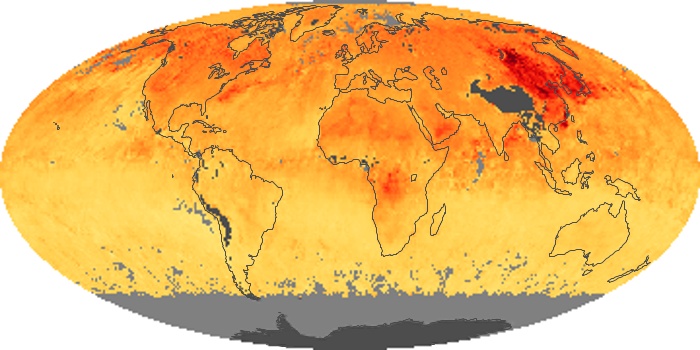
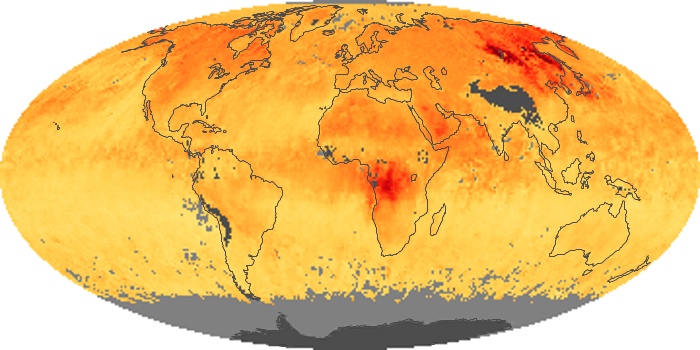
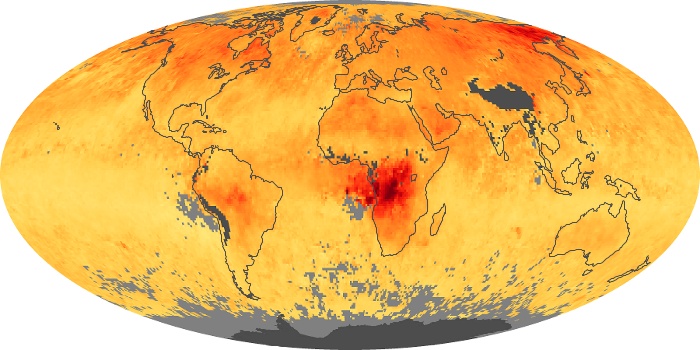
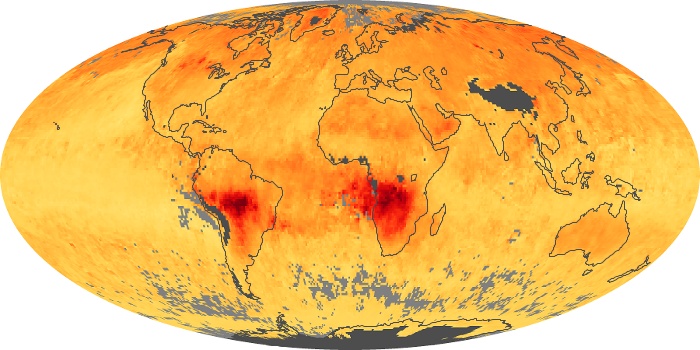
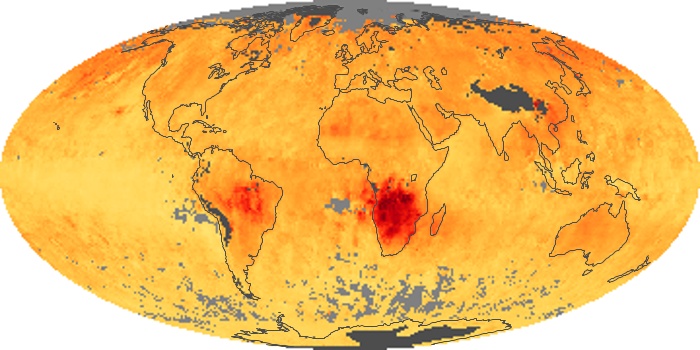
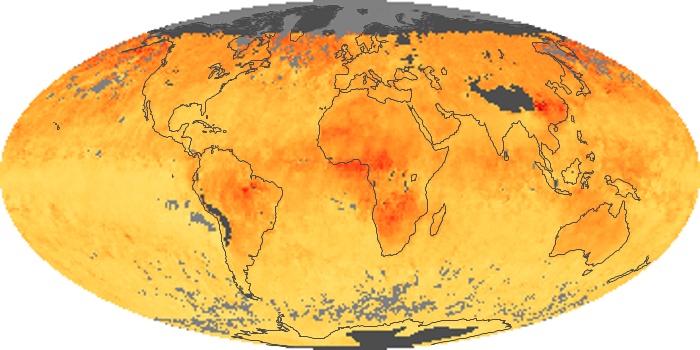
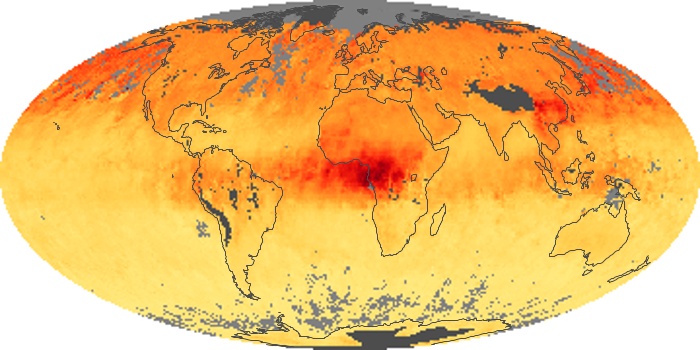
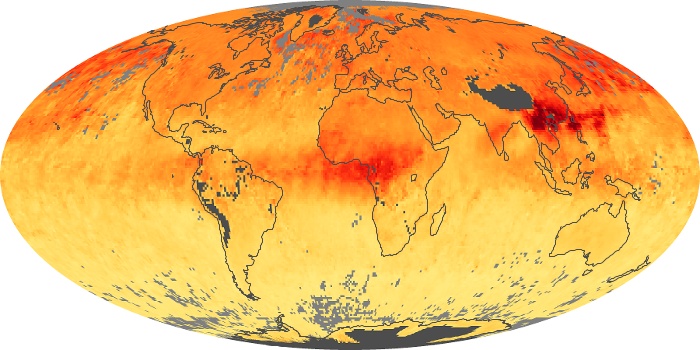
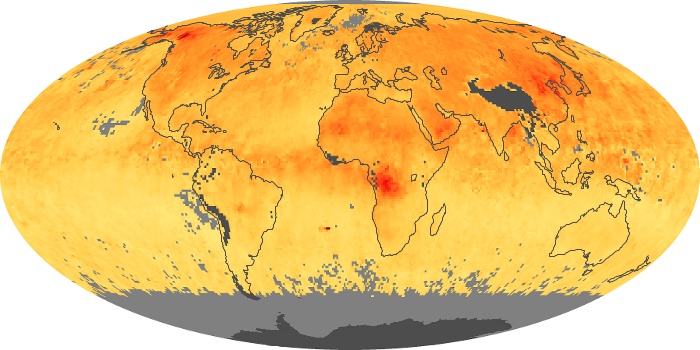
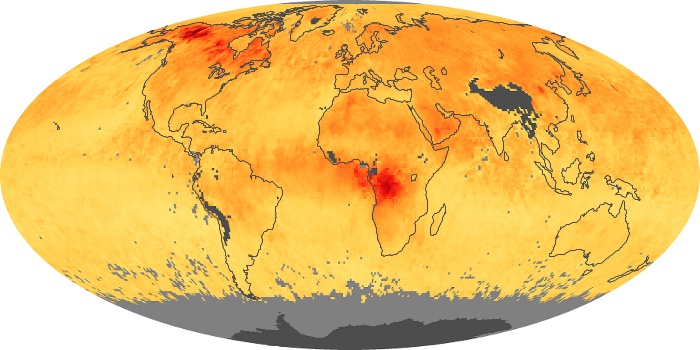
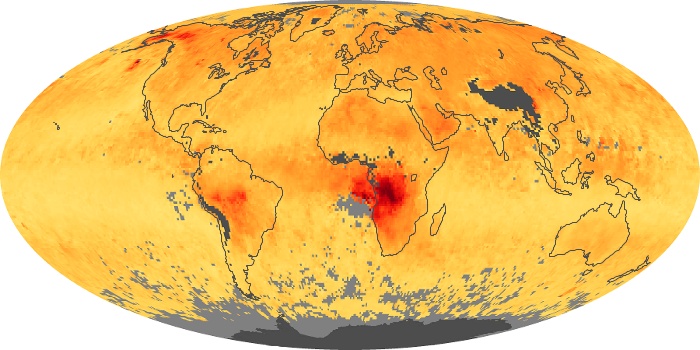
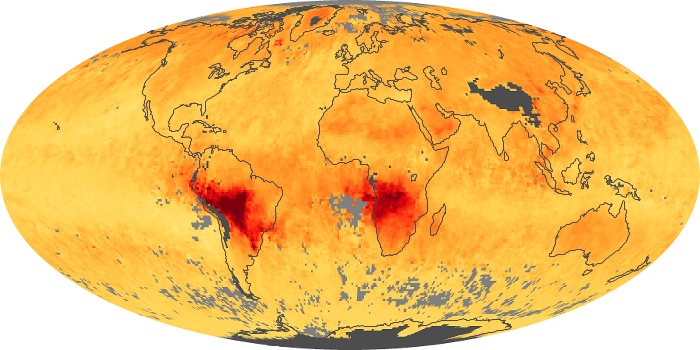
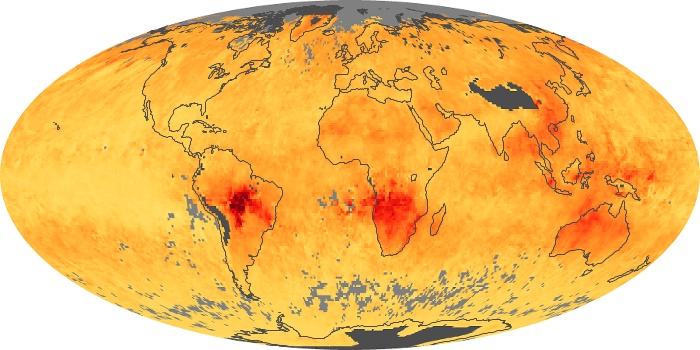
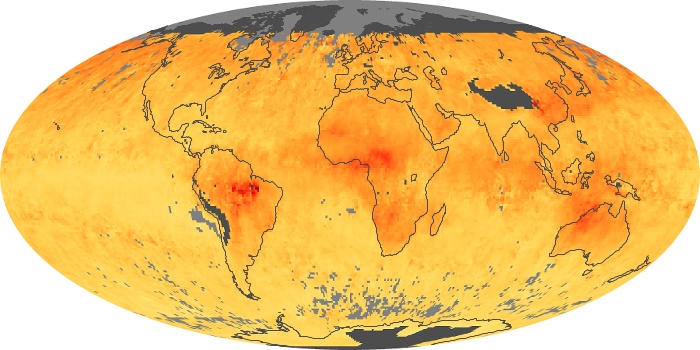
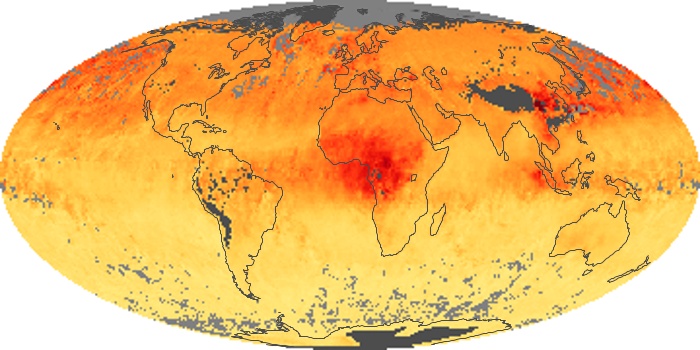
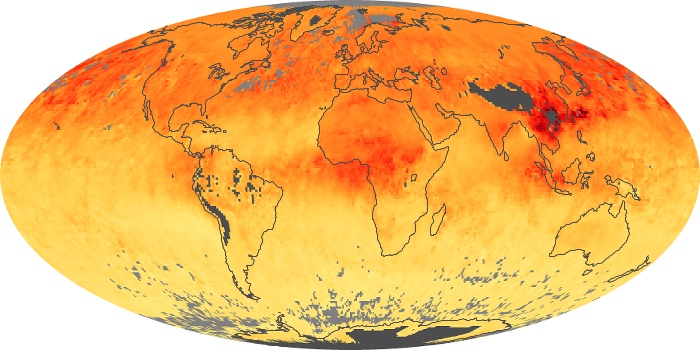
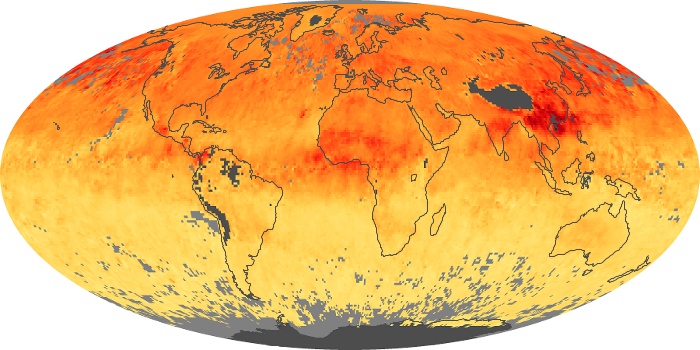
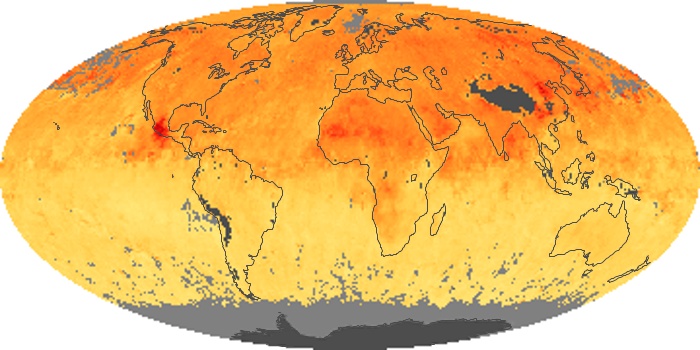
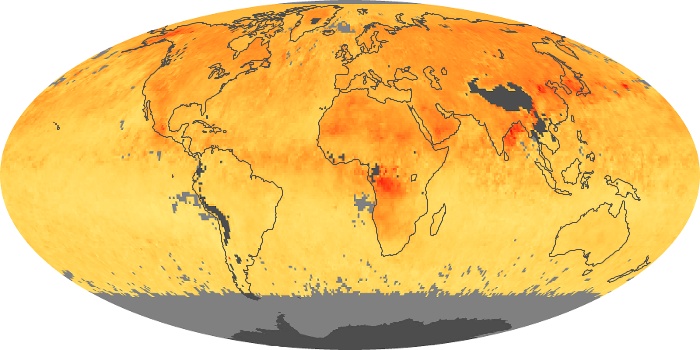
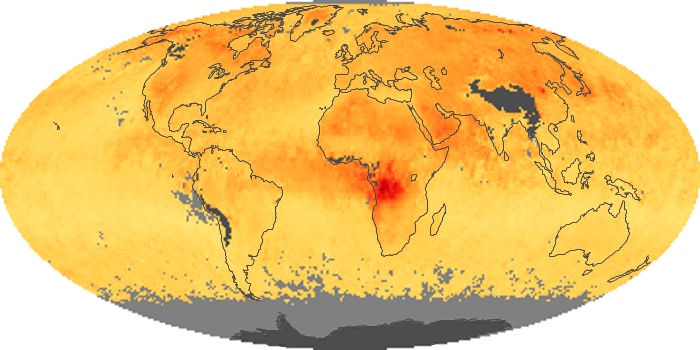
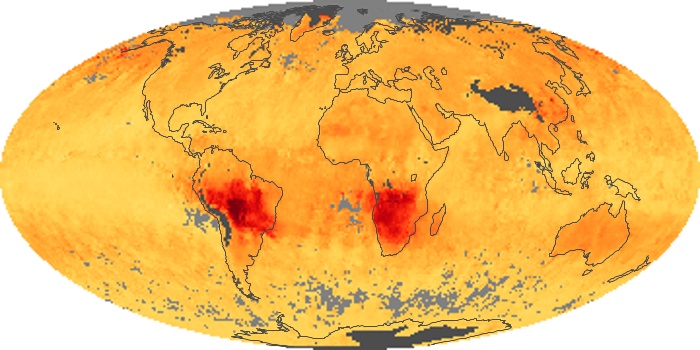
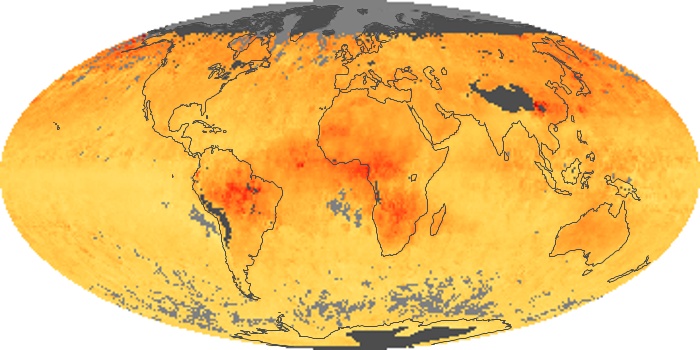
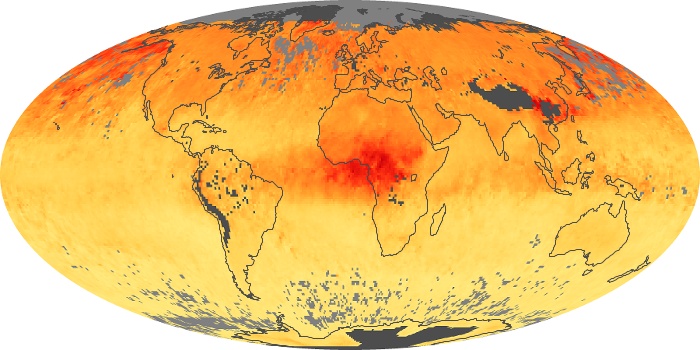
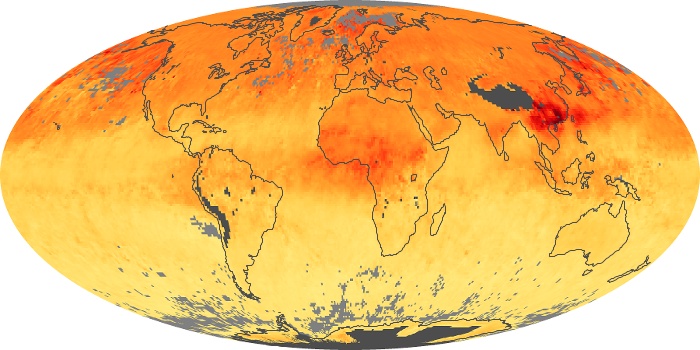
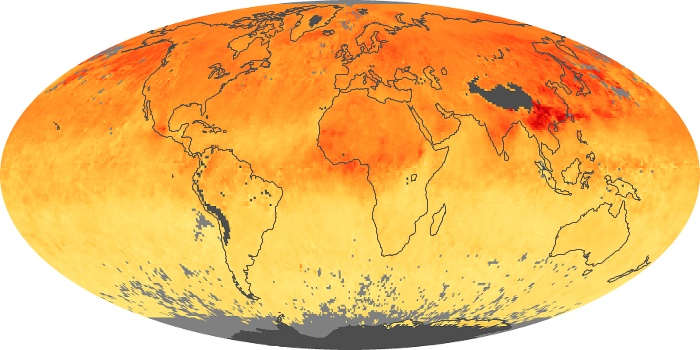
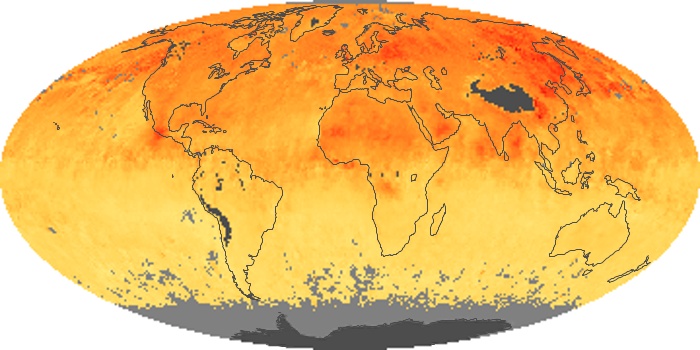
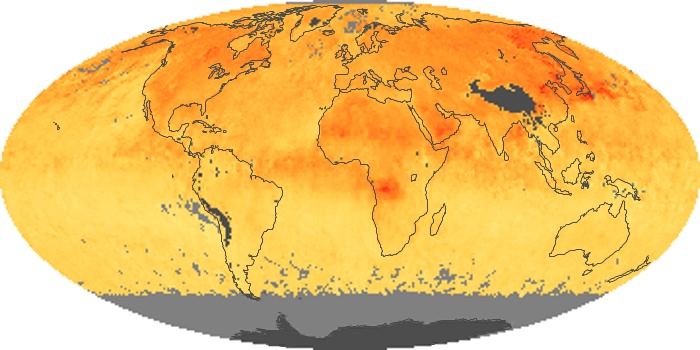
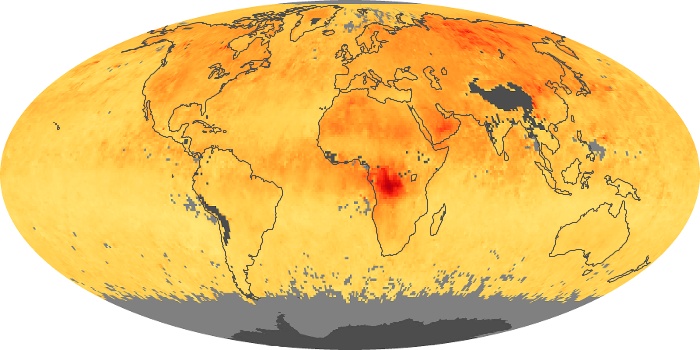
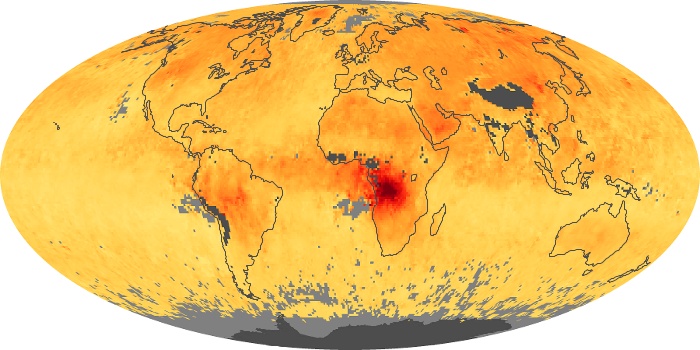
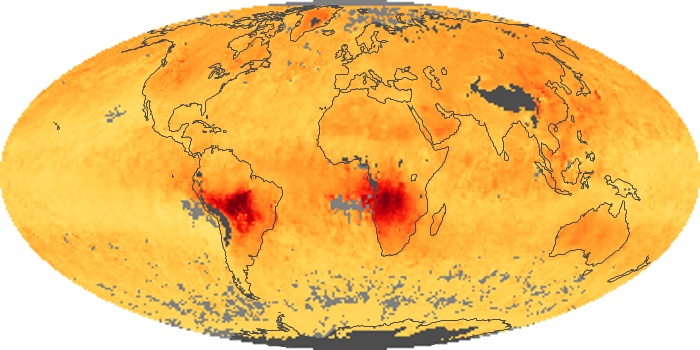
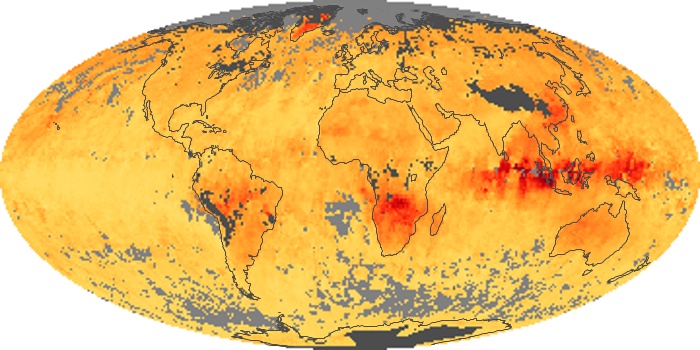
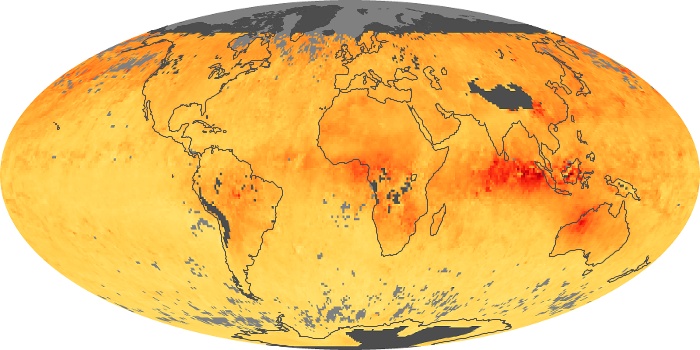
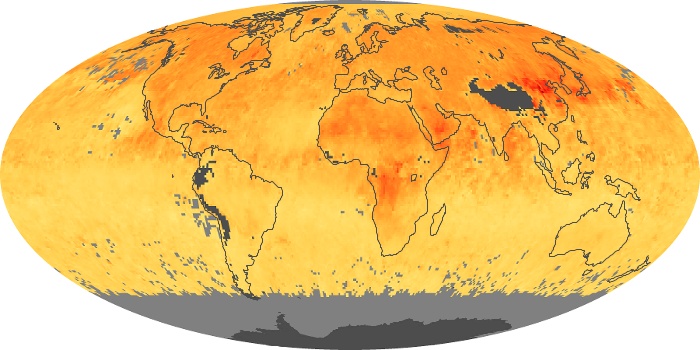

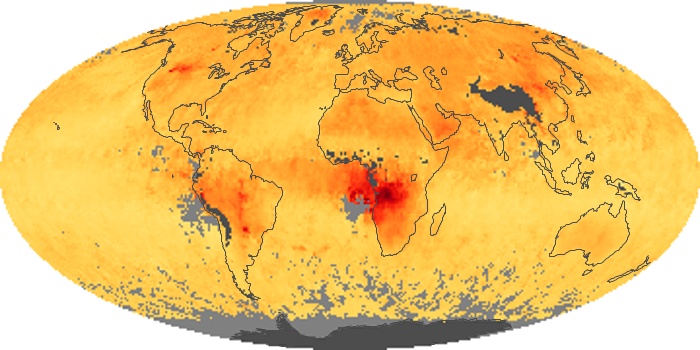
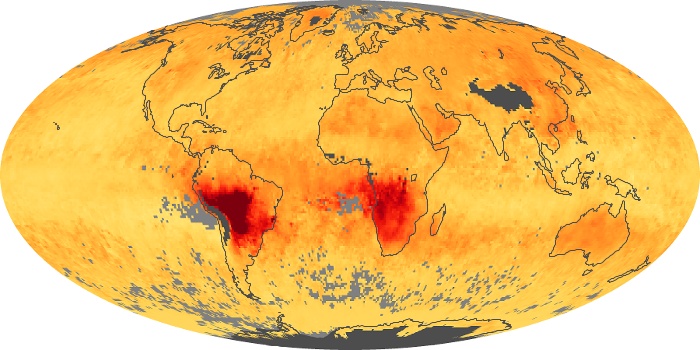
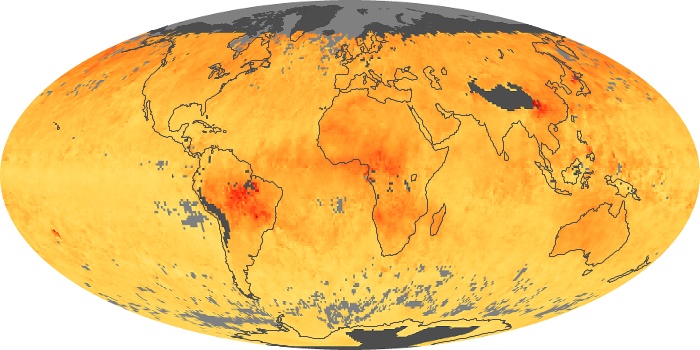
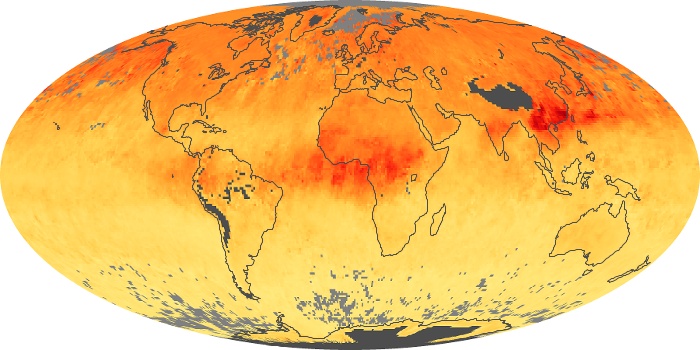
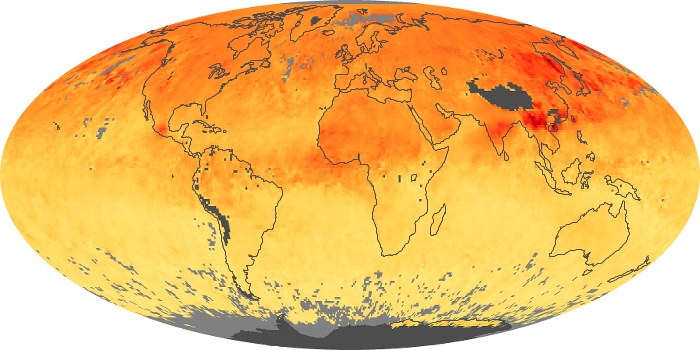
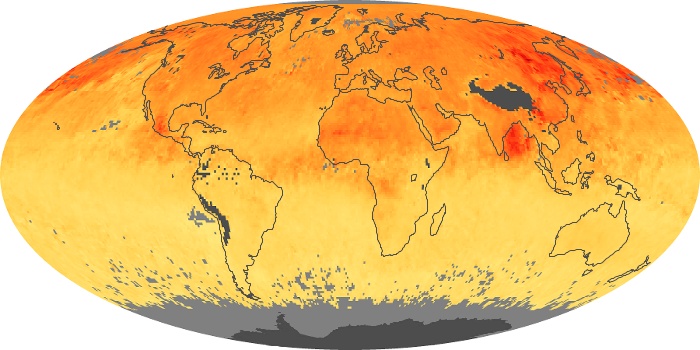
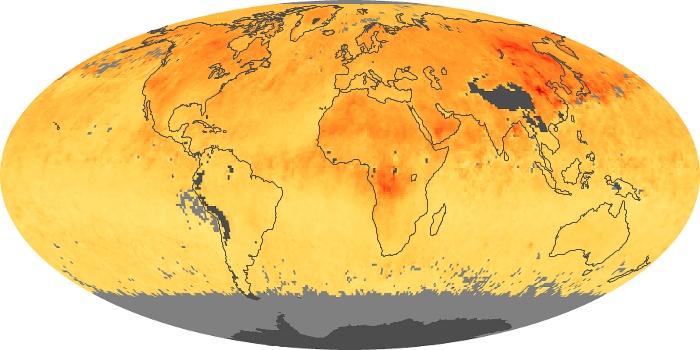
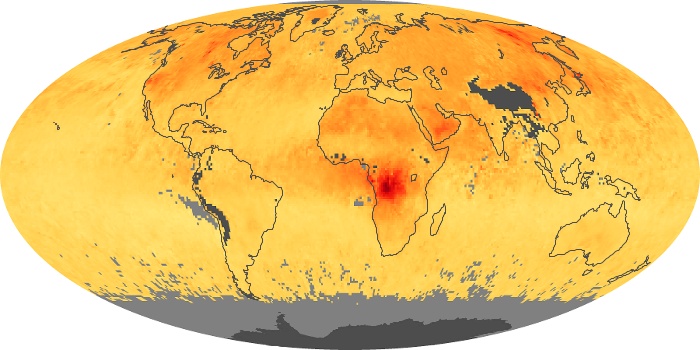
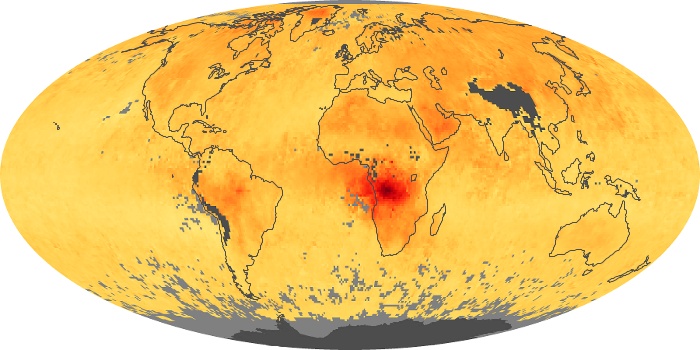
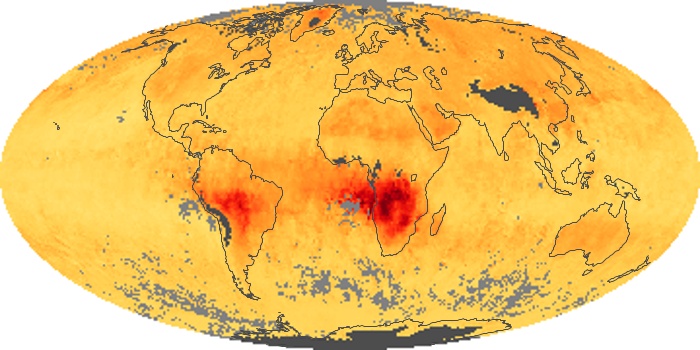
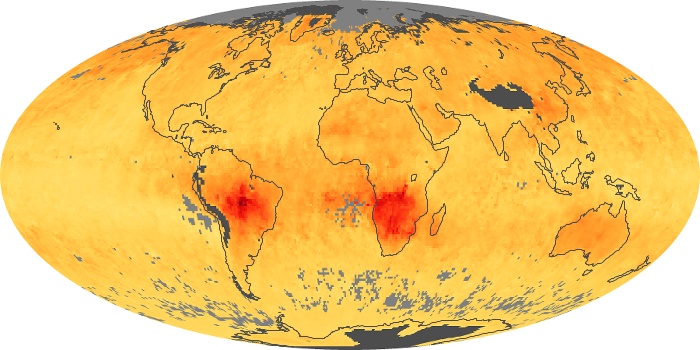
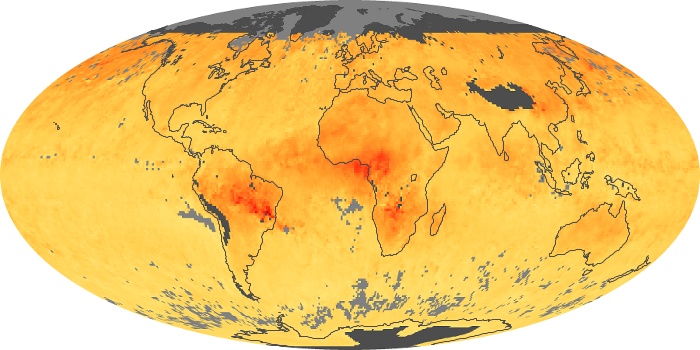
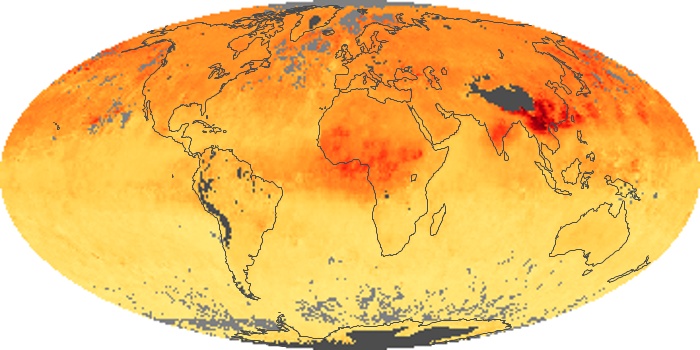
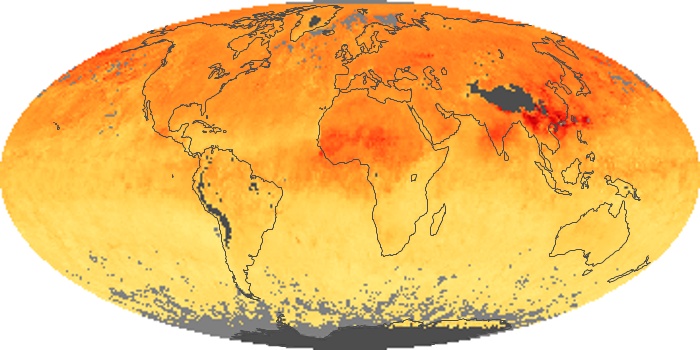
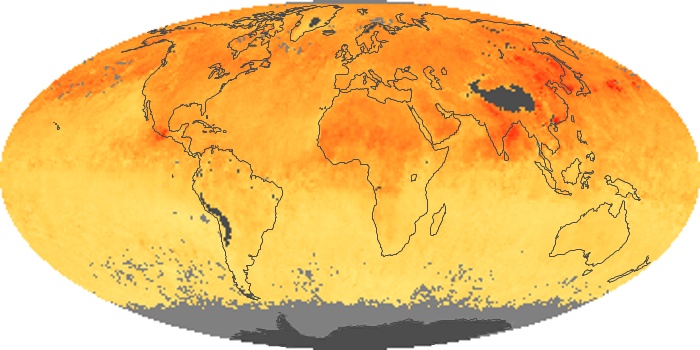
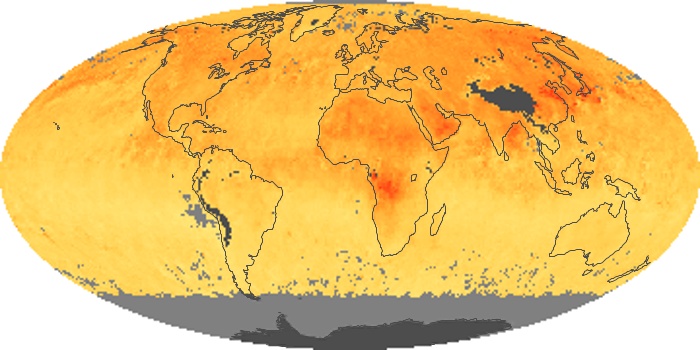
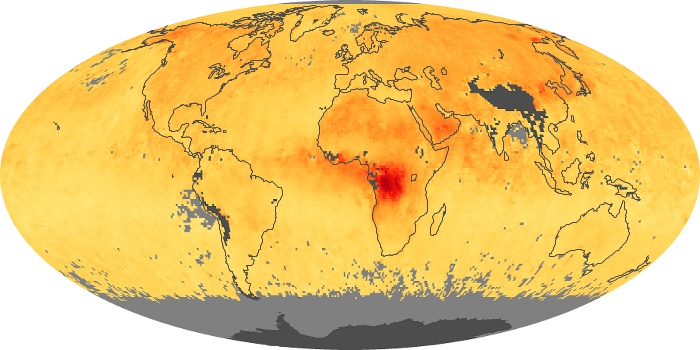


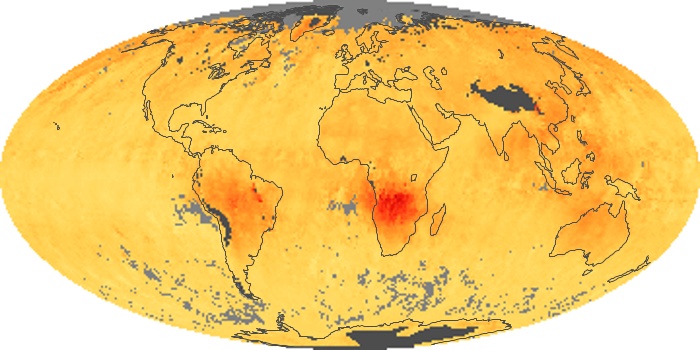
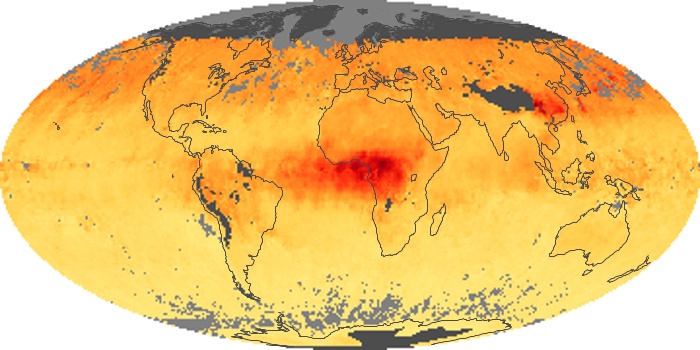
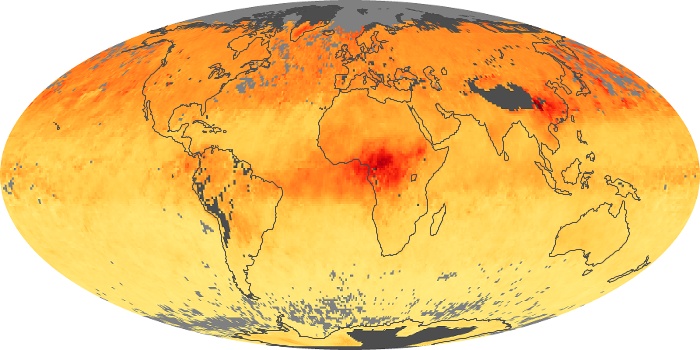
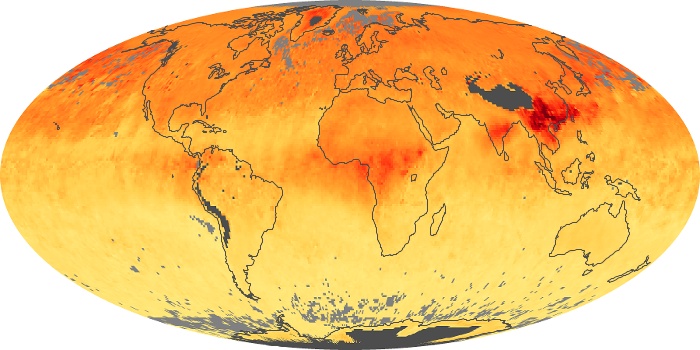
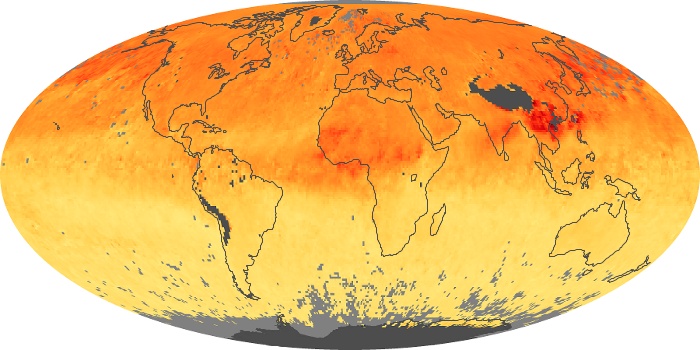
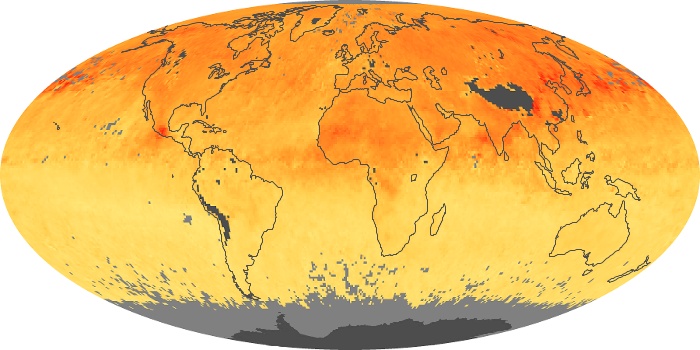
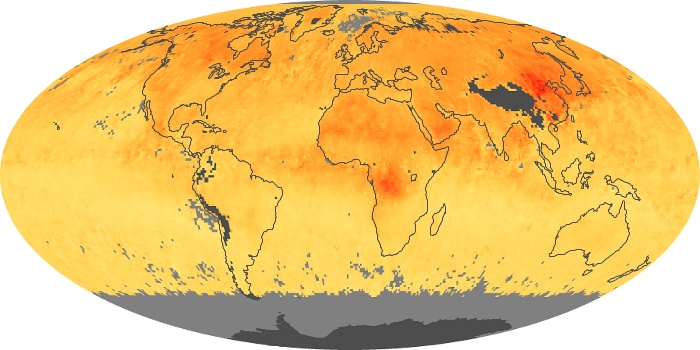
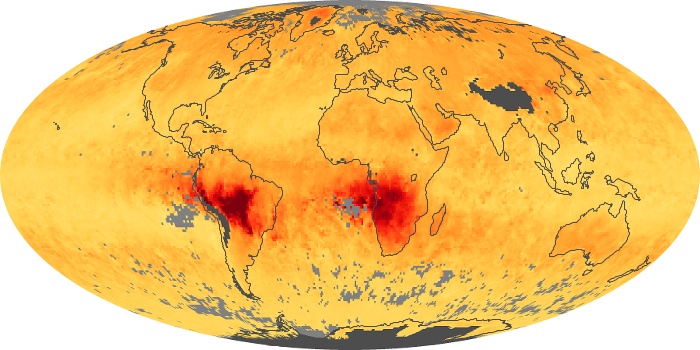
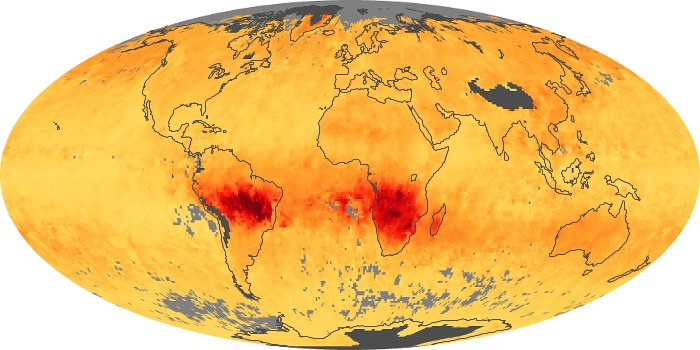
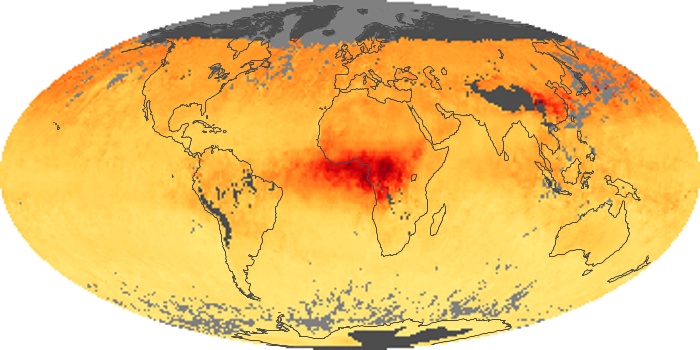
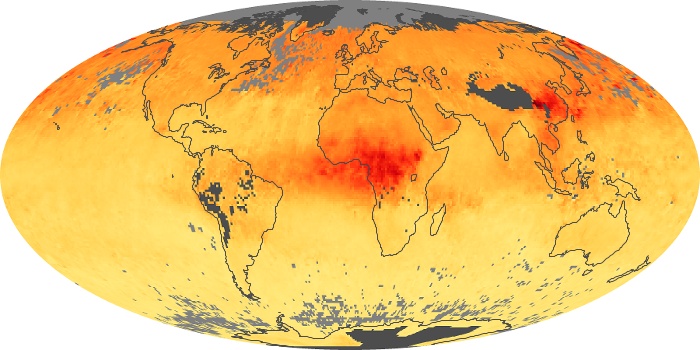
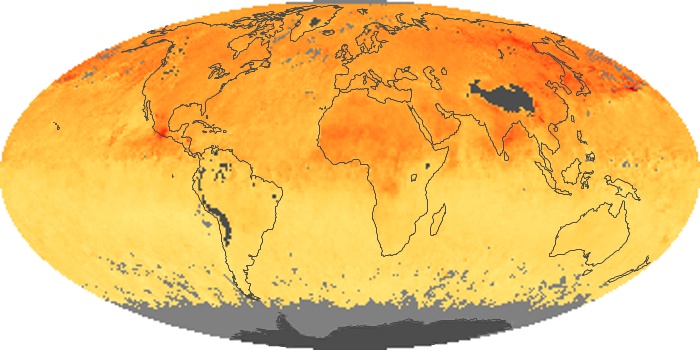
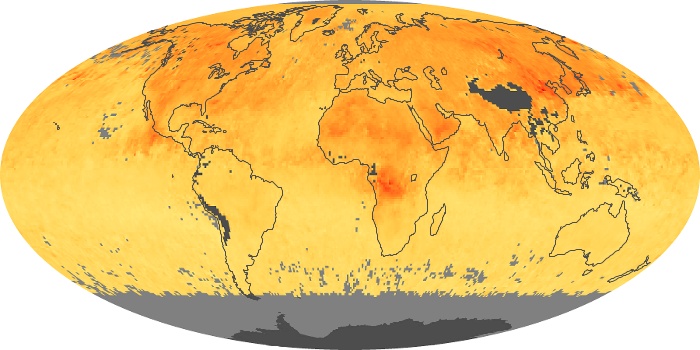
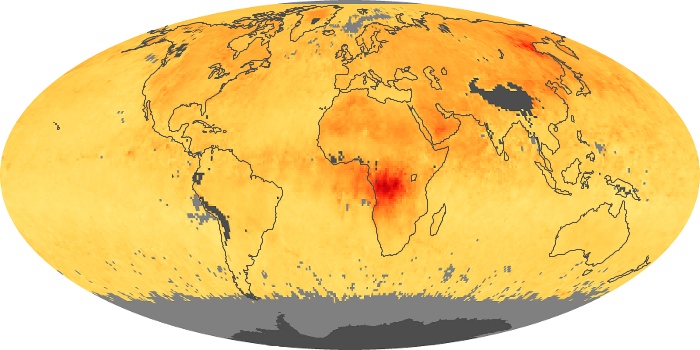
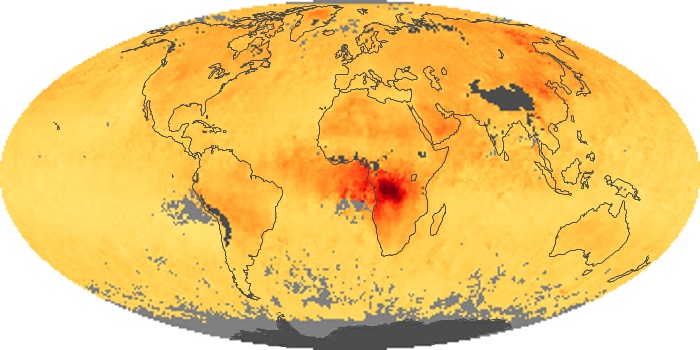
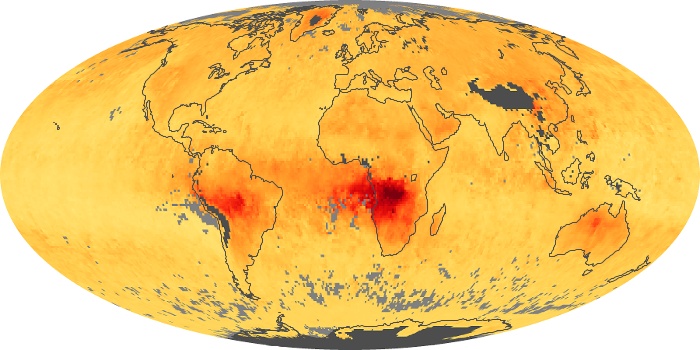
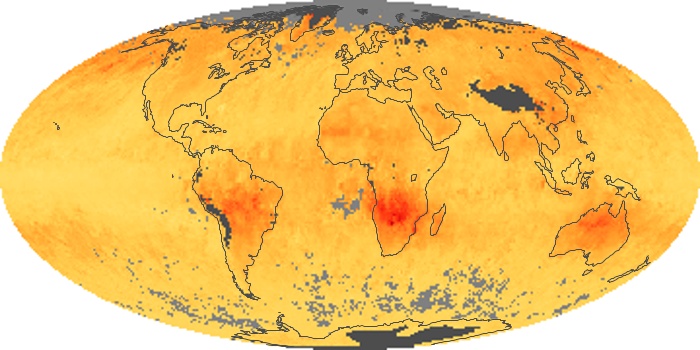
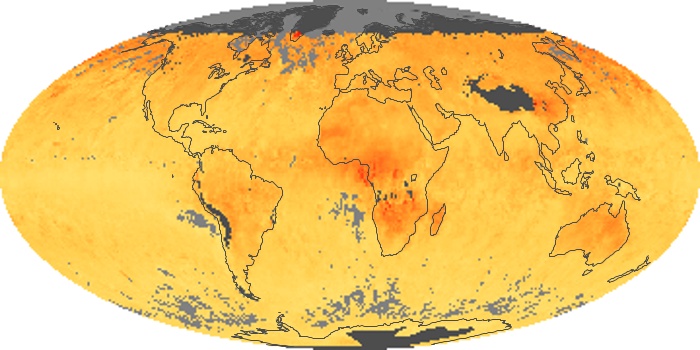
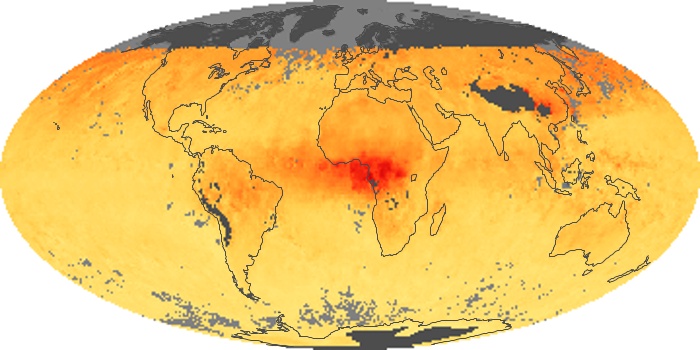

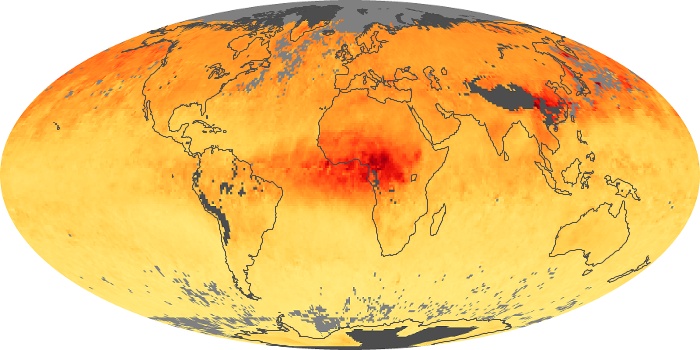
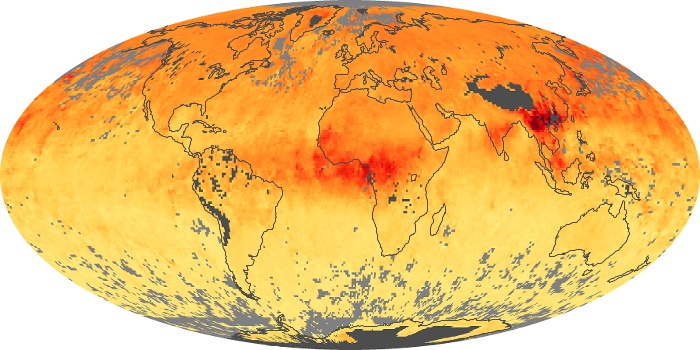
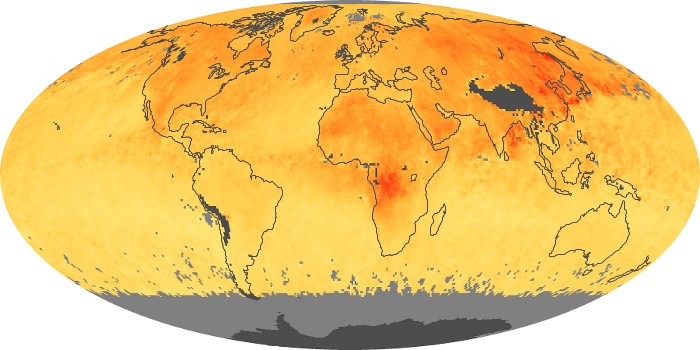
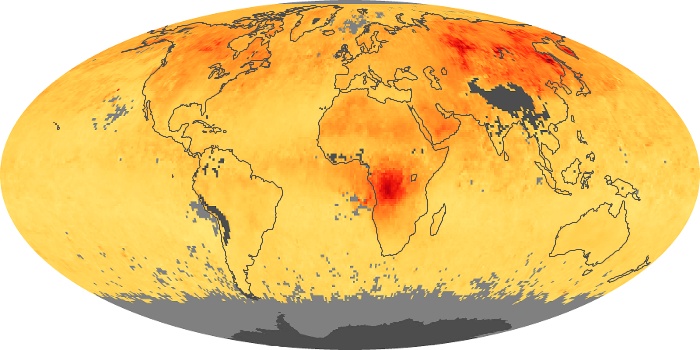
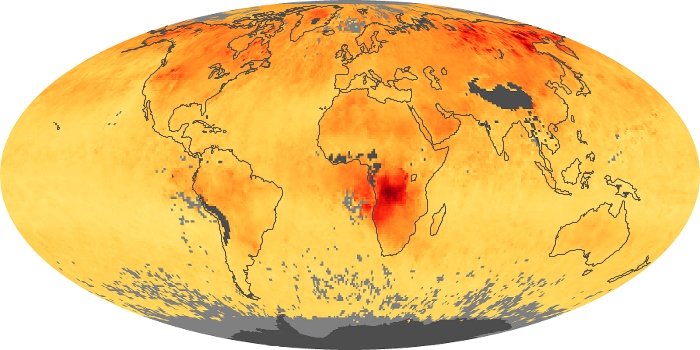
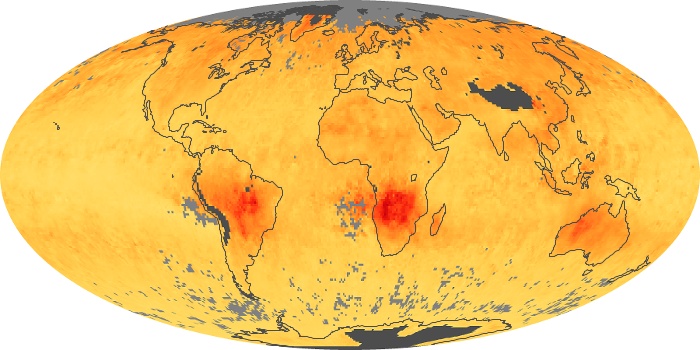
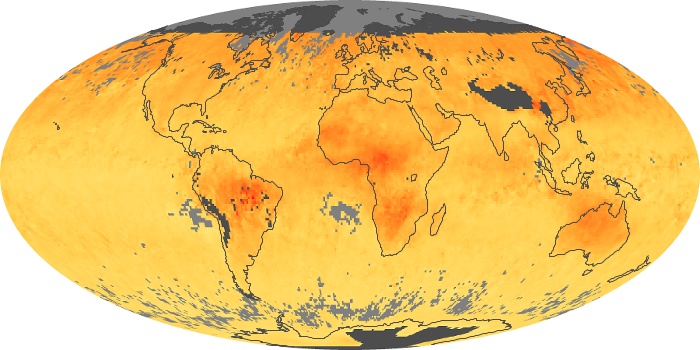
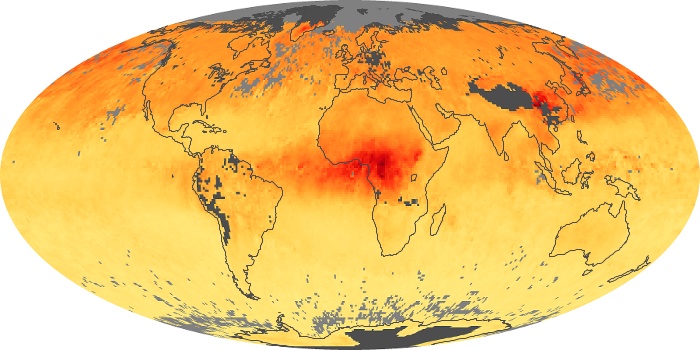
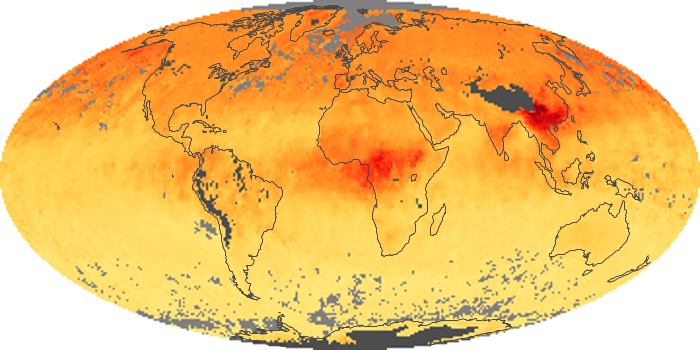
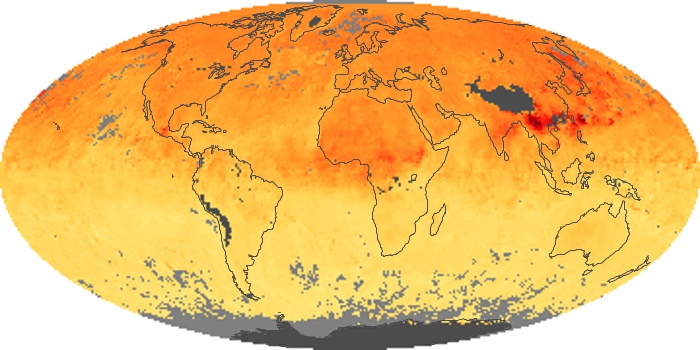
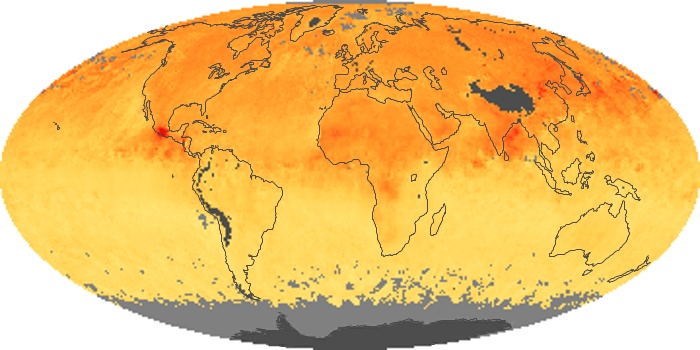
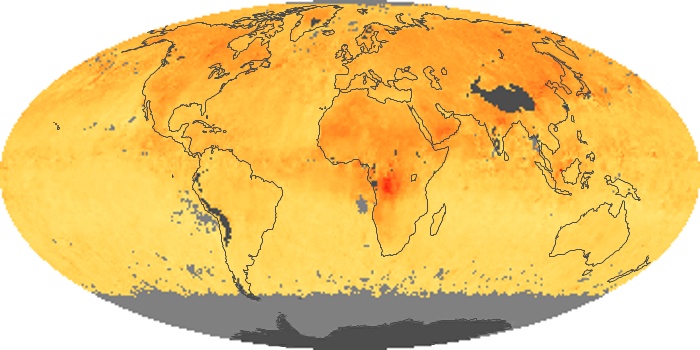
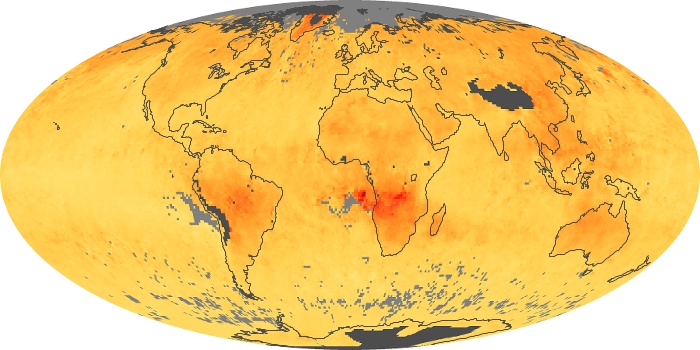
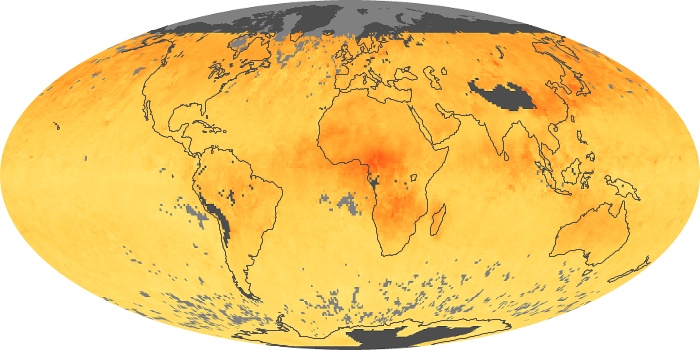
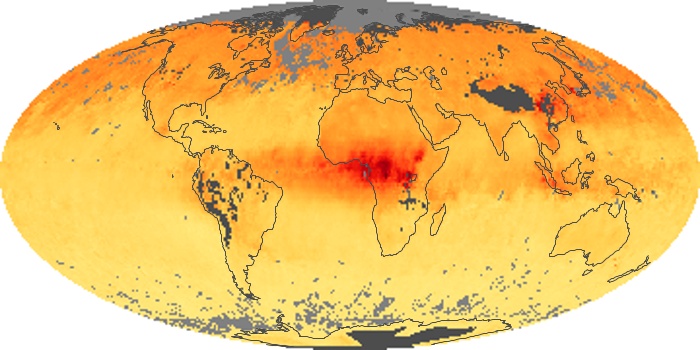
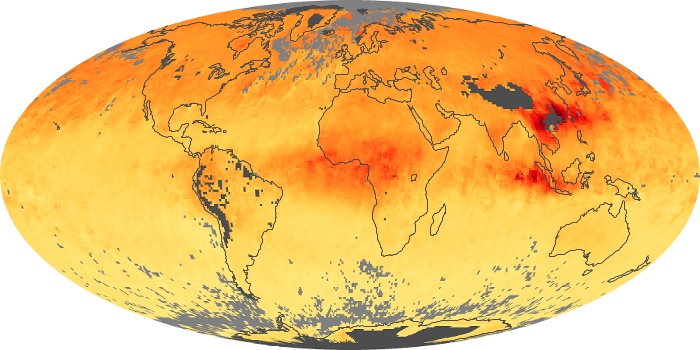
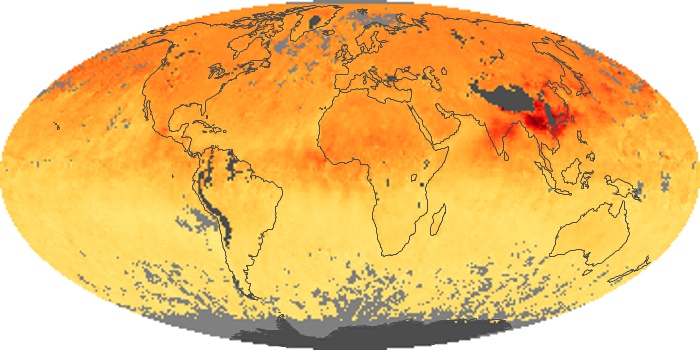
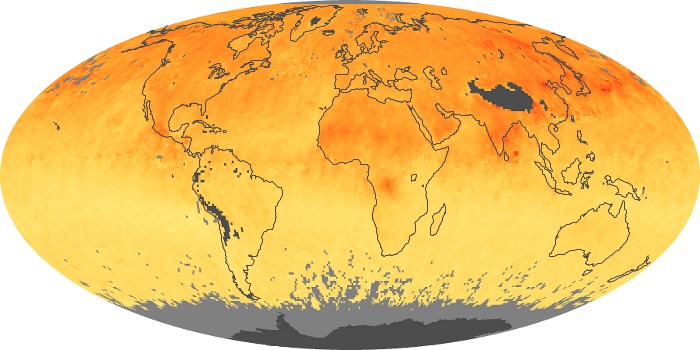
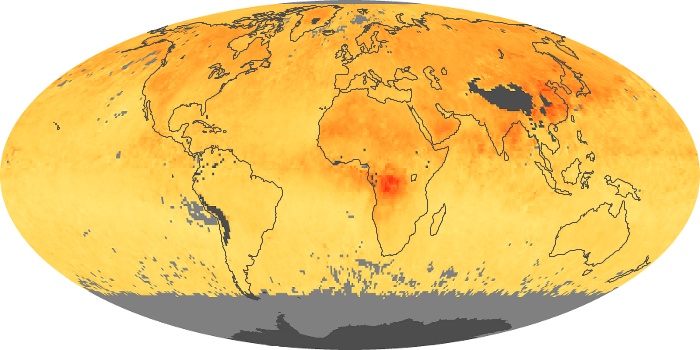
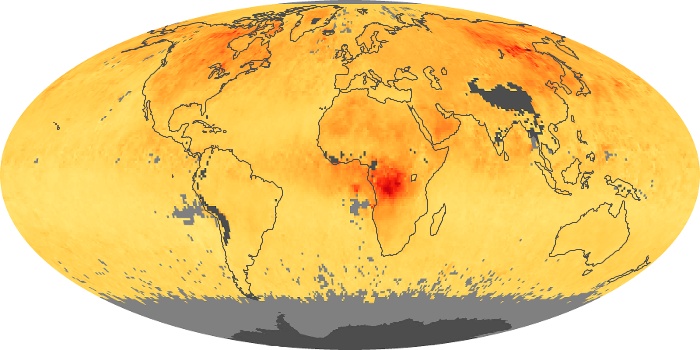
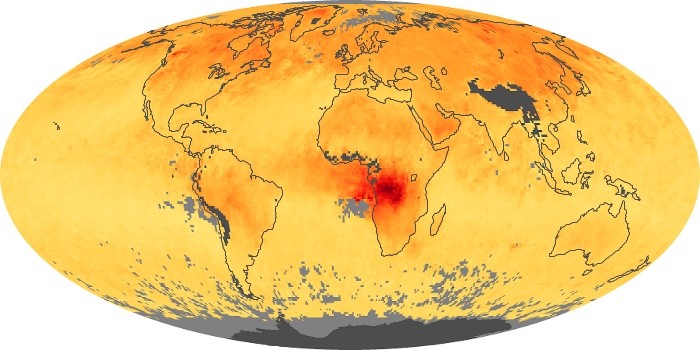
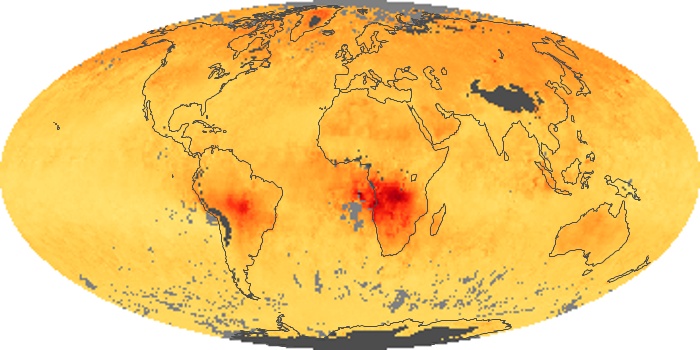
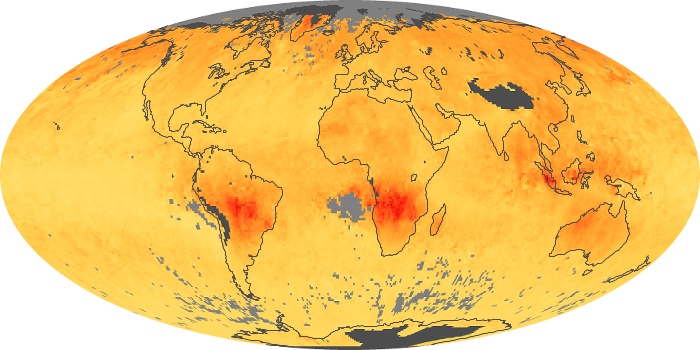
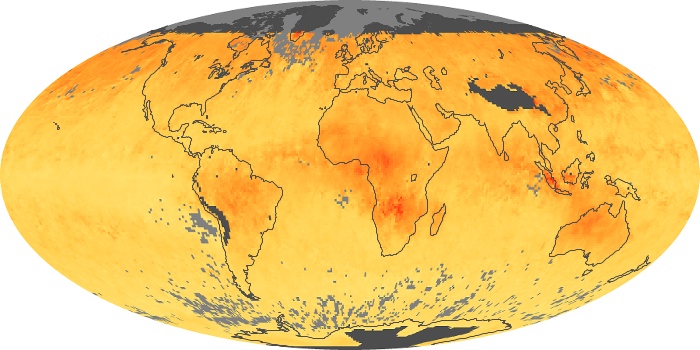
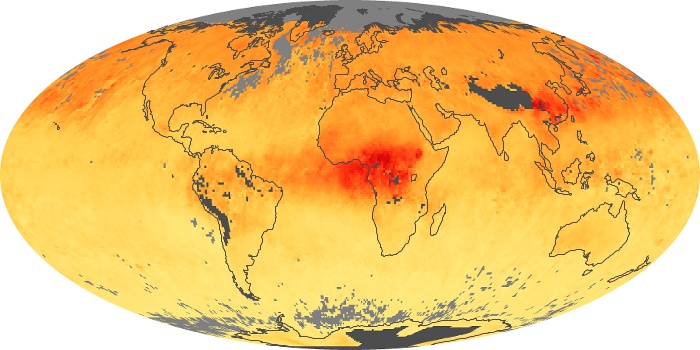
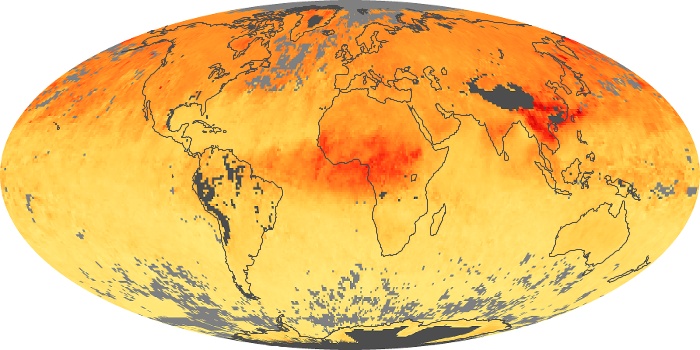
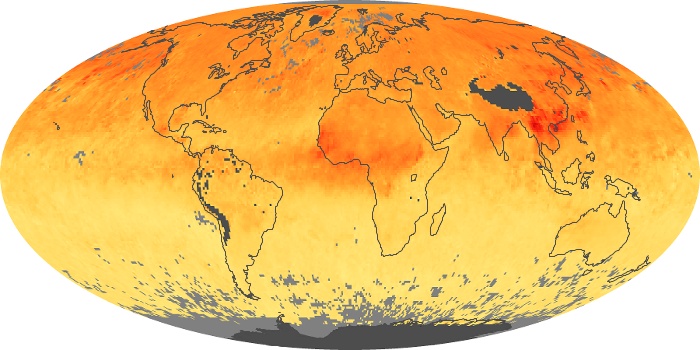
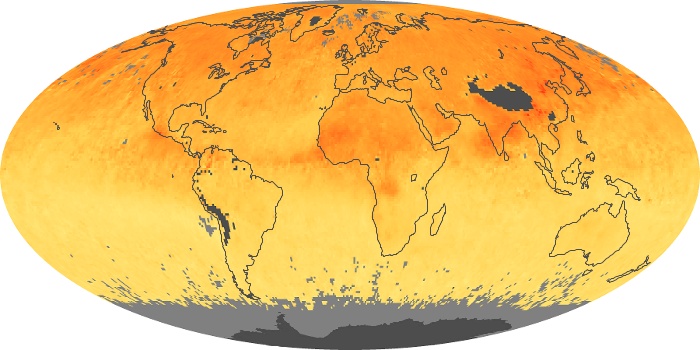
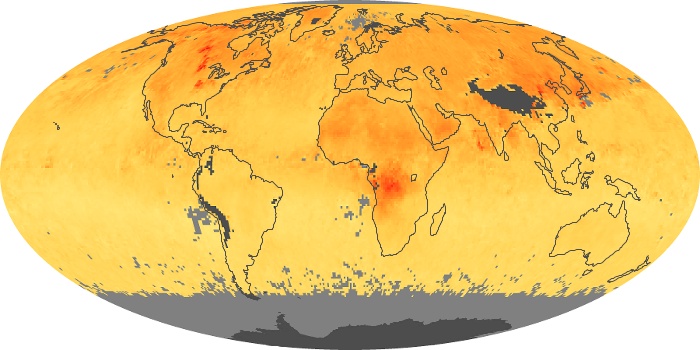
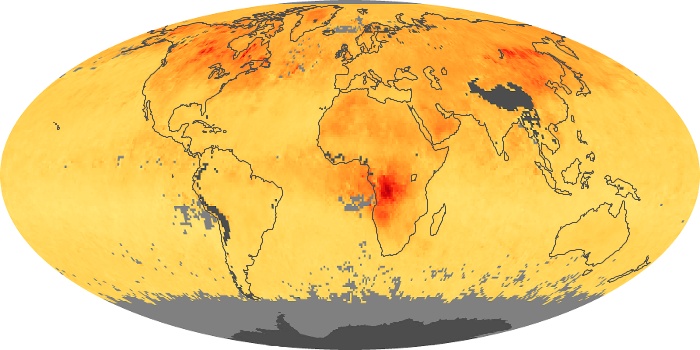
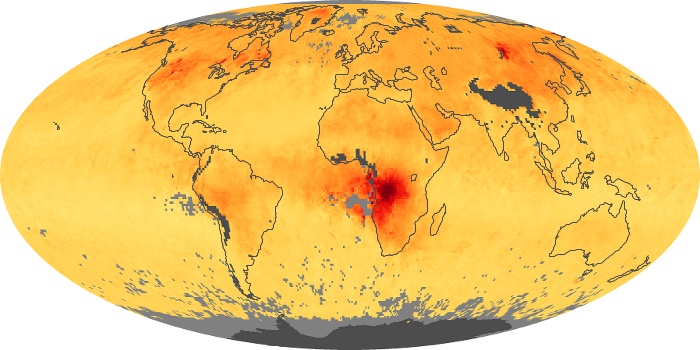
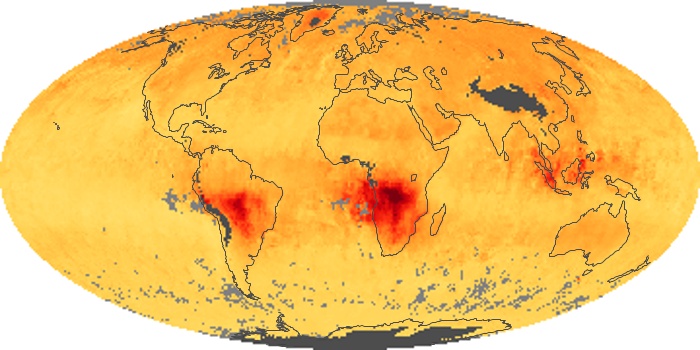
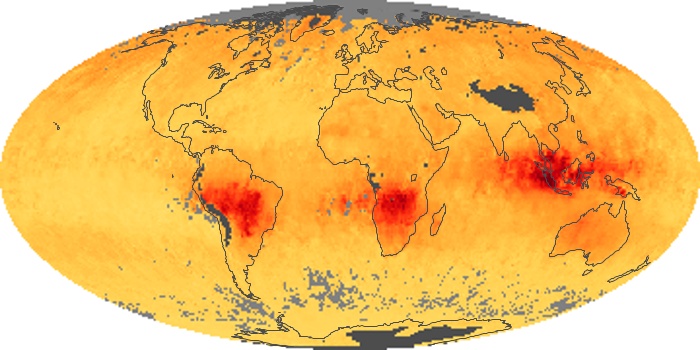
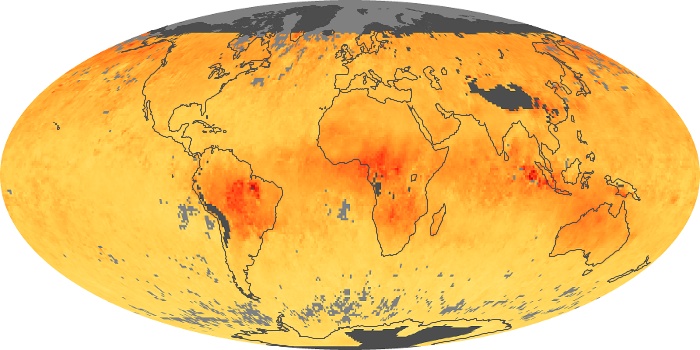
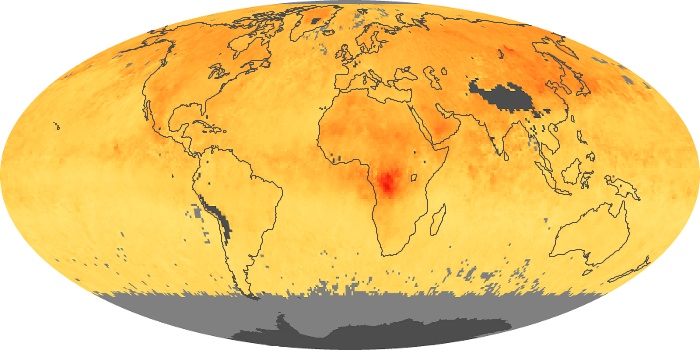
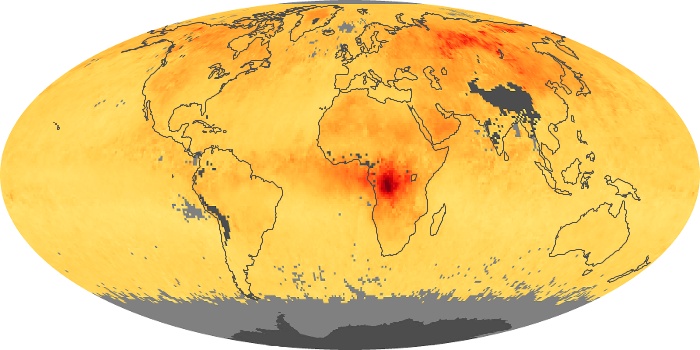
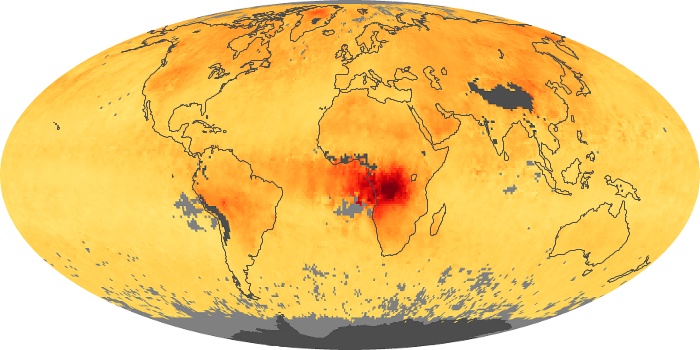
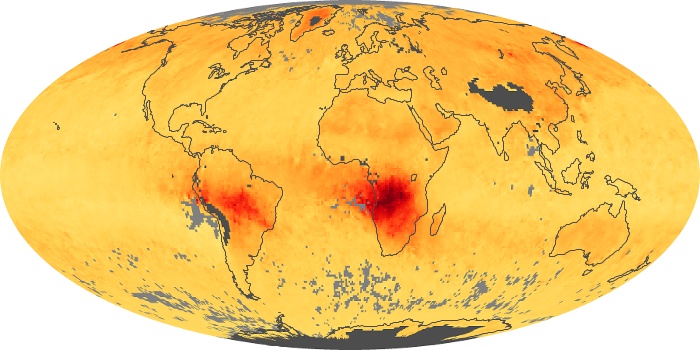
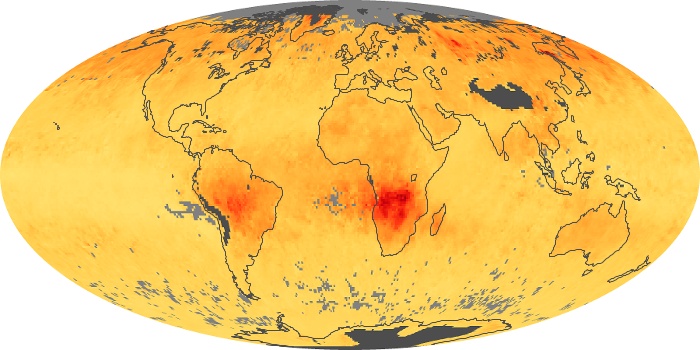
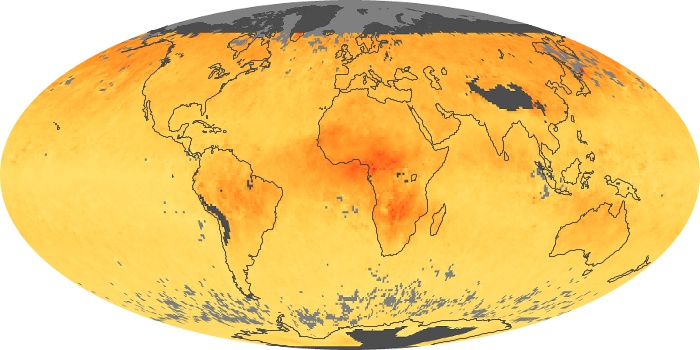
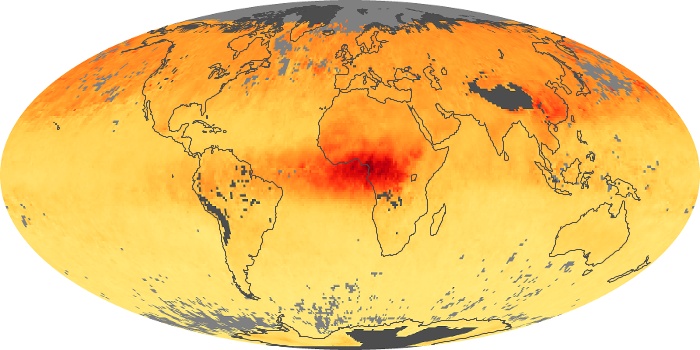
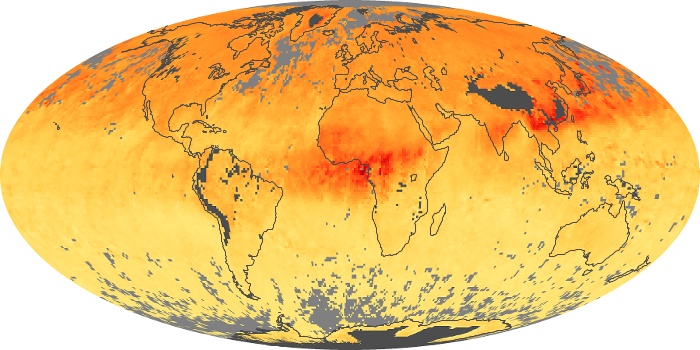
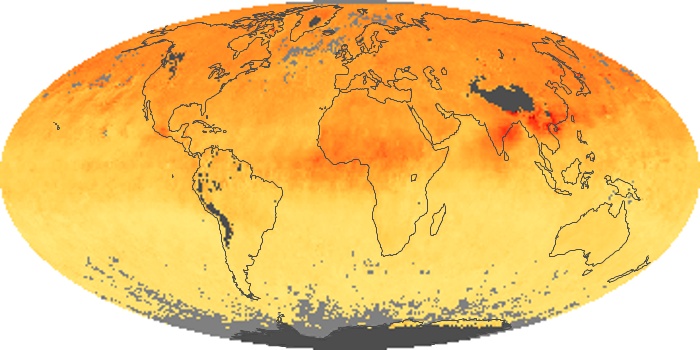
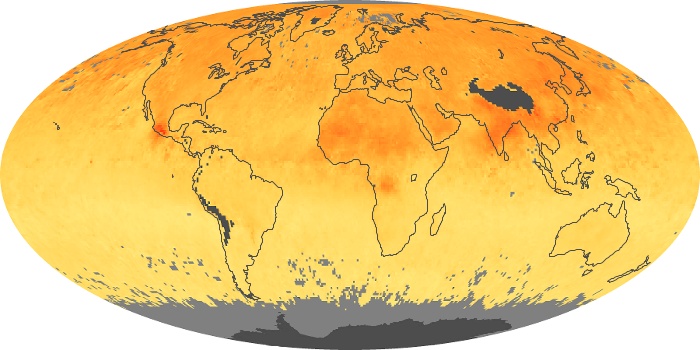
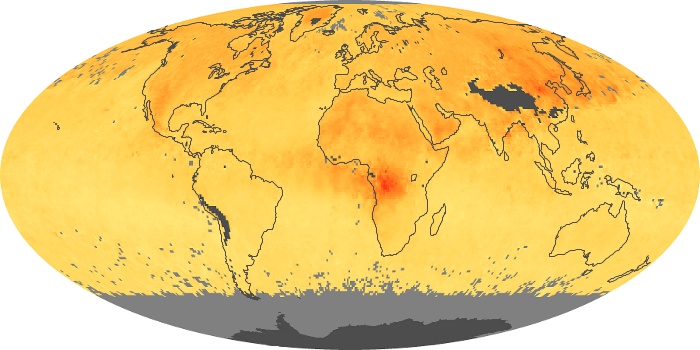
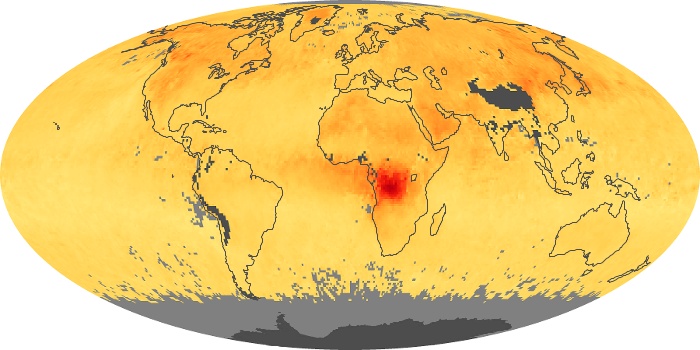
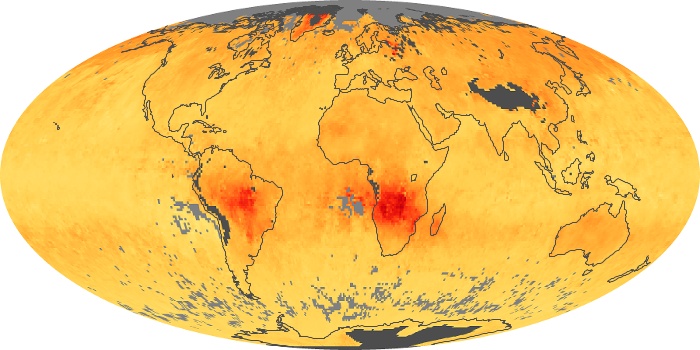
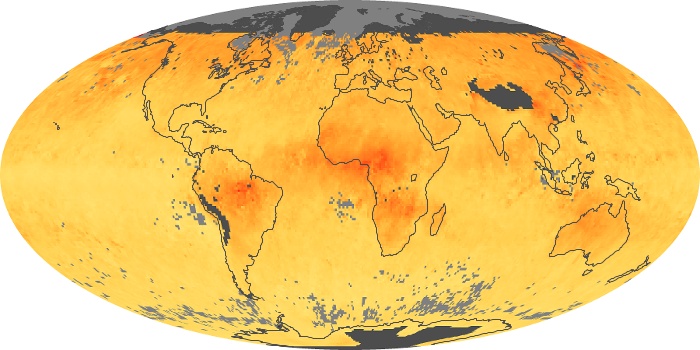
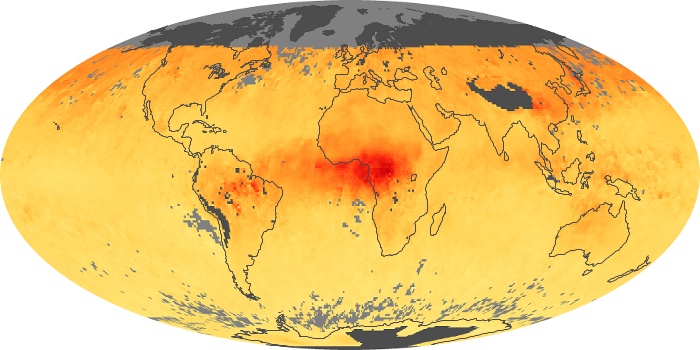
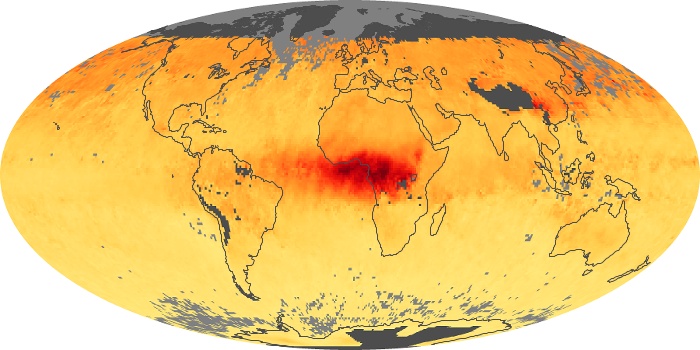
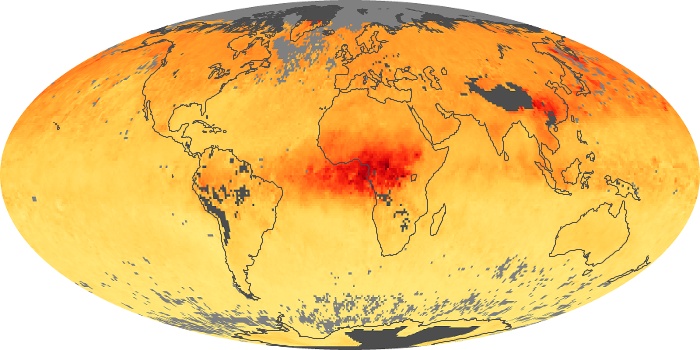
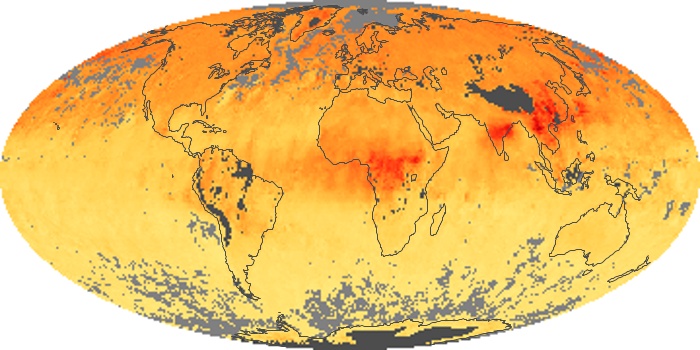
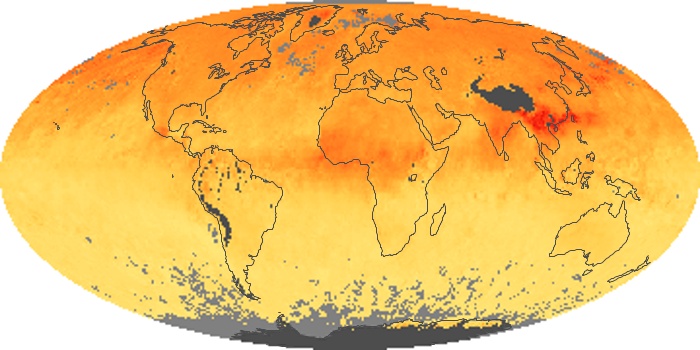
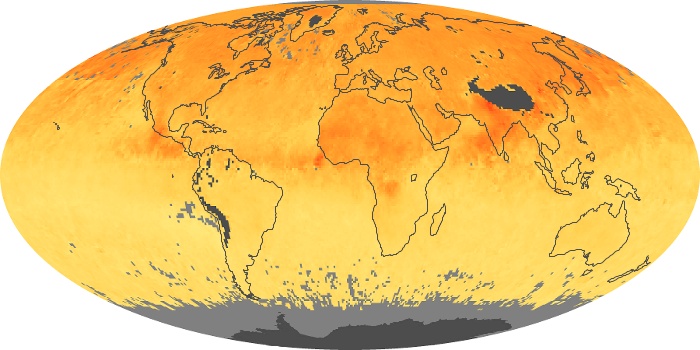
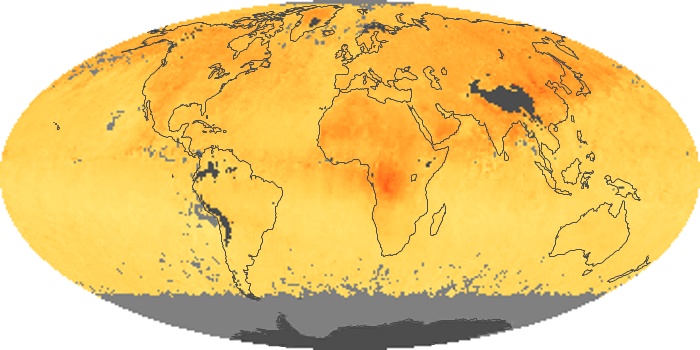
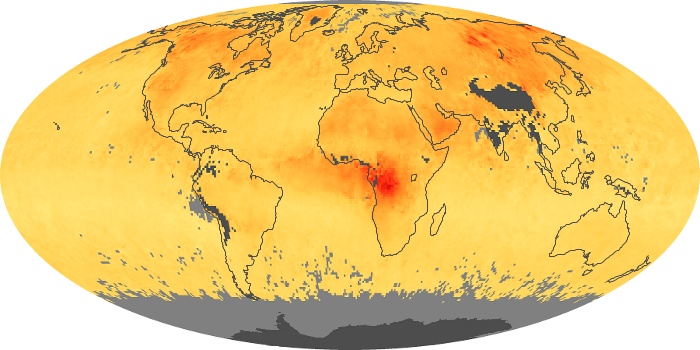
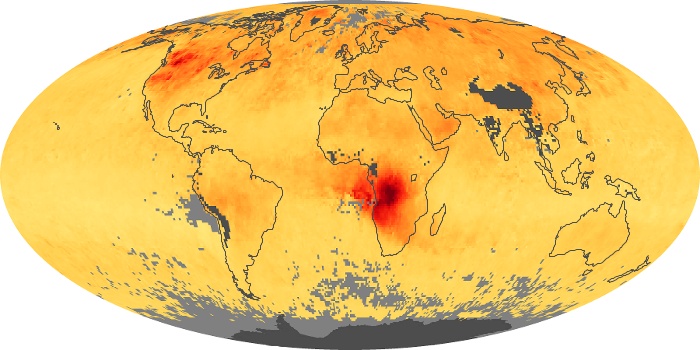
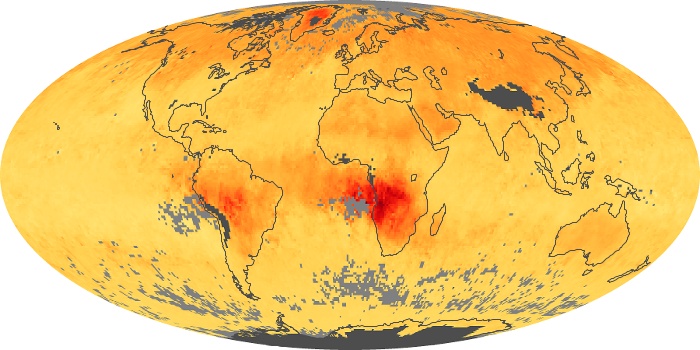
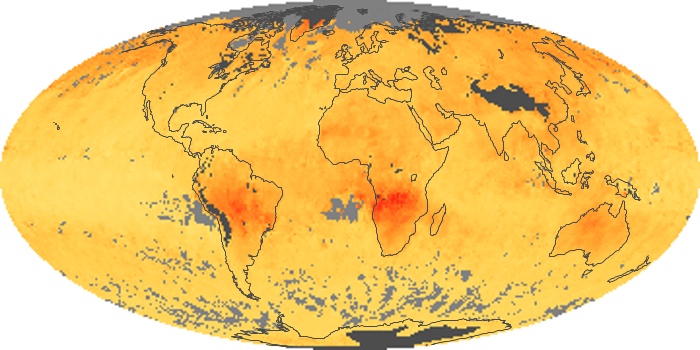
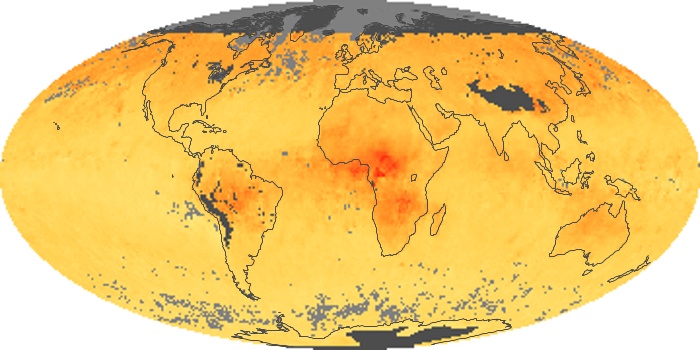
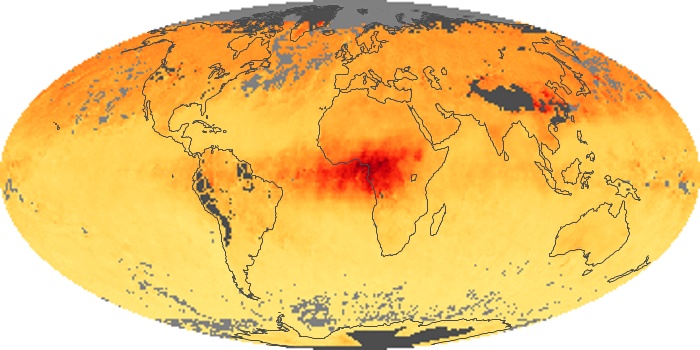
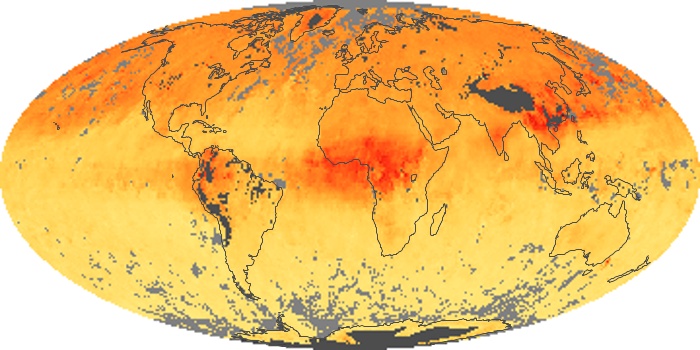
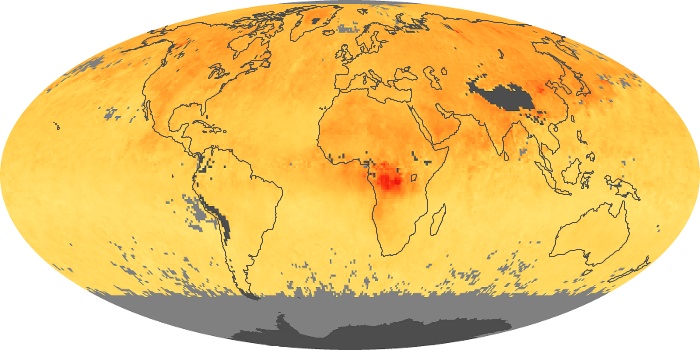
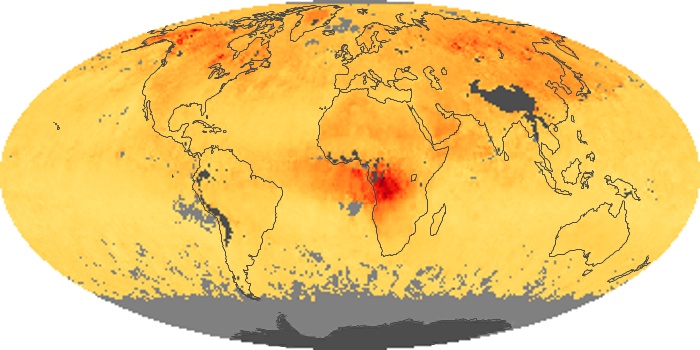
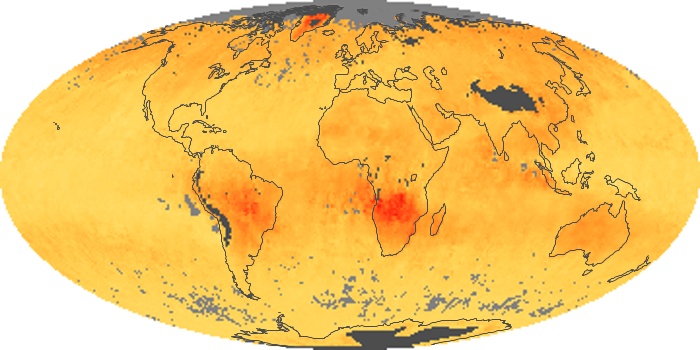
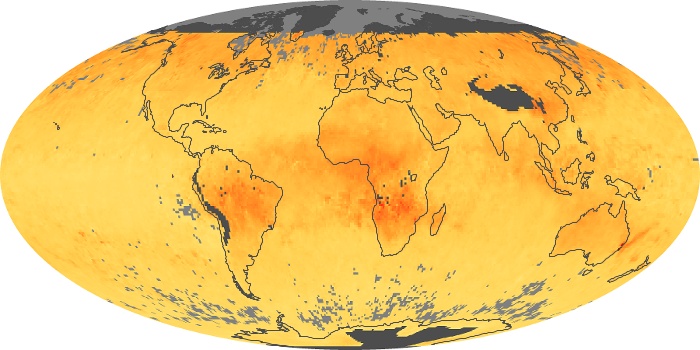
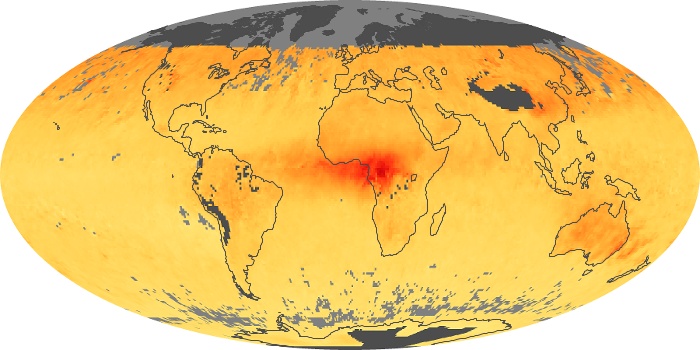
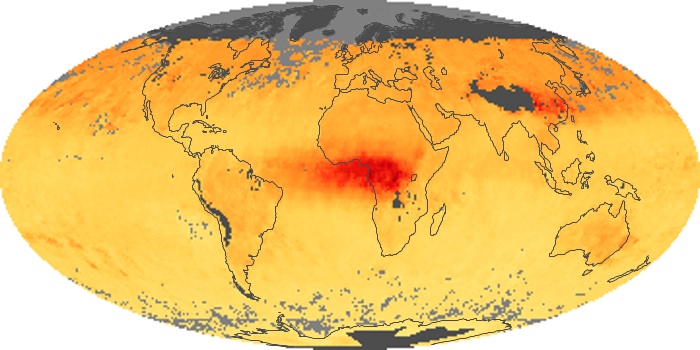
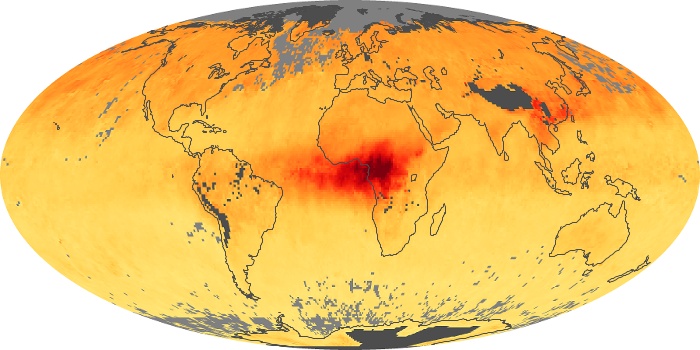
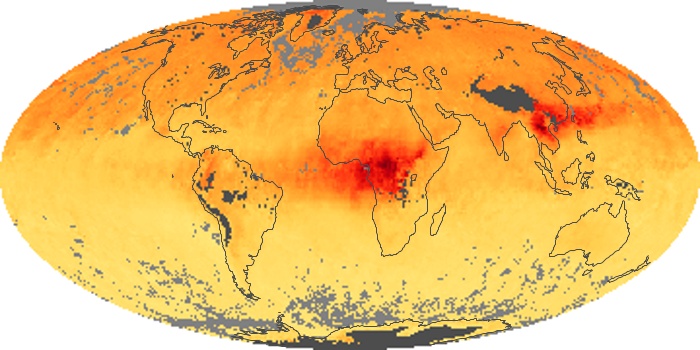

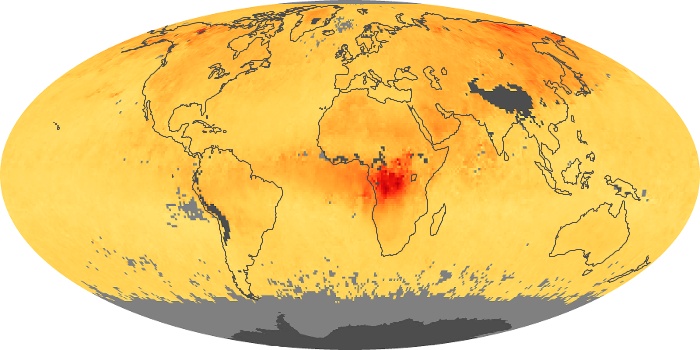
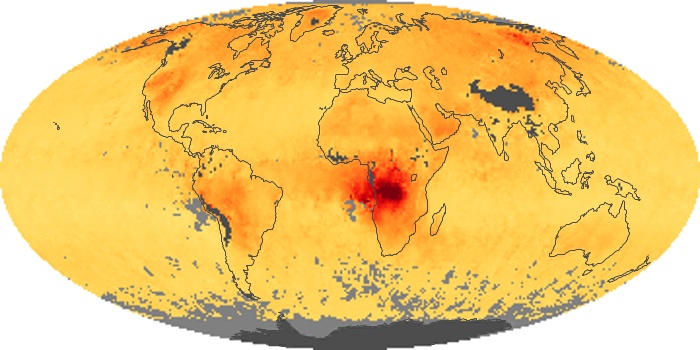
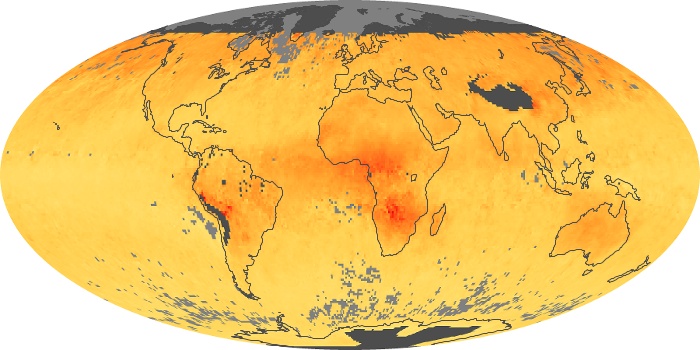
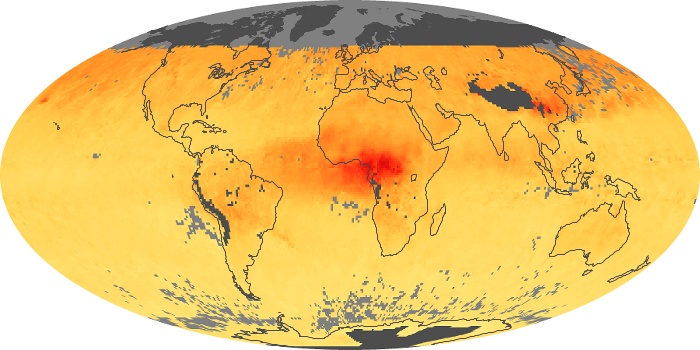
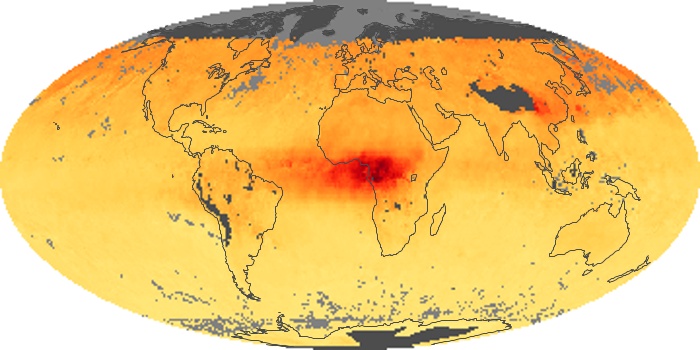
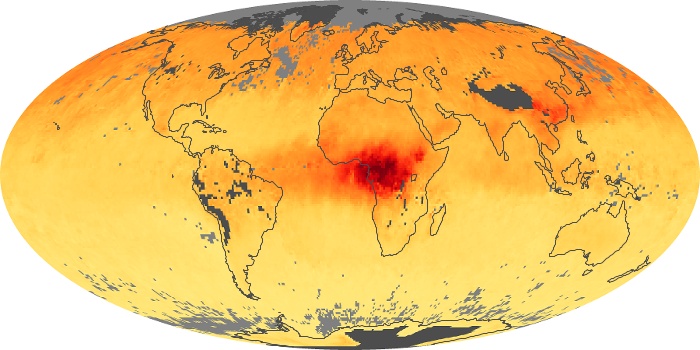
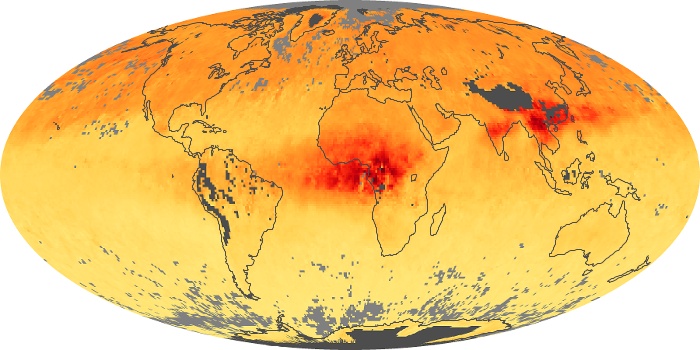
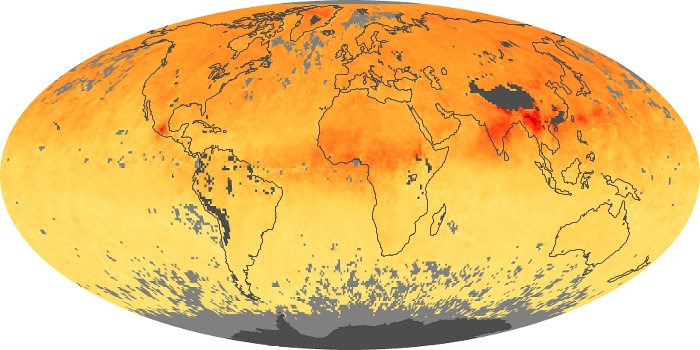
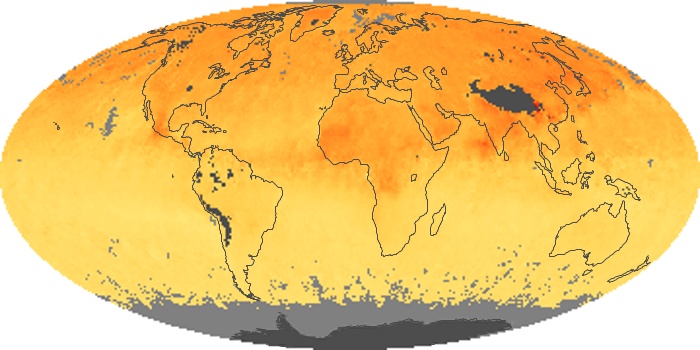
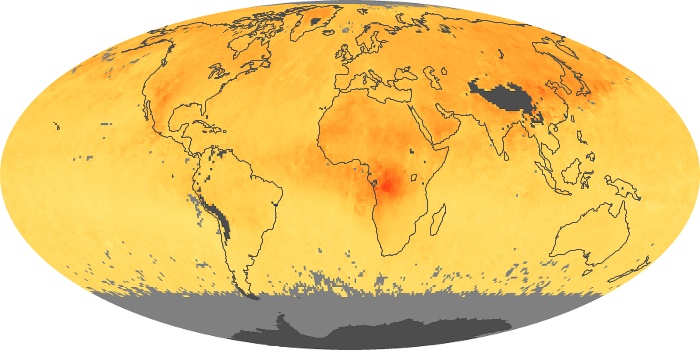
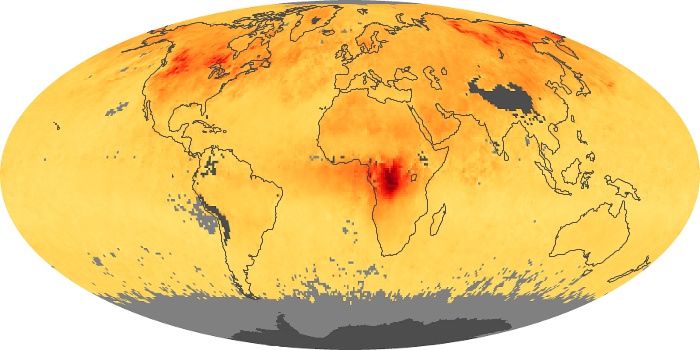
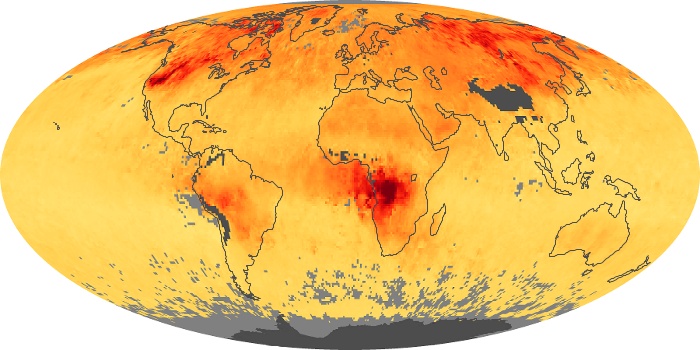
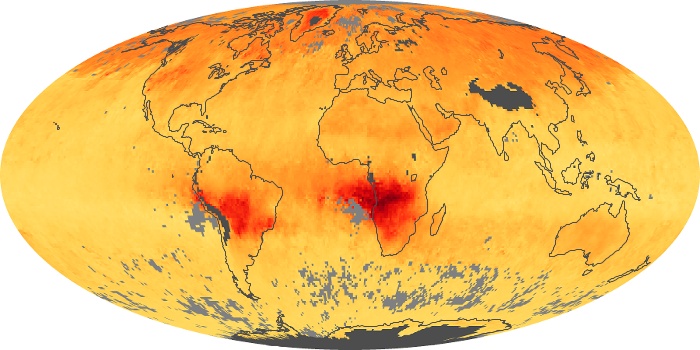
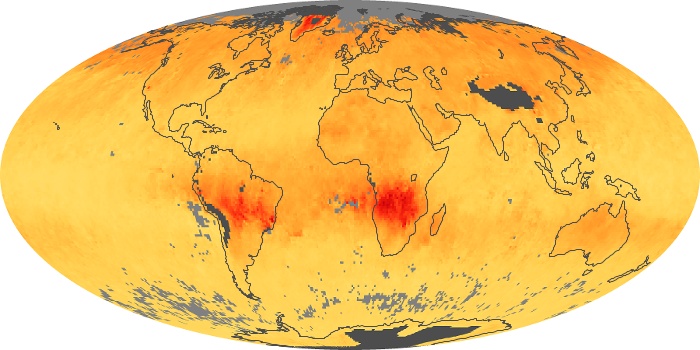
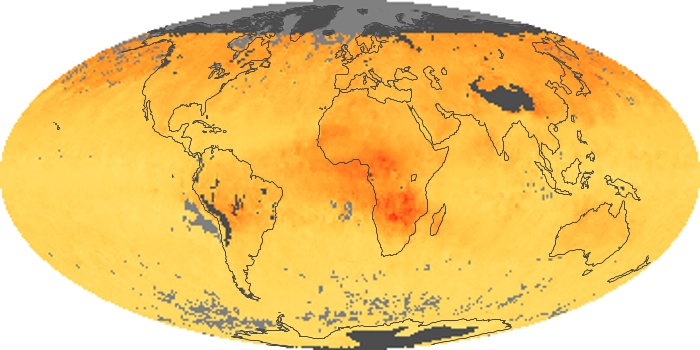
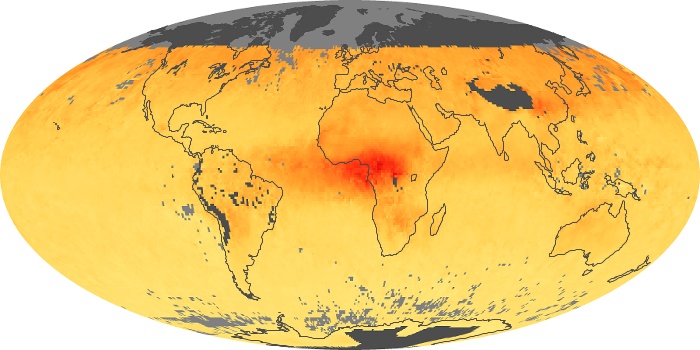
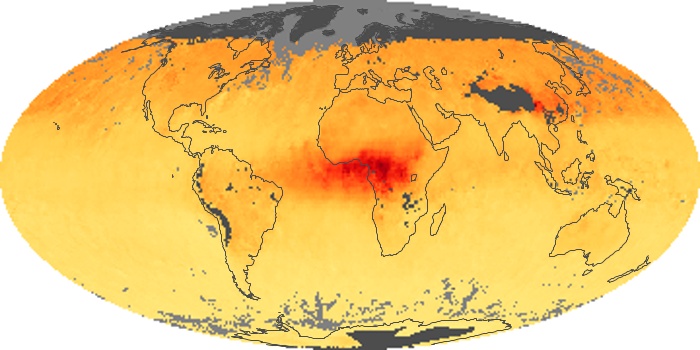
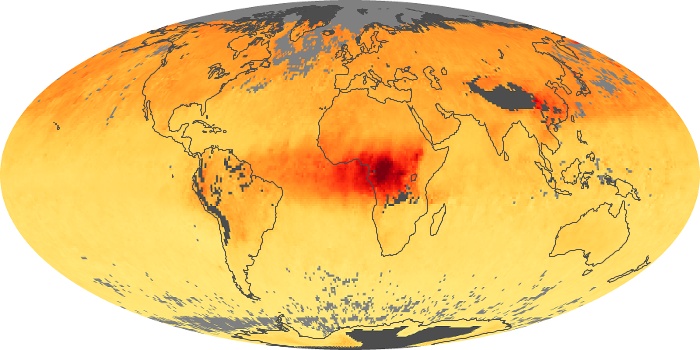
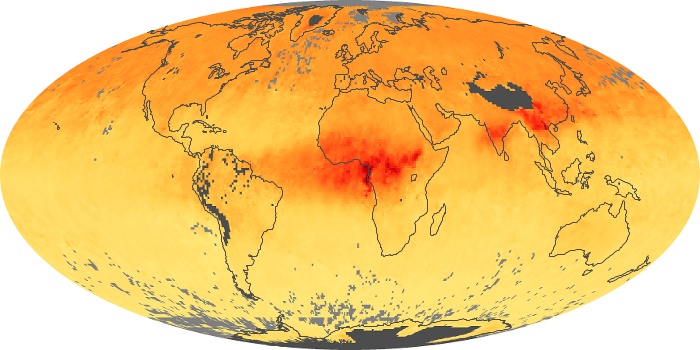
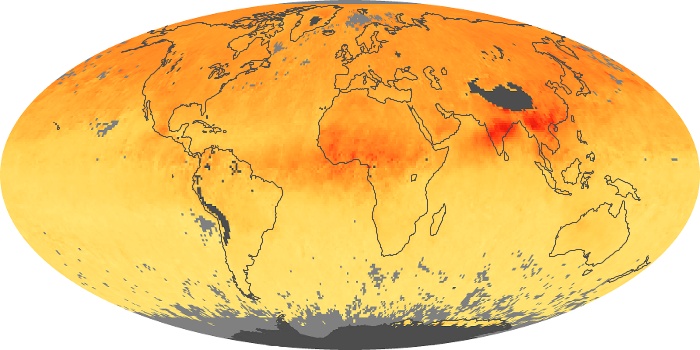
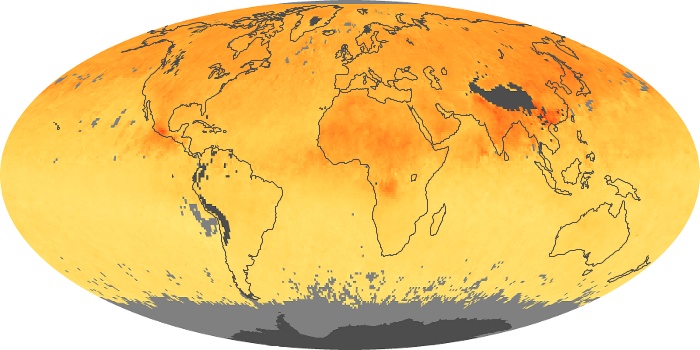
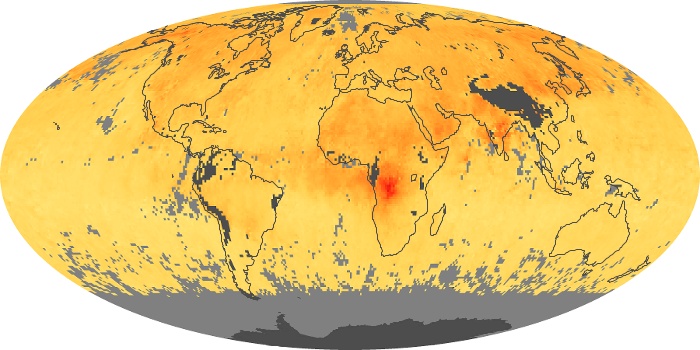
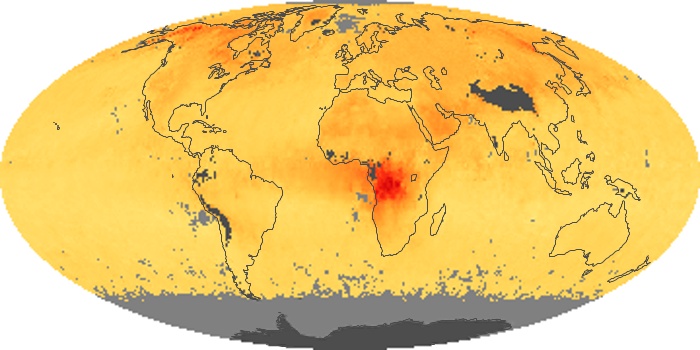
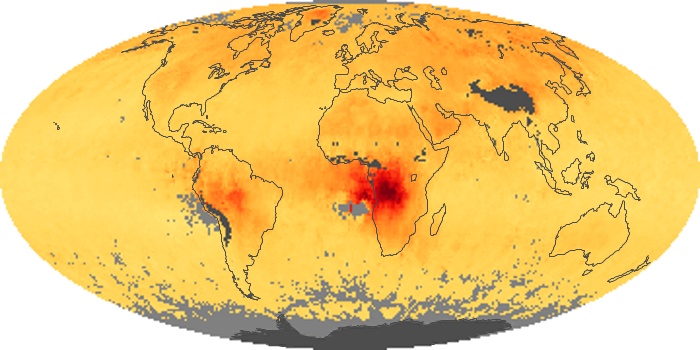
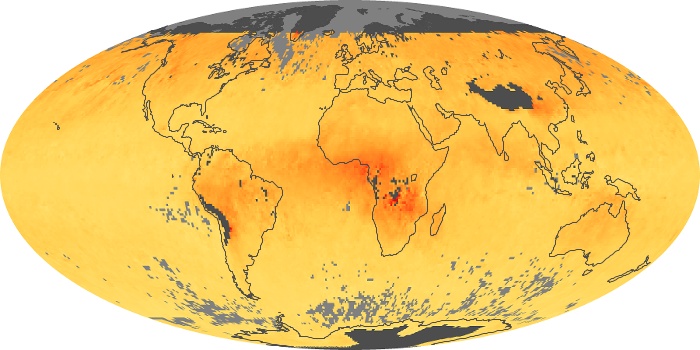
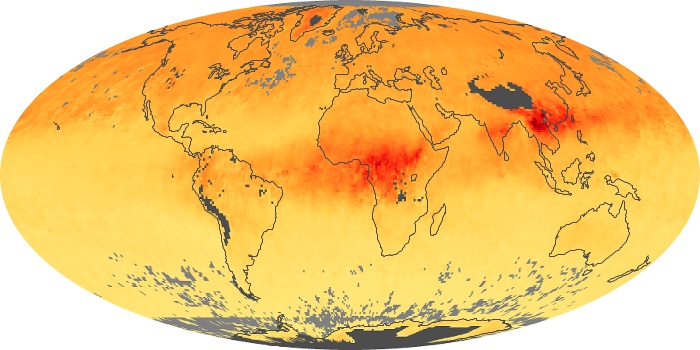
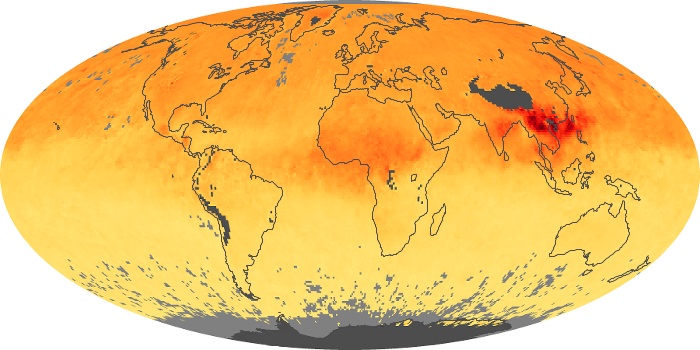
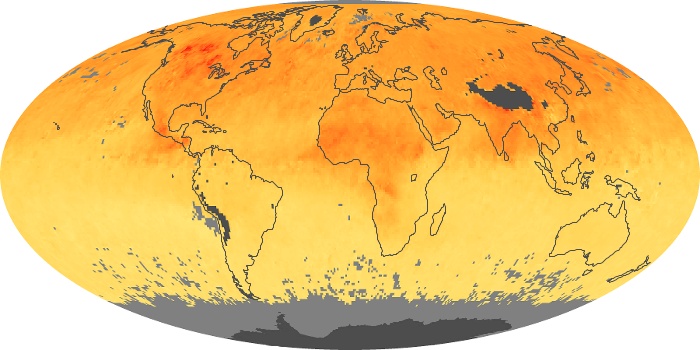
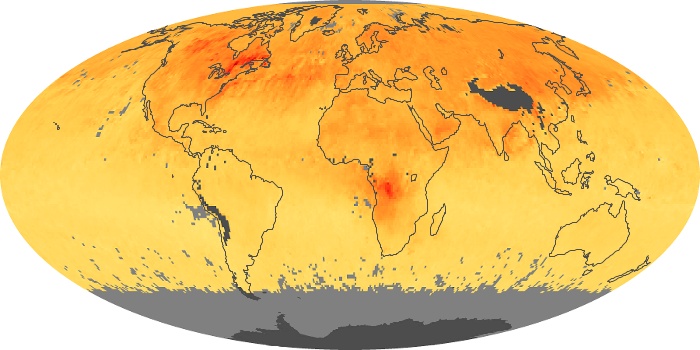
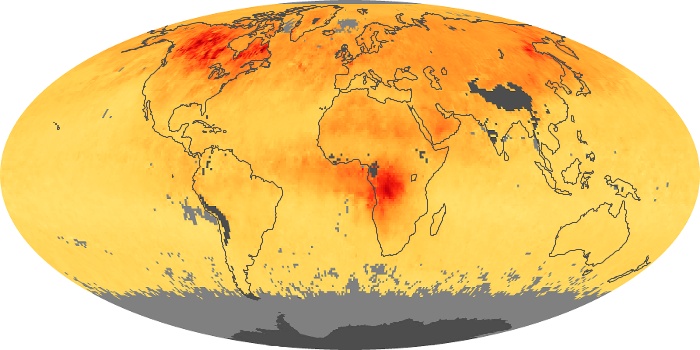
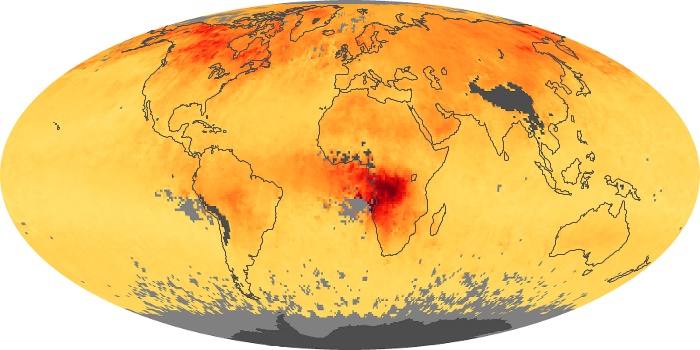
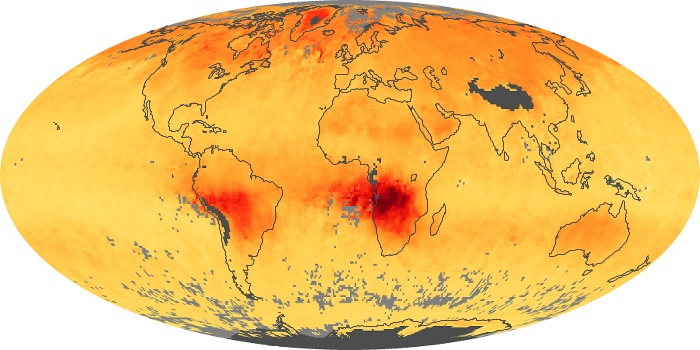
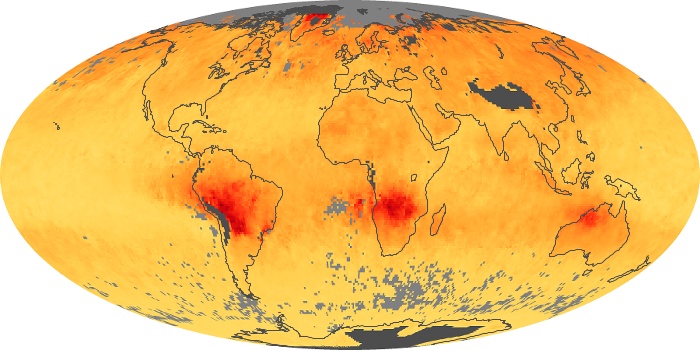
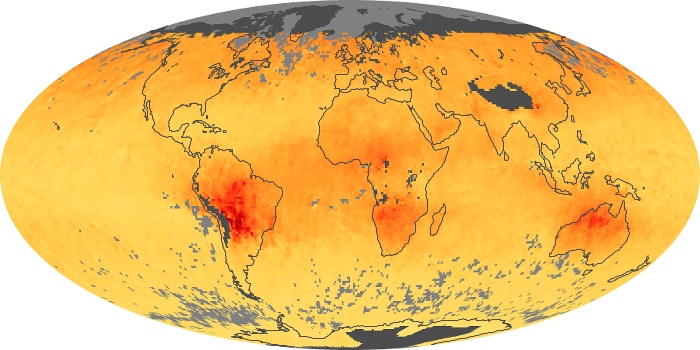
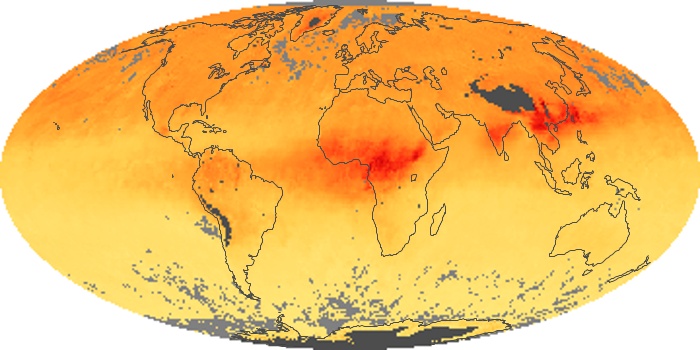
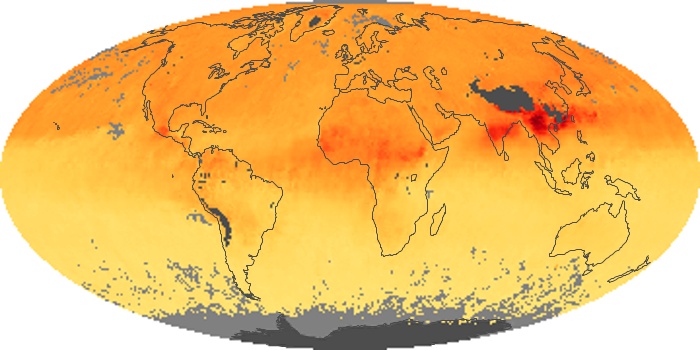
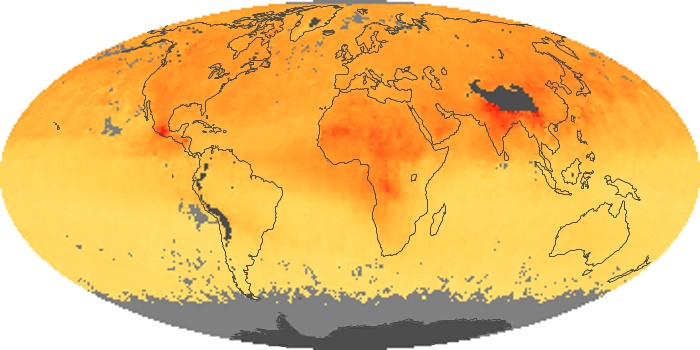
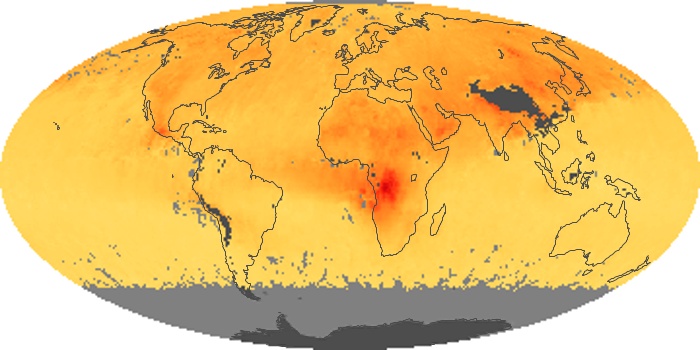
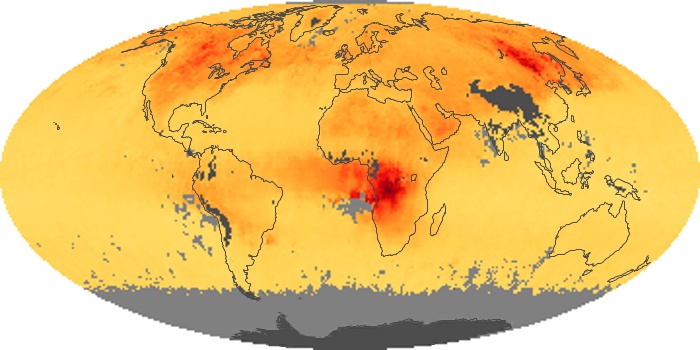
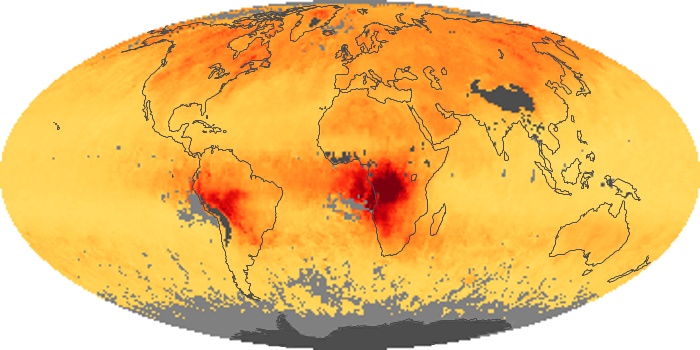
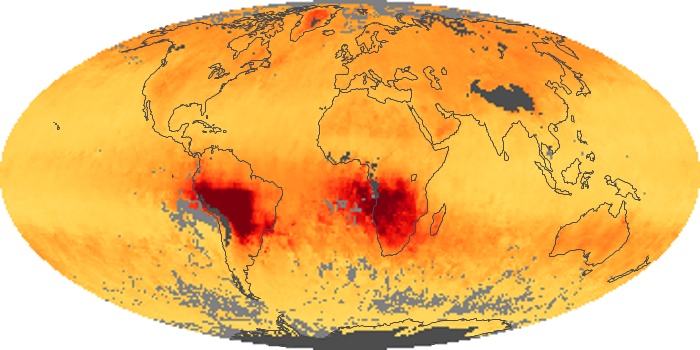
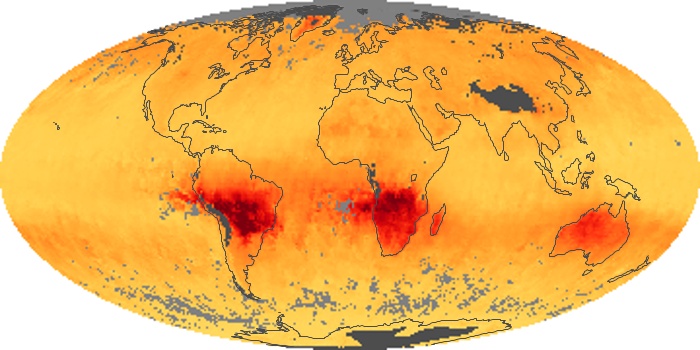
The aerosol maps show average monthly aerosol amounts around the world based on observations from the MODIS sensor on NASA's Terra satellite. Satellite measurements of aerosols, called aerosol optical thickness, are based on the fact that the particles change the way the atmosphere reflects and absorbs visible and infrared light. An optical thickness of less than 0.1 (palest yellow) indicates a crystal clear sky with maximum visibility, whereas a value of 1 (reddish brown) indicates very hazy conditions.
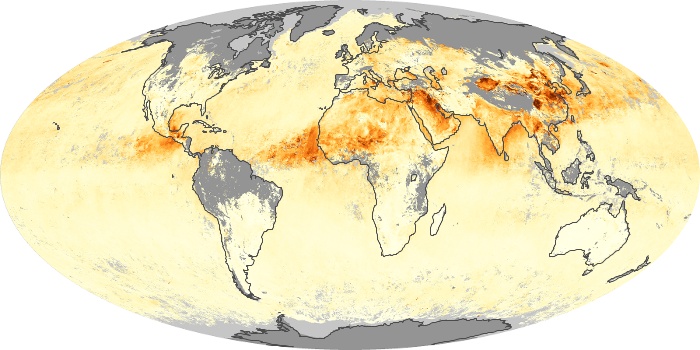
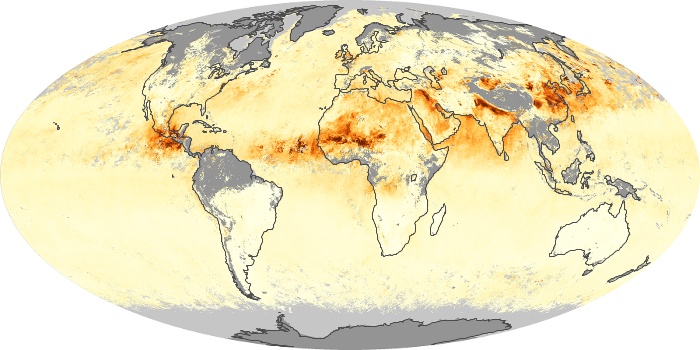
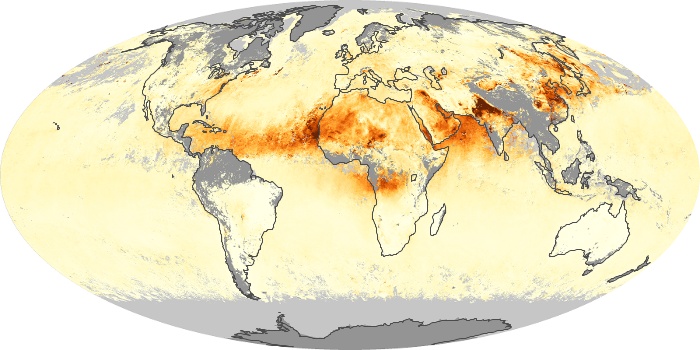
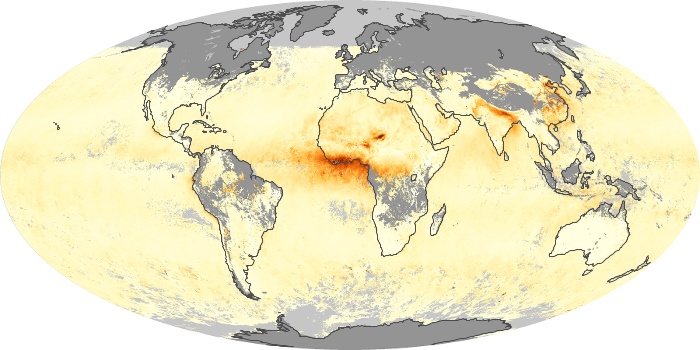
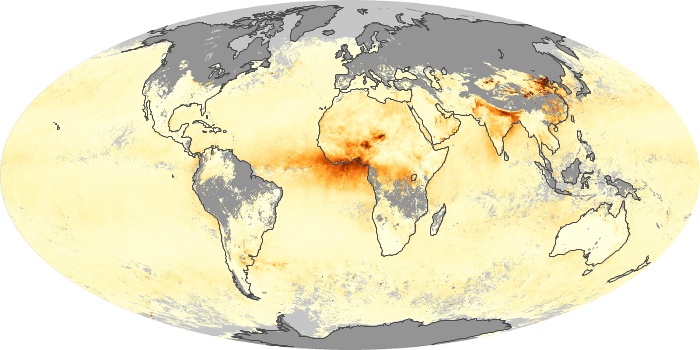
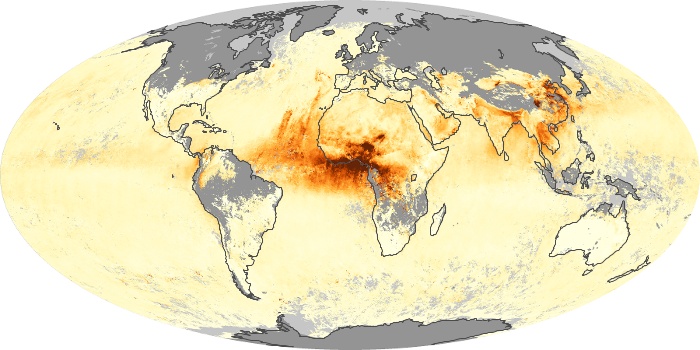
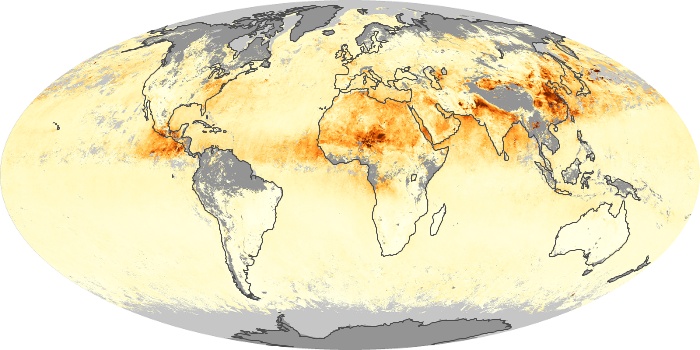
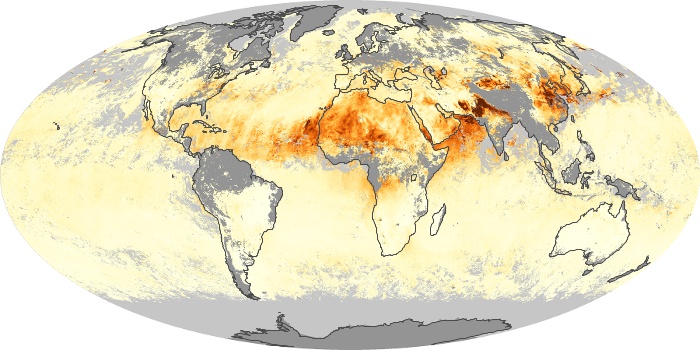
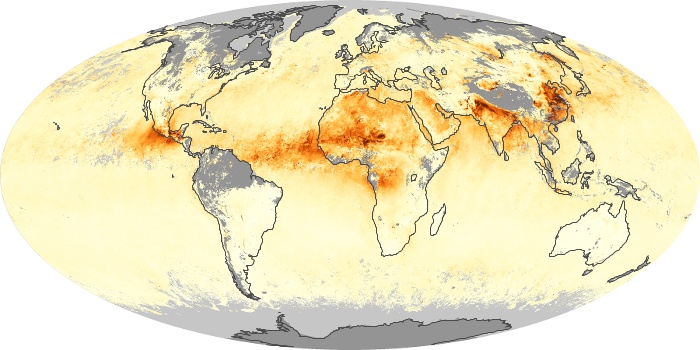
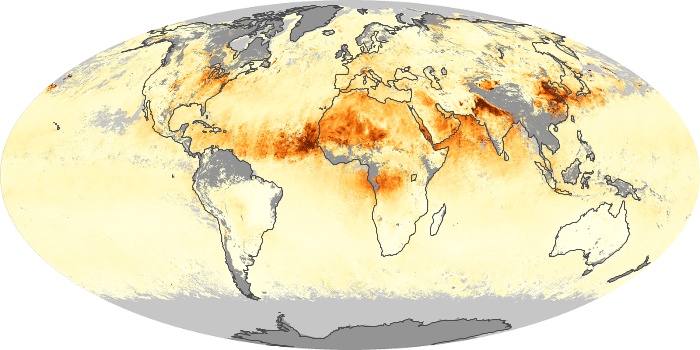
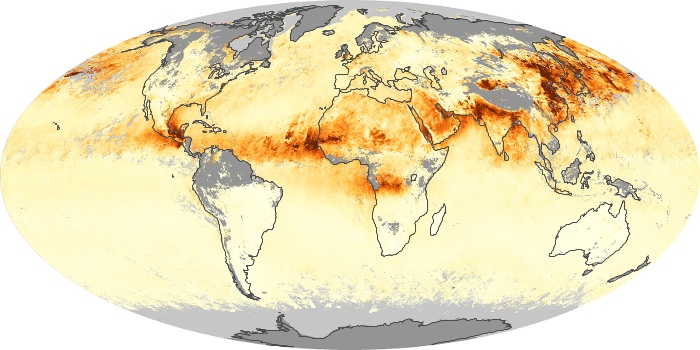
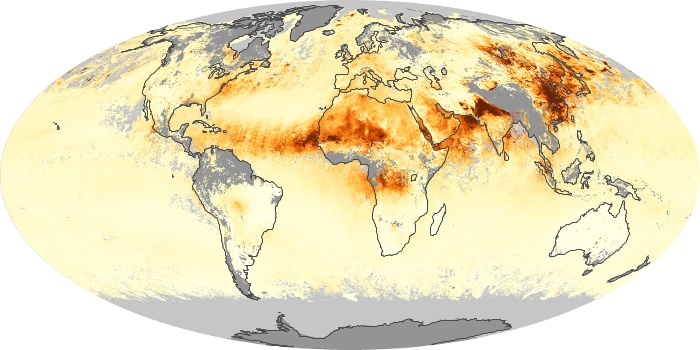
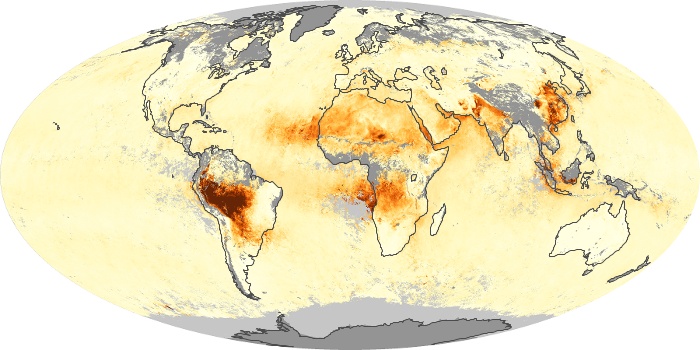
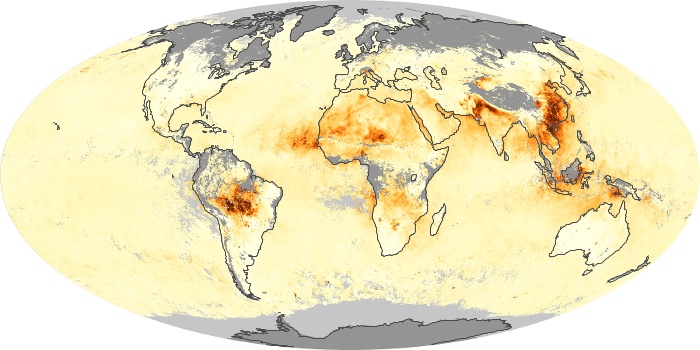
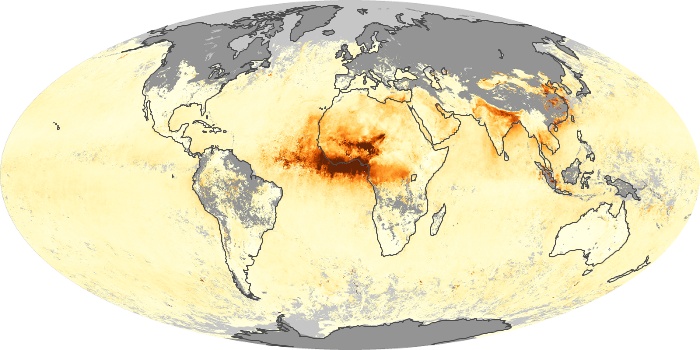
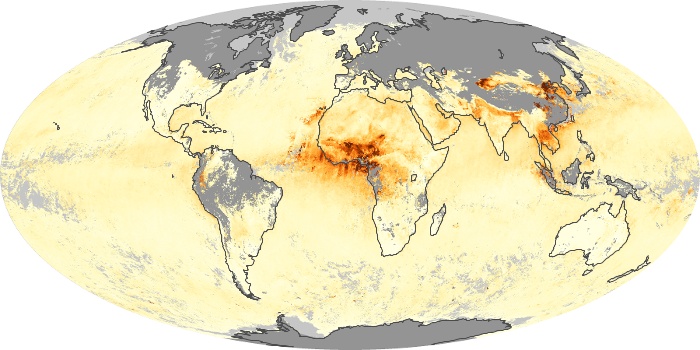
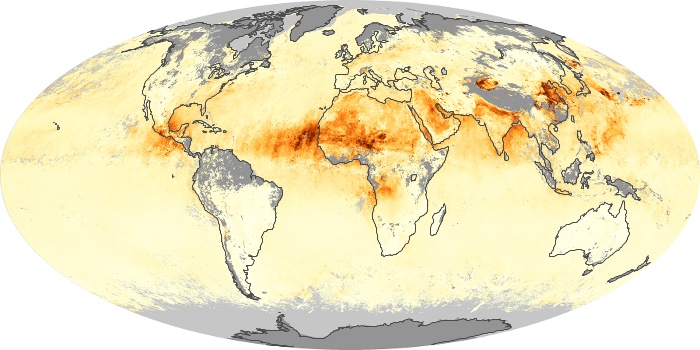
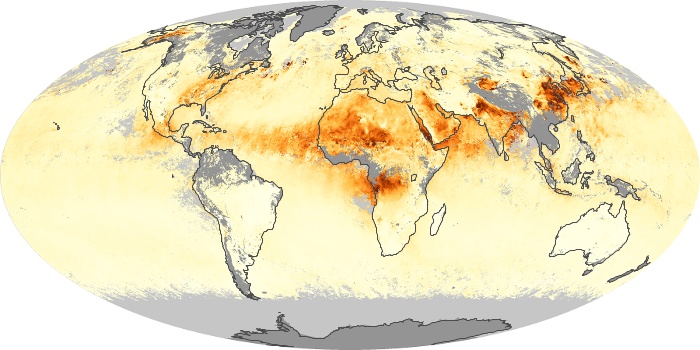
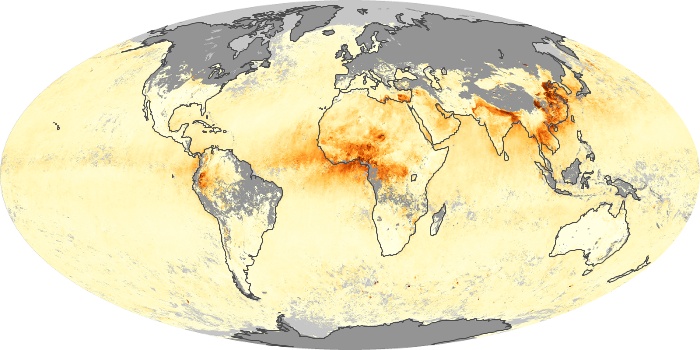
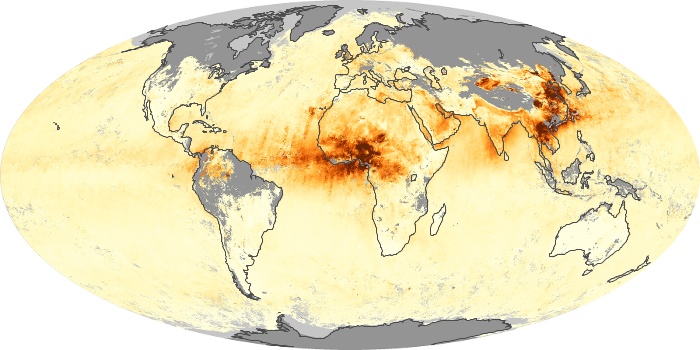
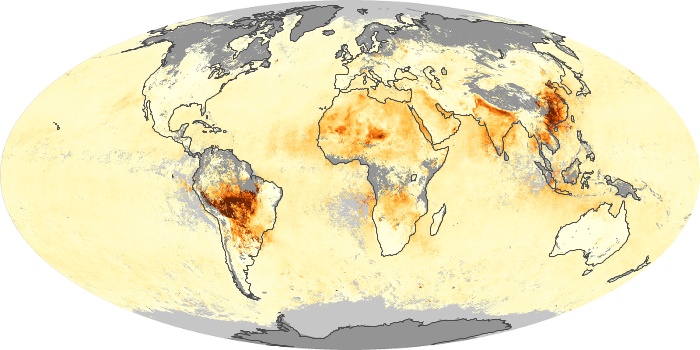
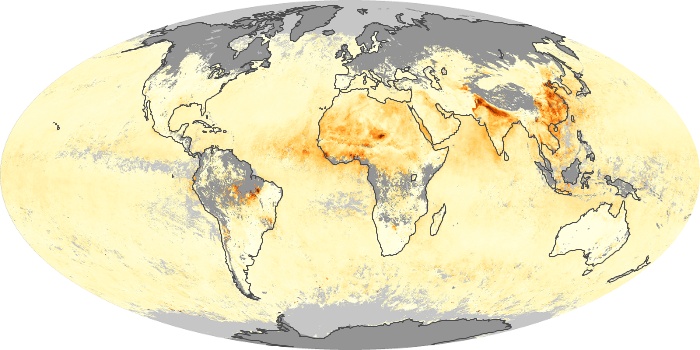
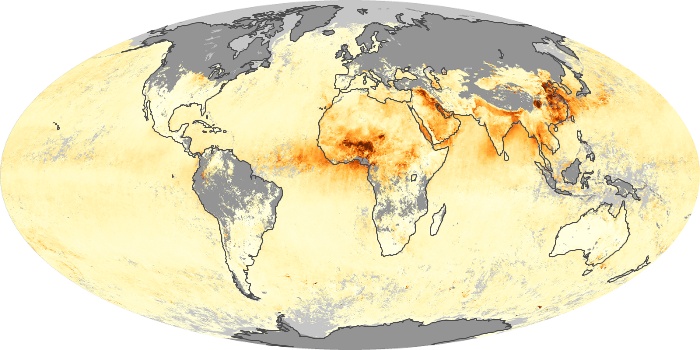
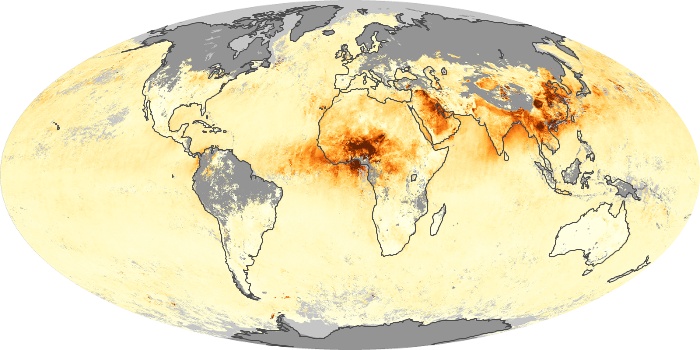
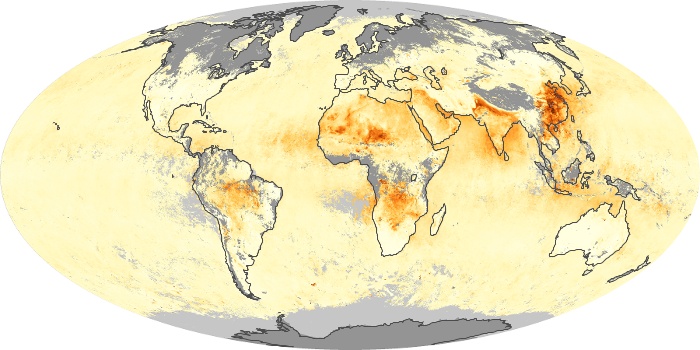
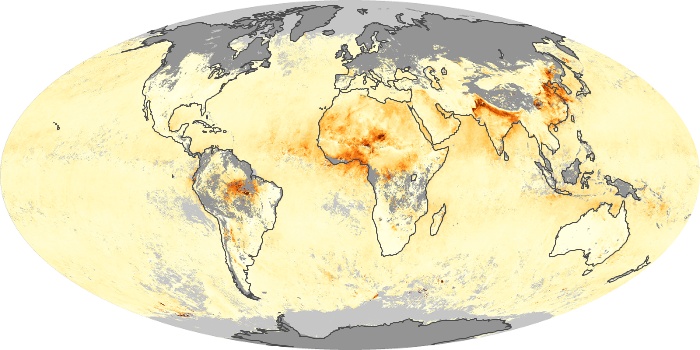
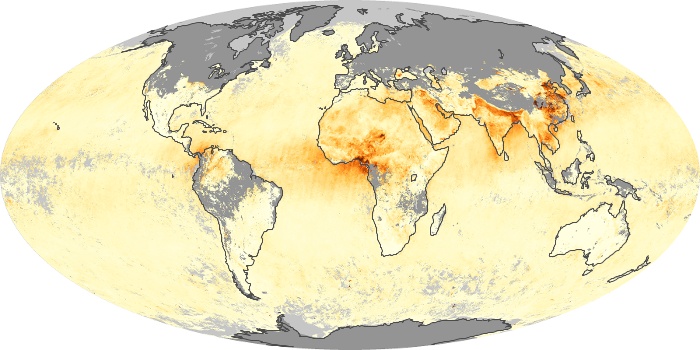
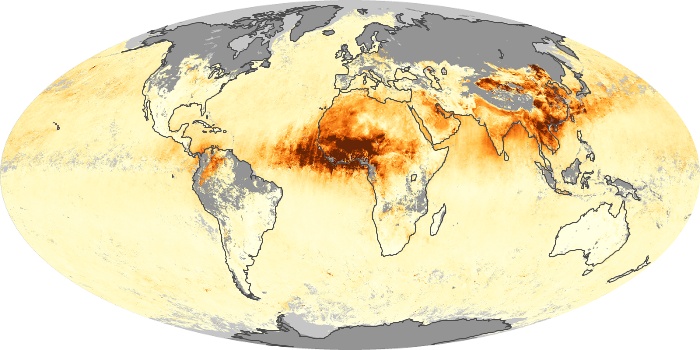
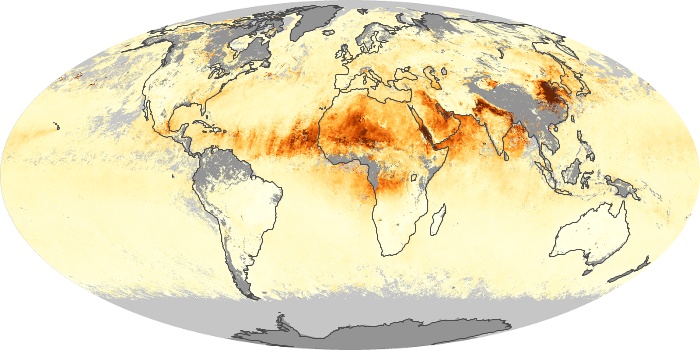
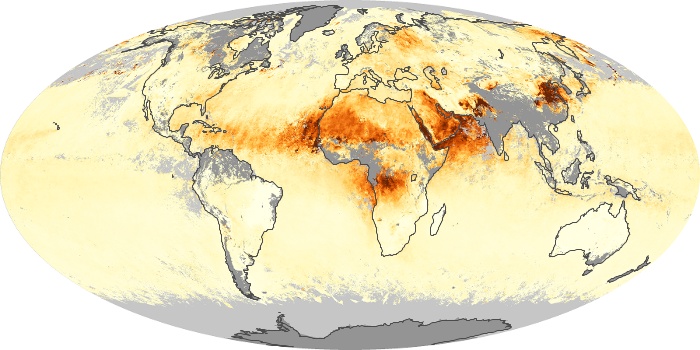
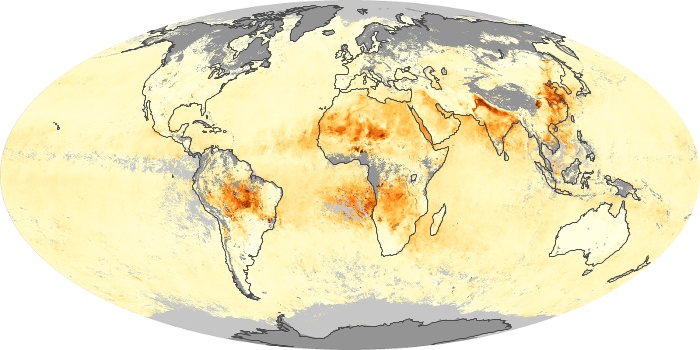
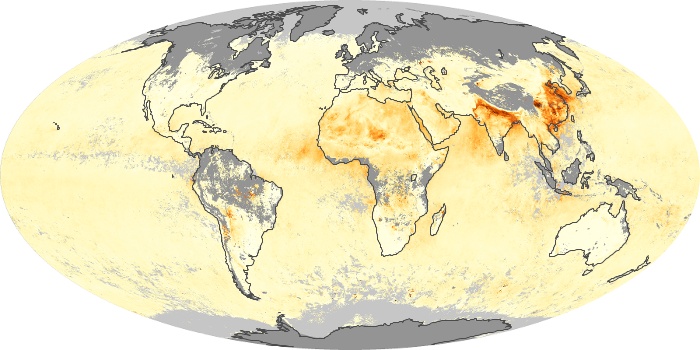
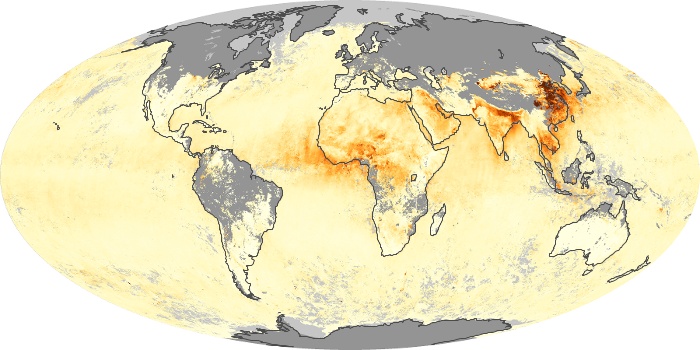
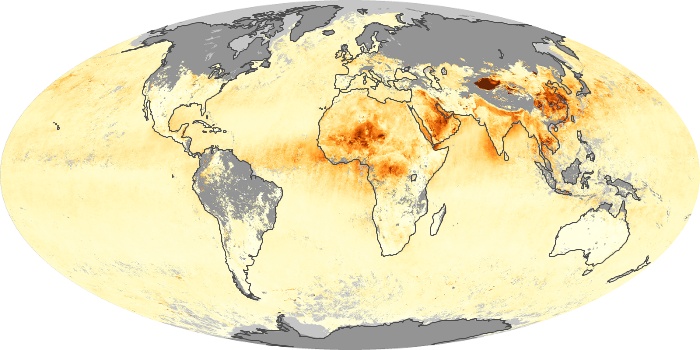
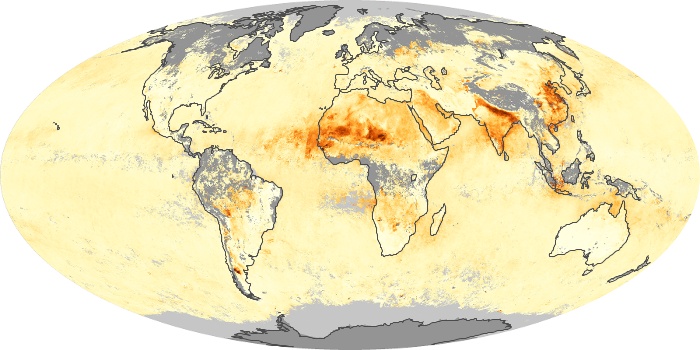
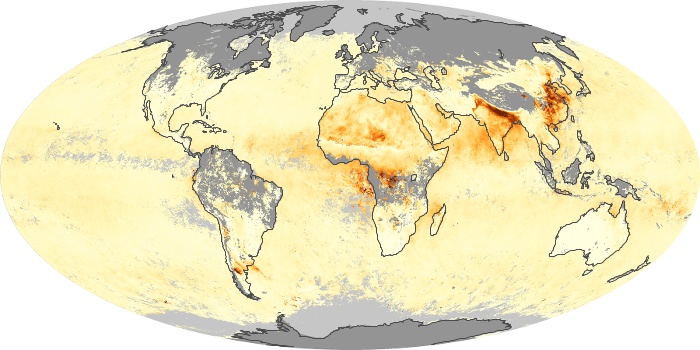
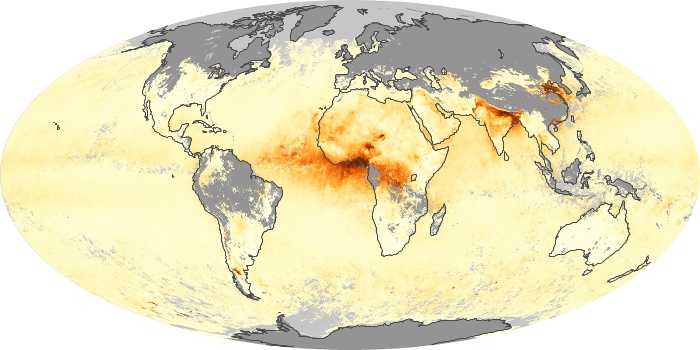
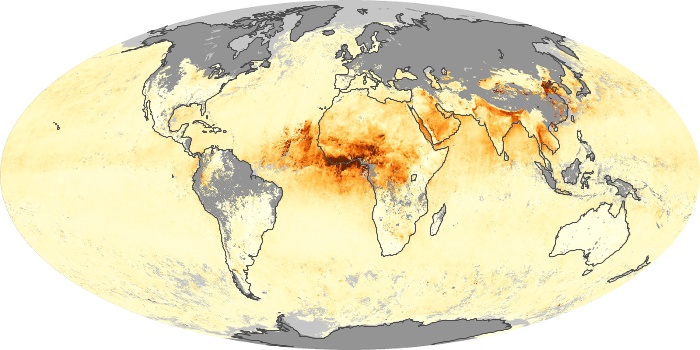
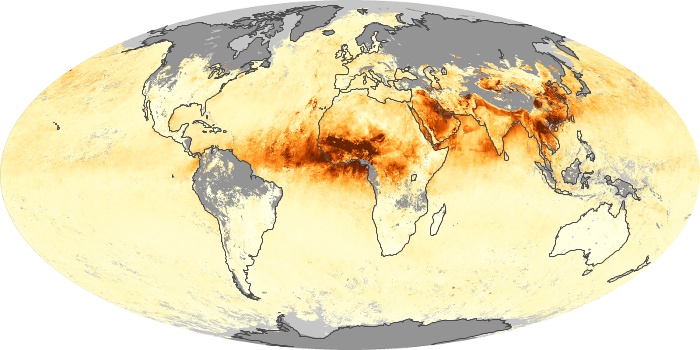
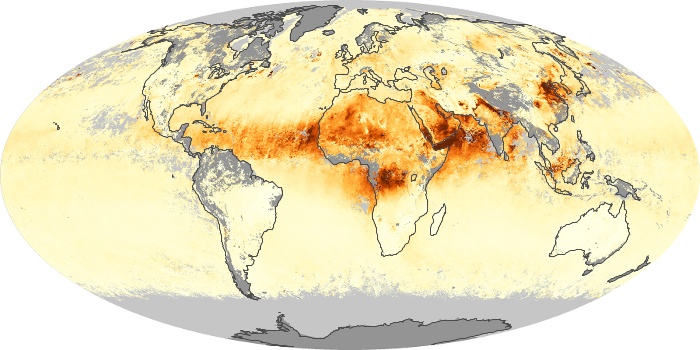
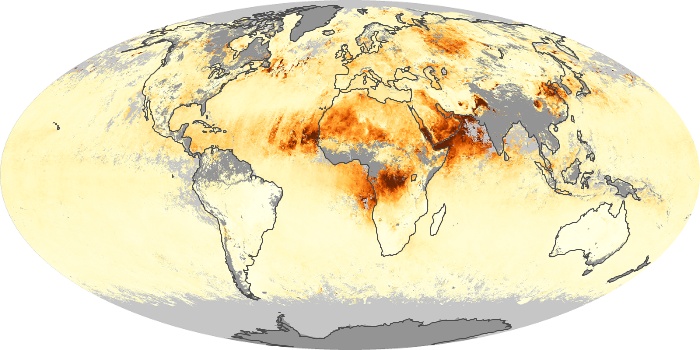
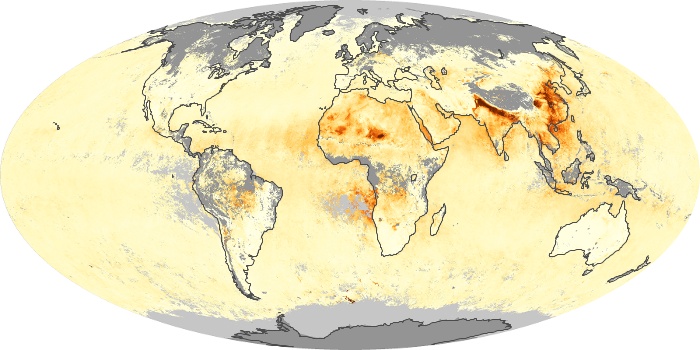
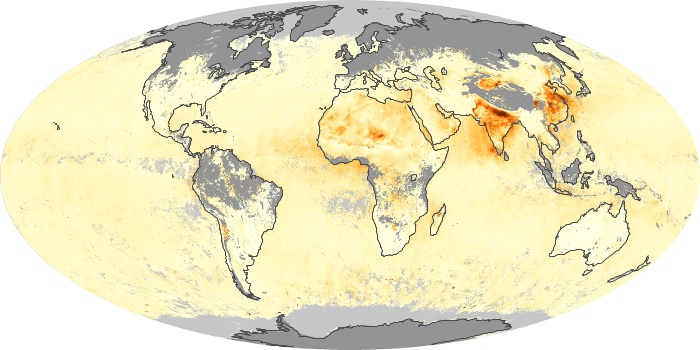
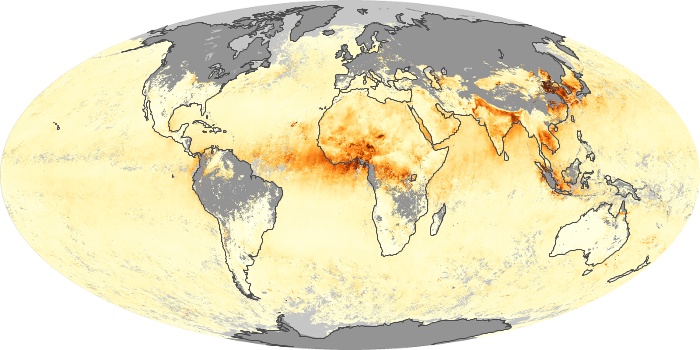
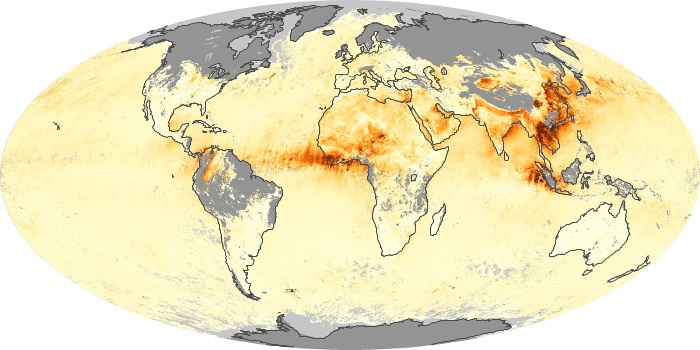
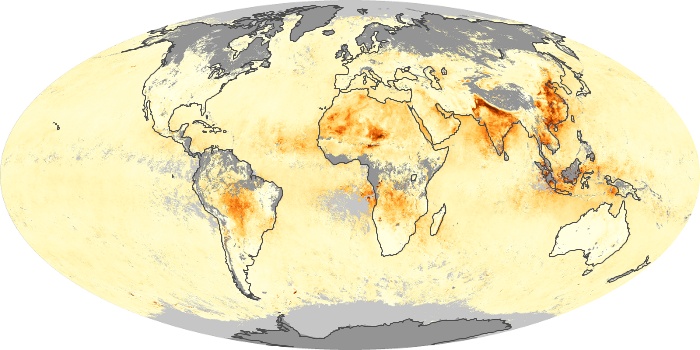
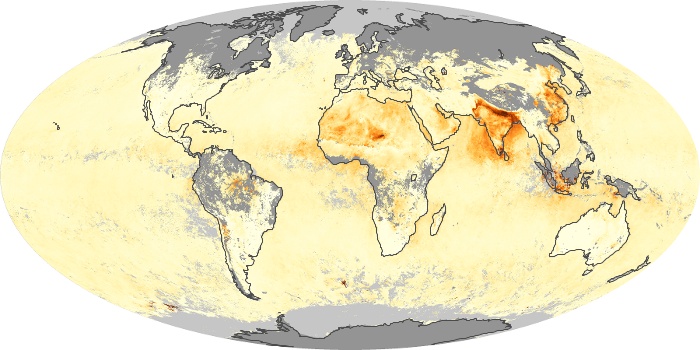
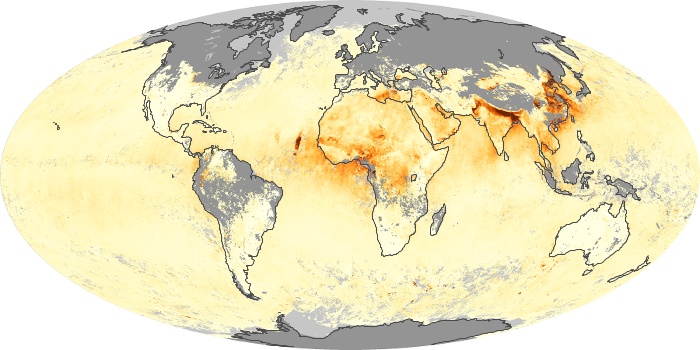
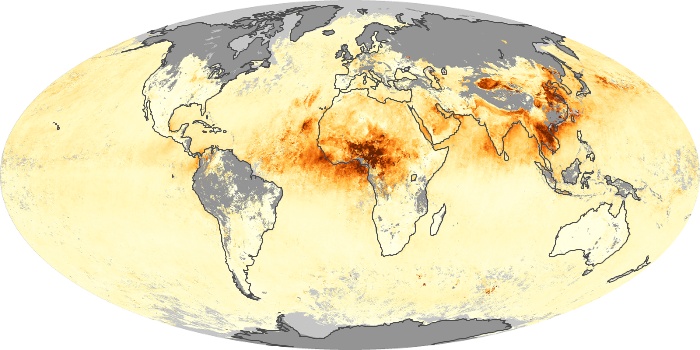
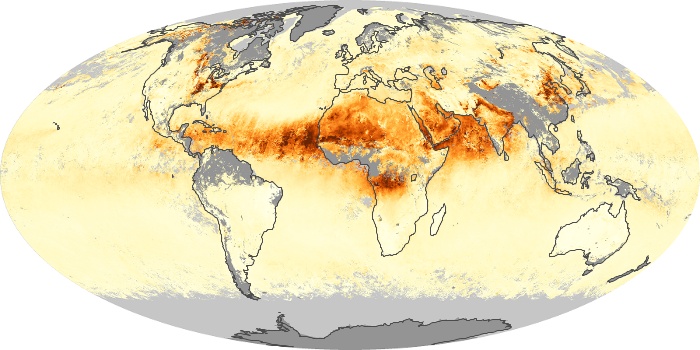
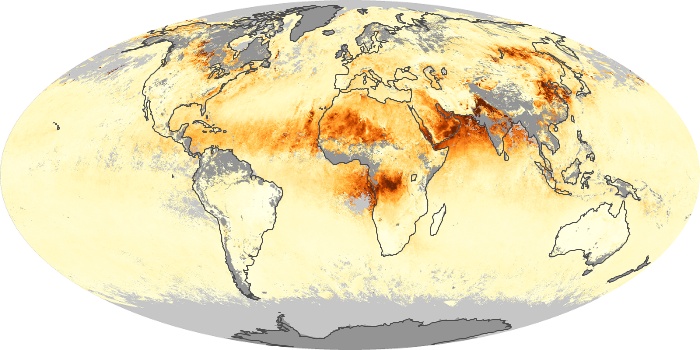
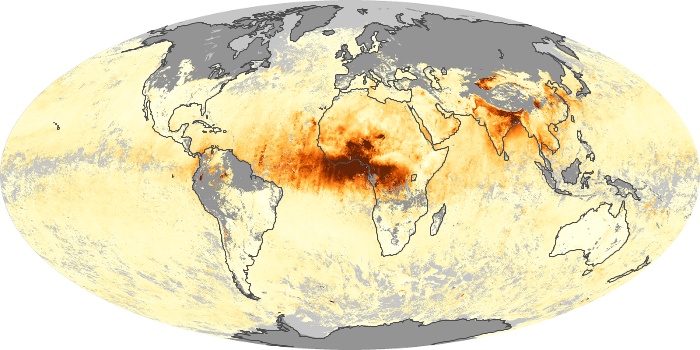
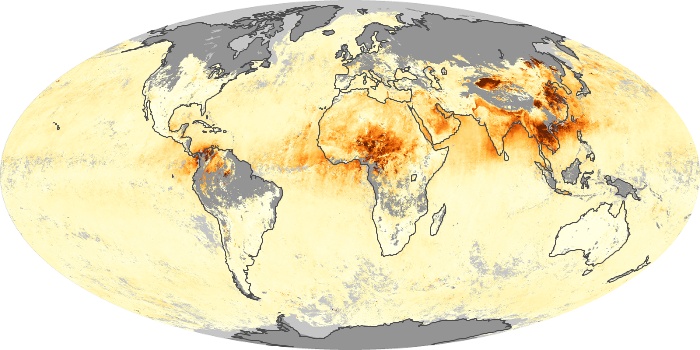
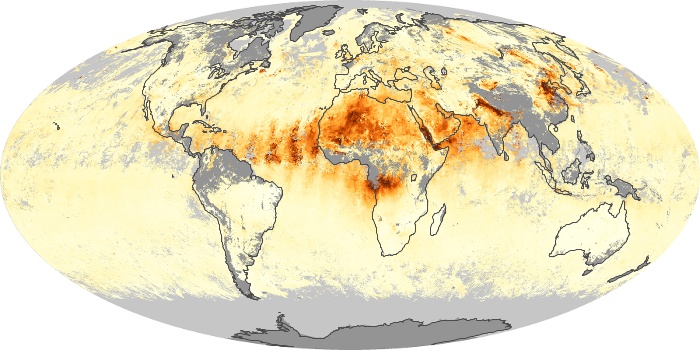
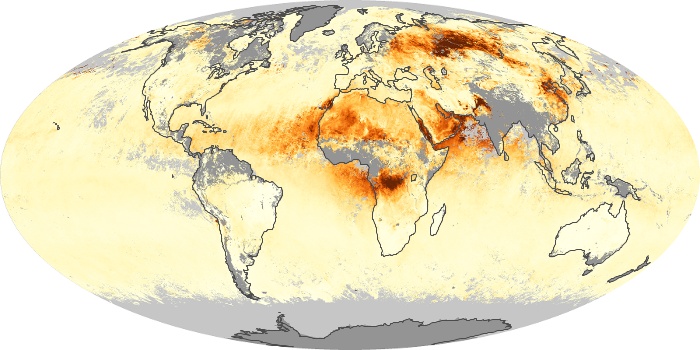
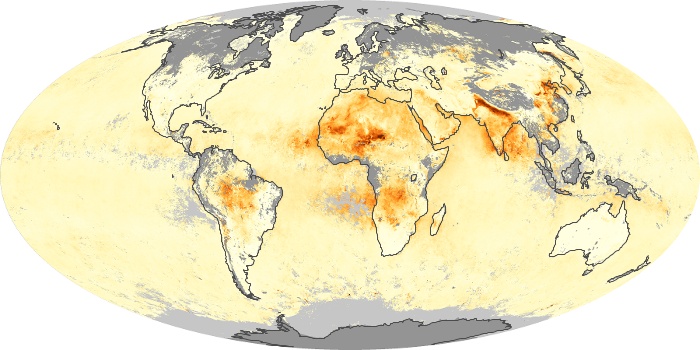
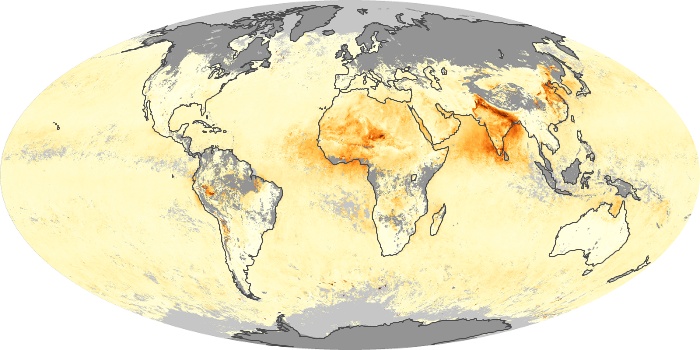
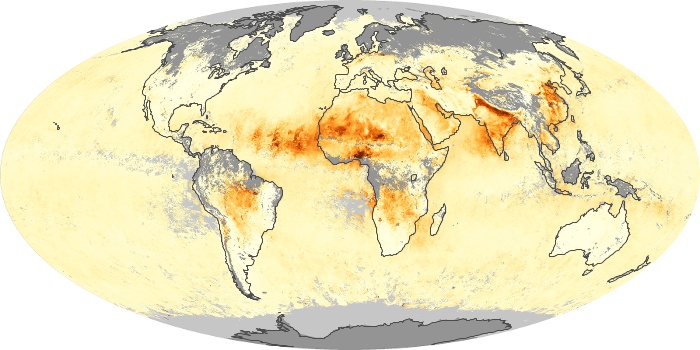
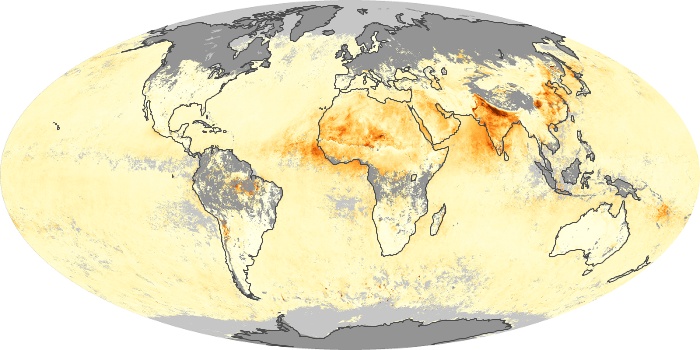
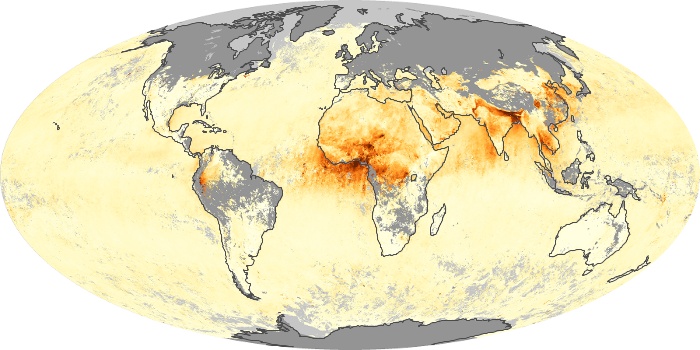
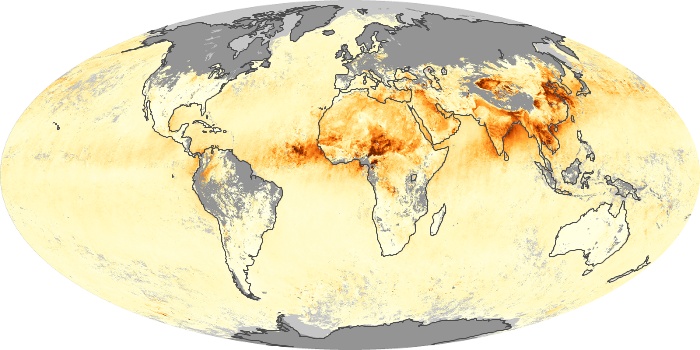
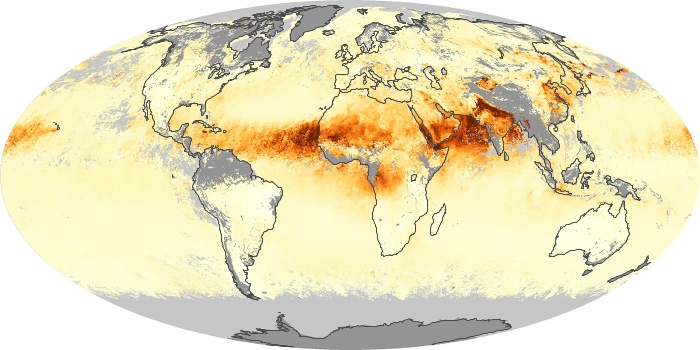
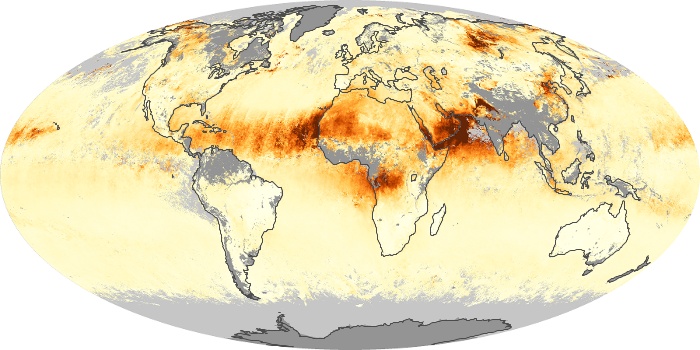
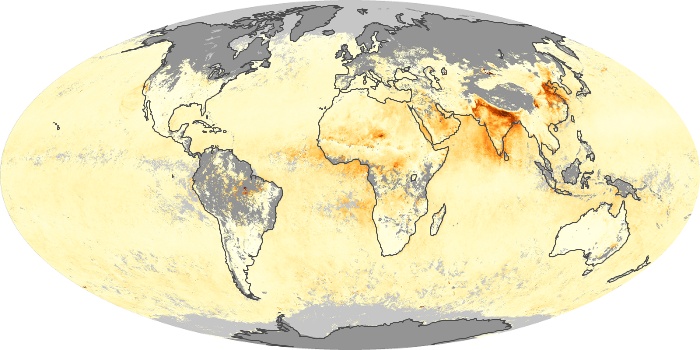
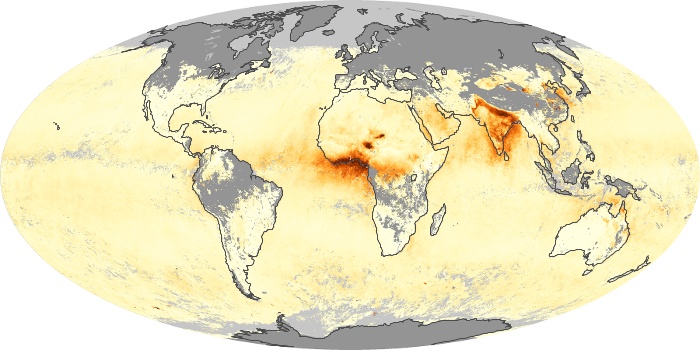
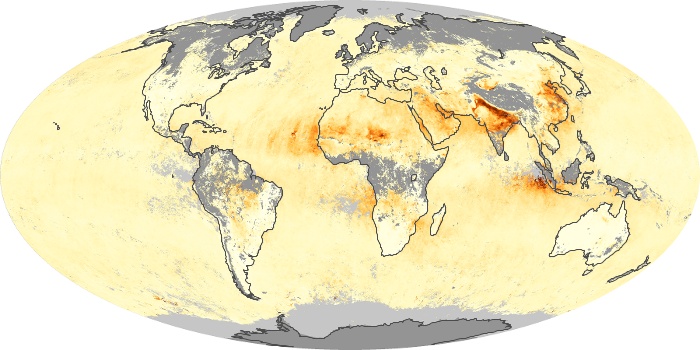
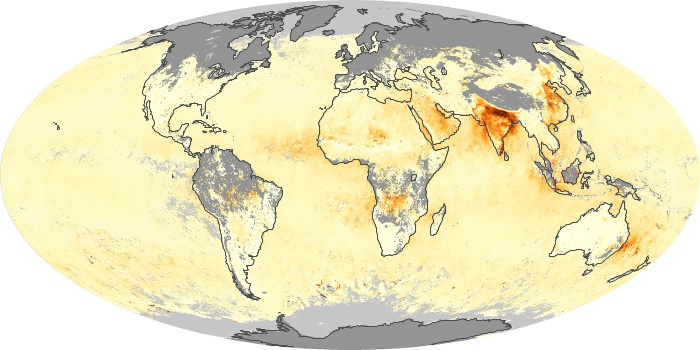
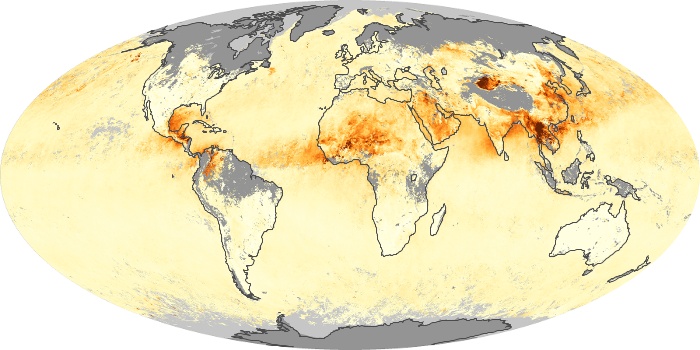
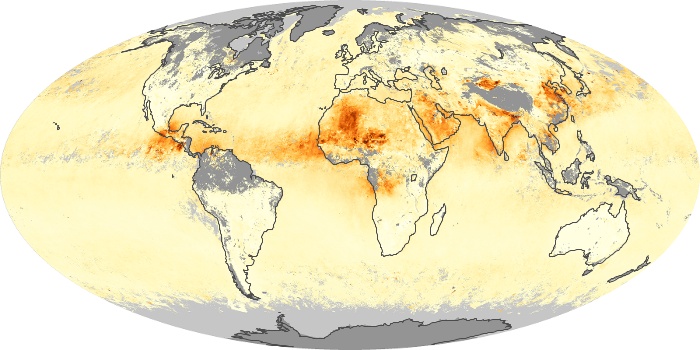
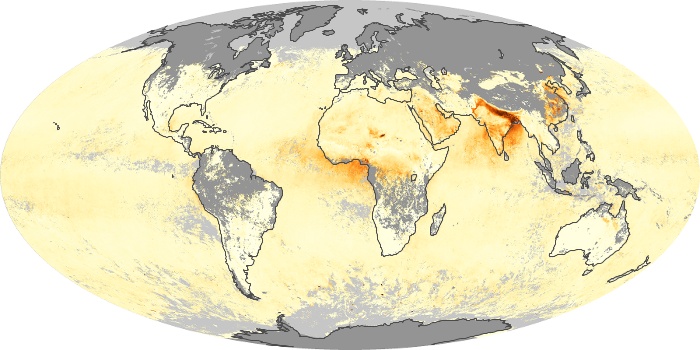
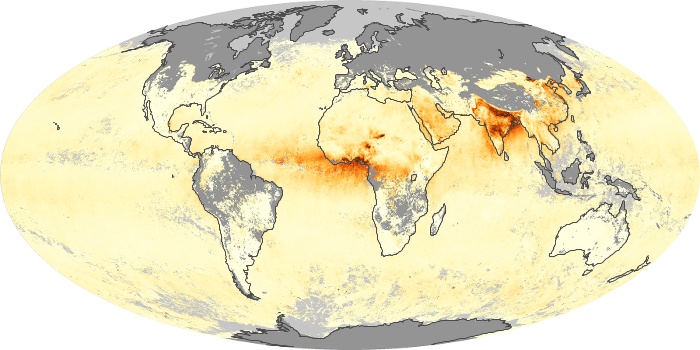
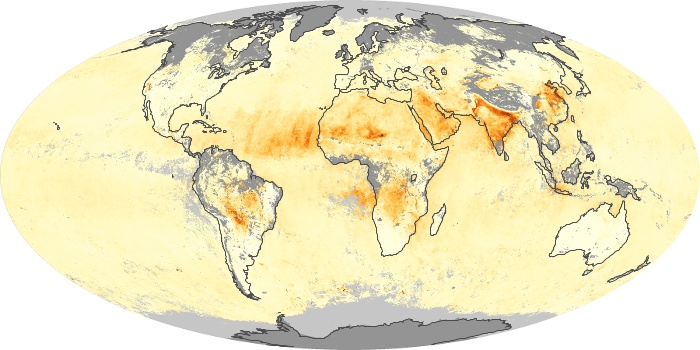
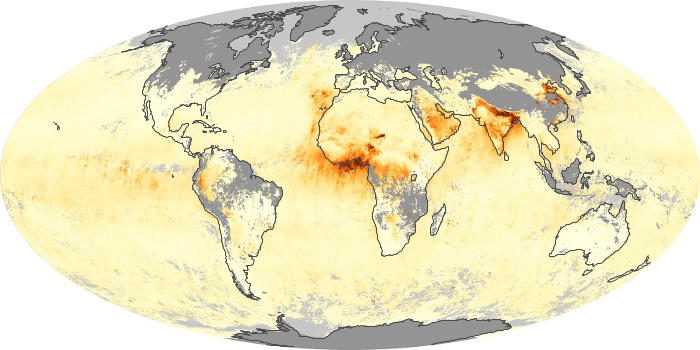
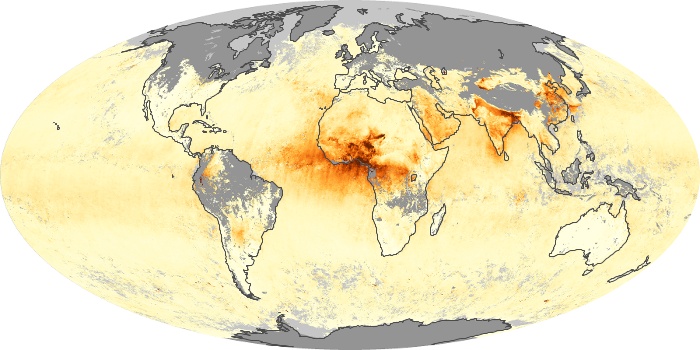
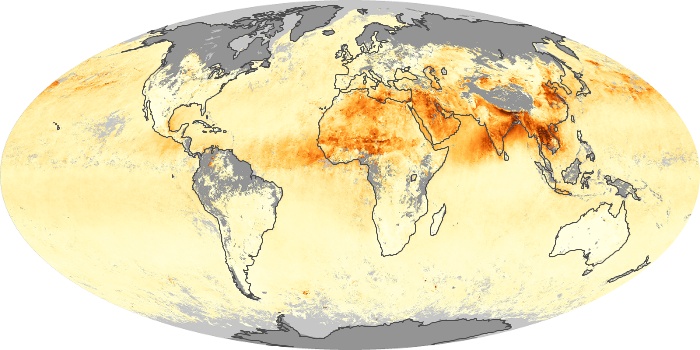
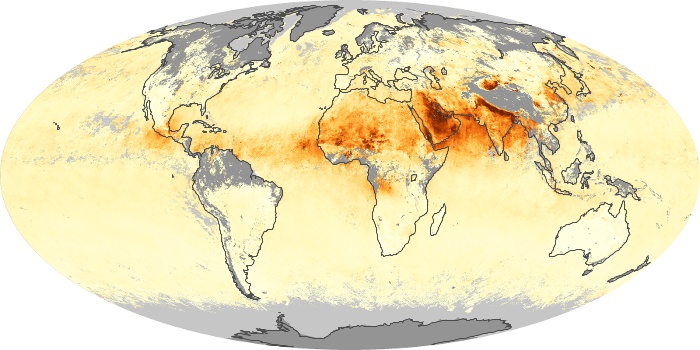
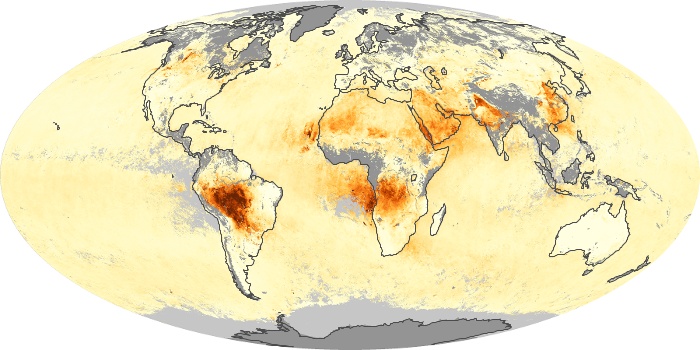
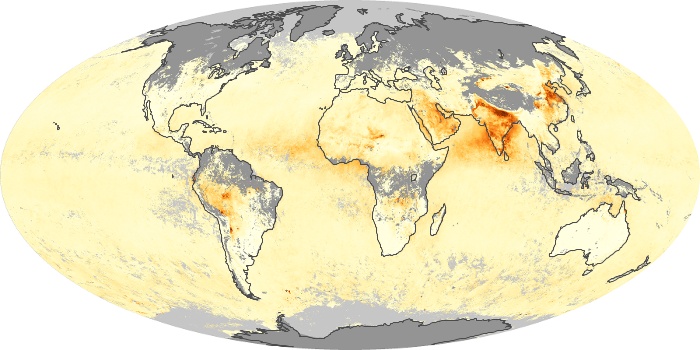
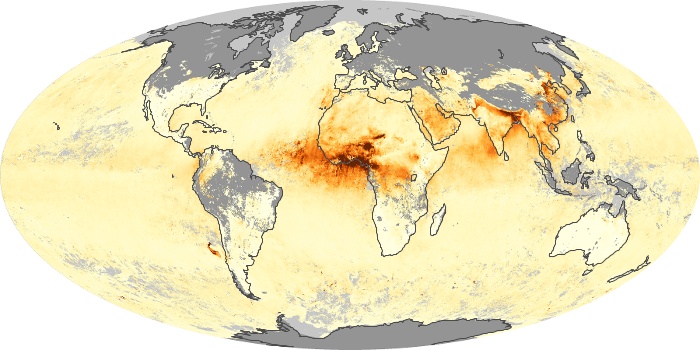
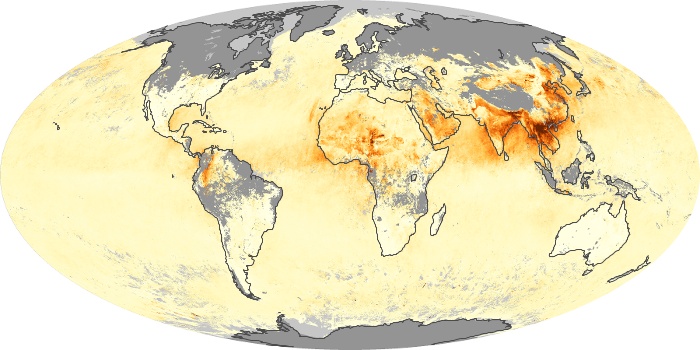
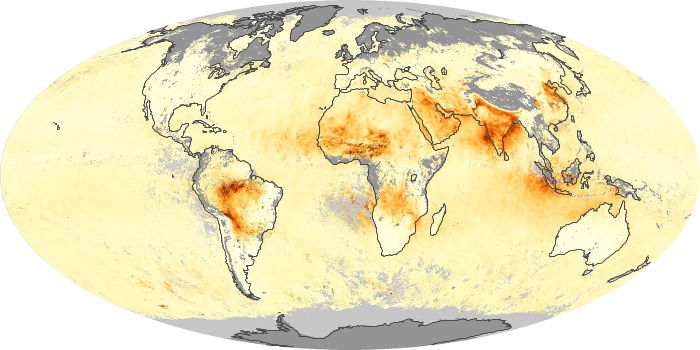
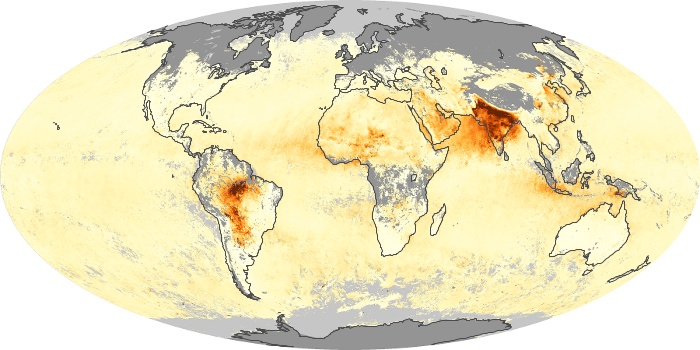
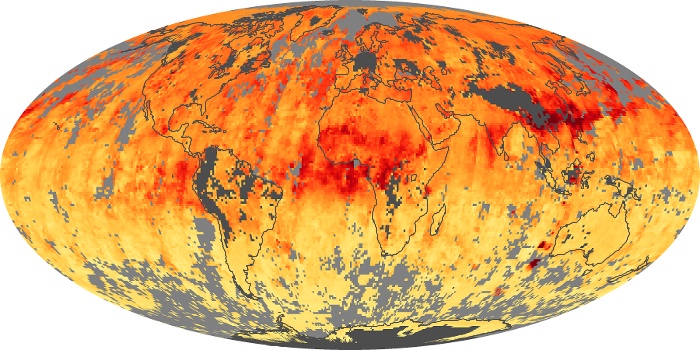
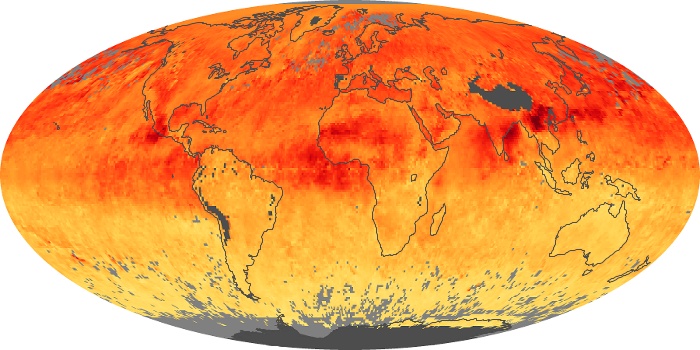
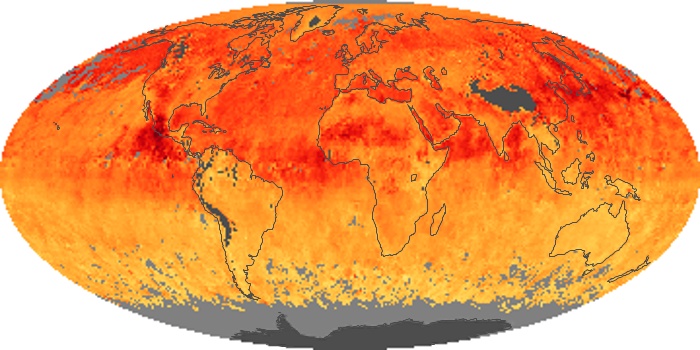
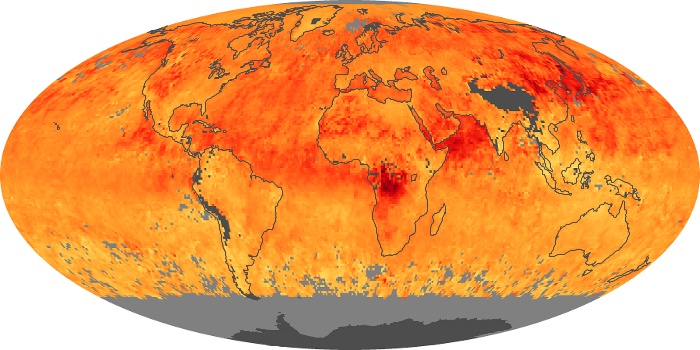
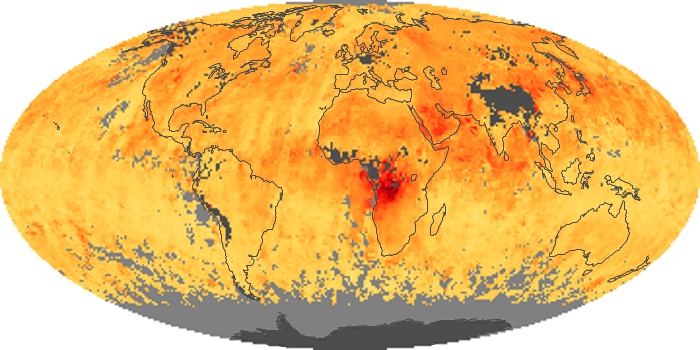
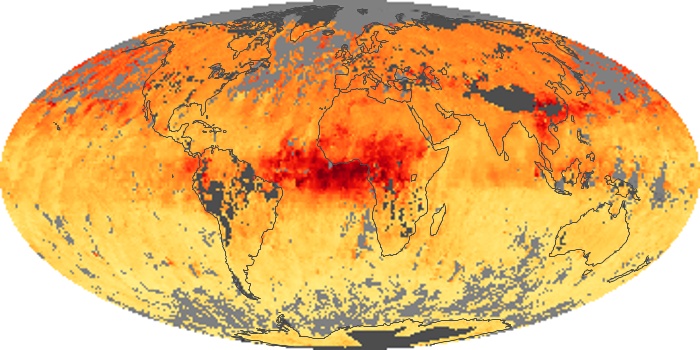
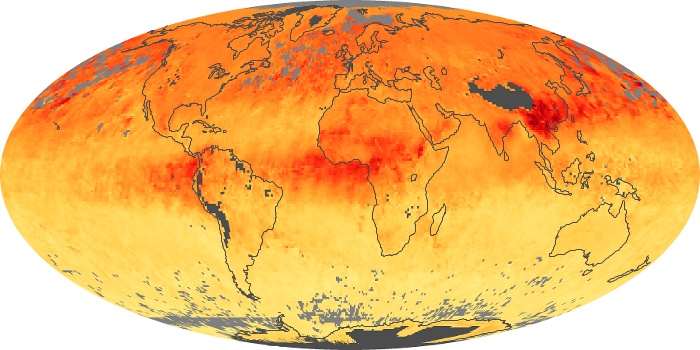
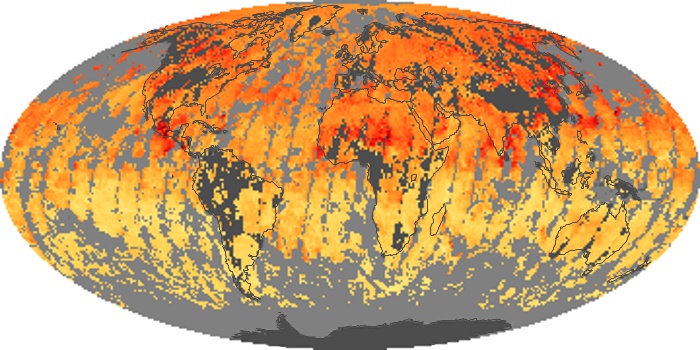
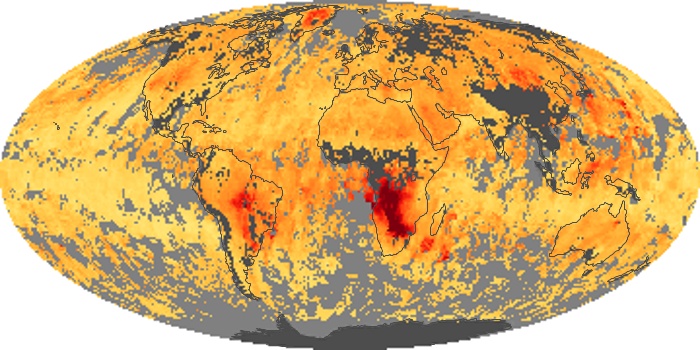
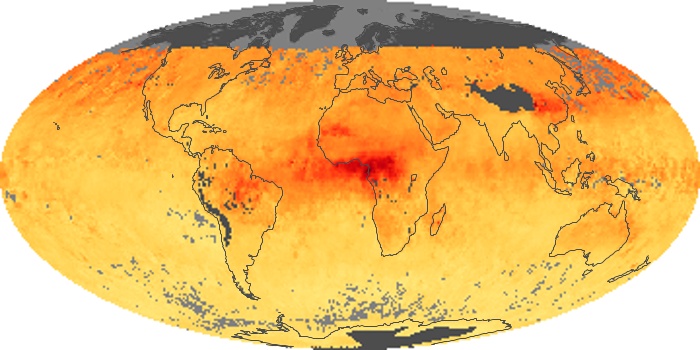
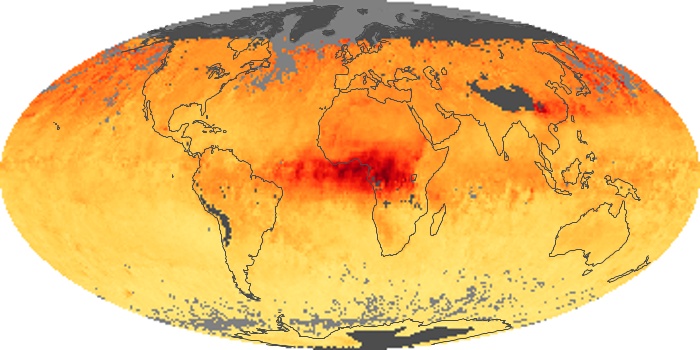
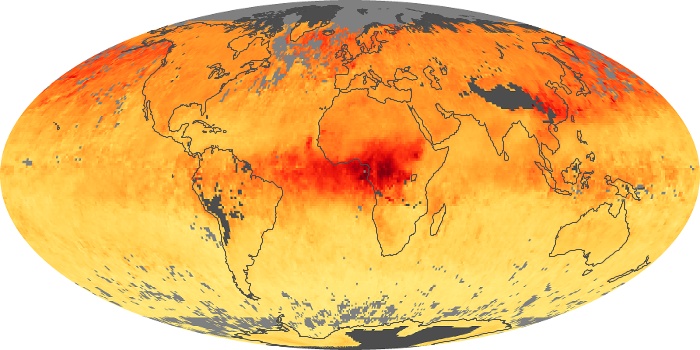
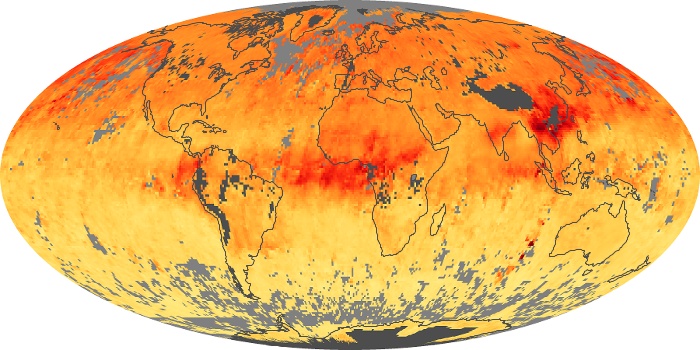
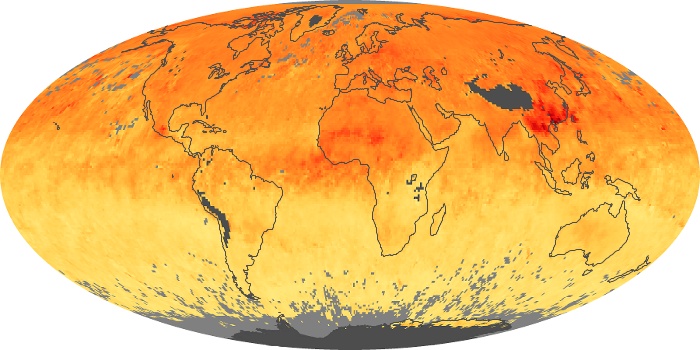
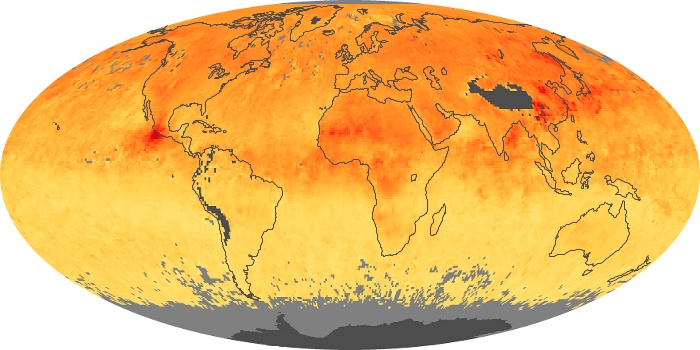
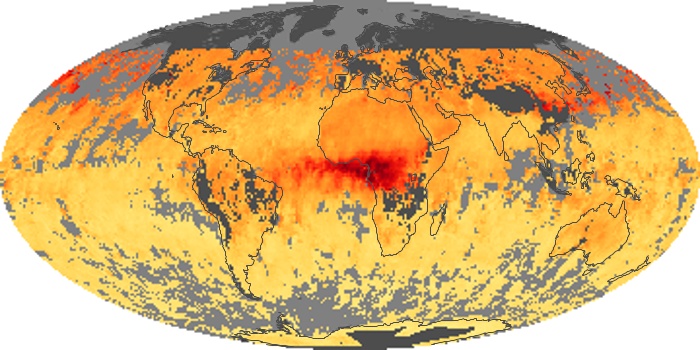
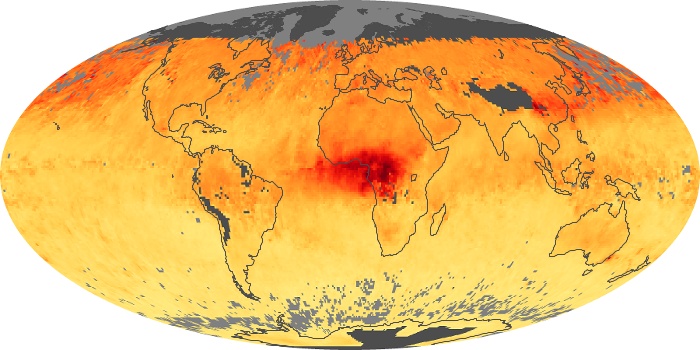
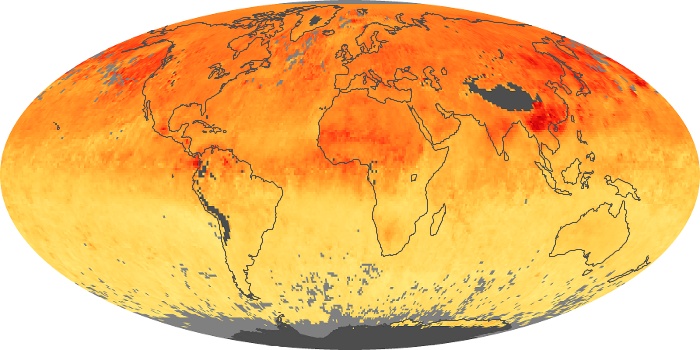
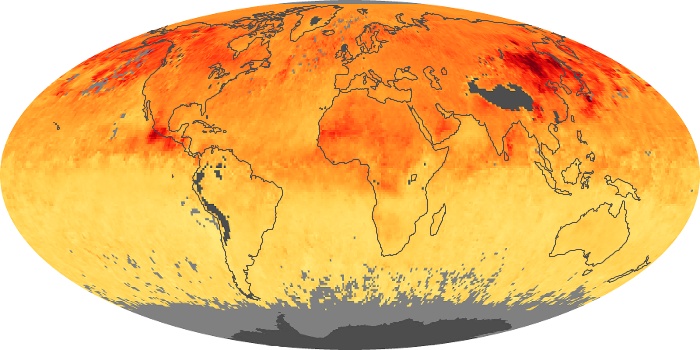
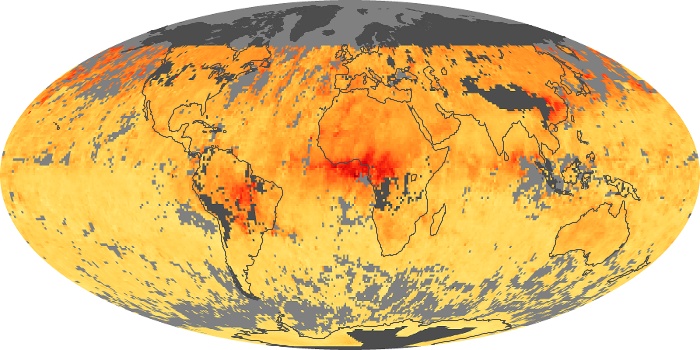
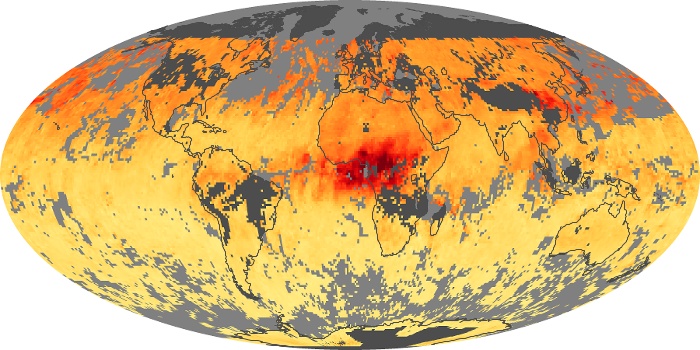
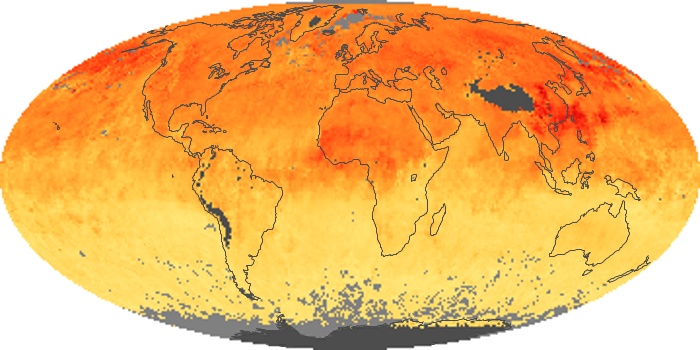
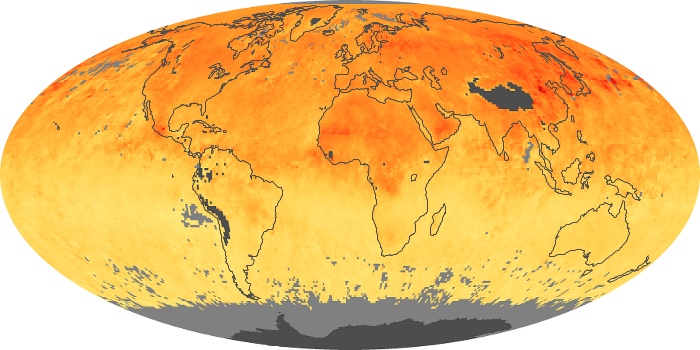
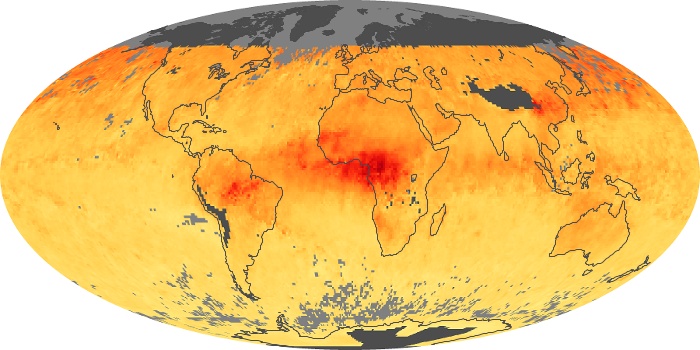
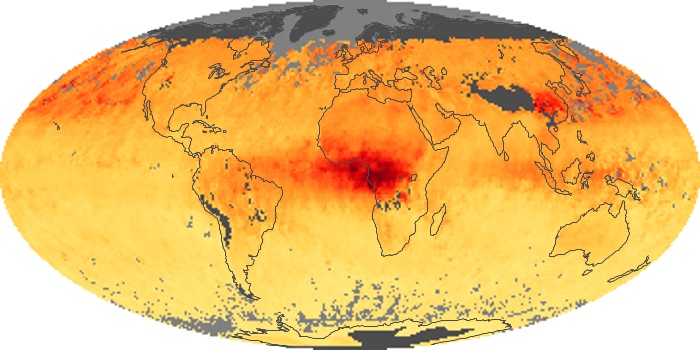
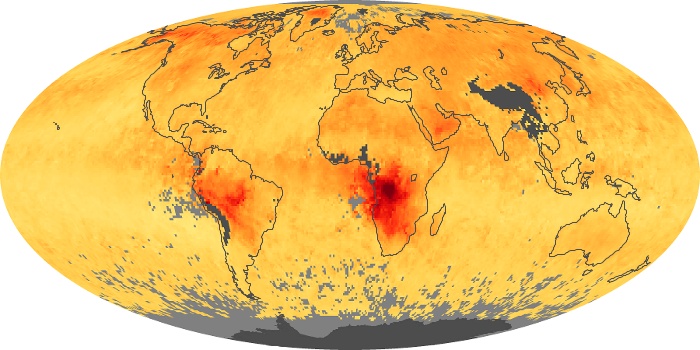
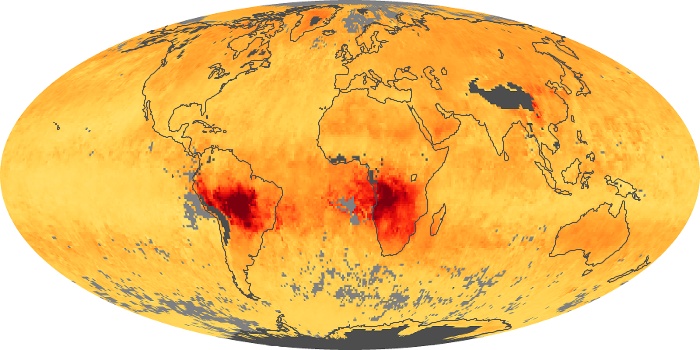
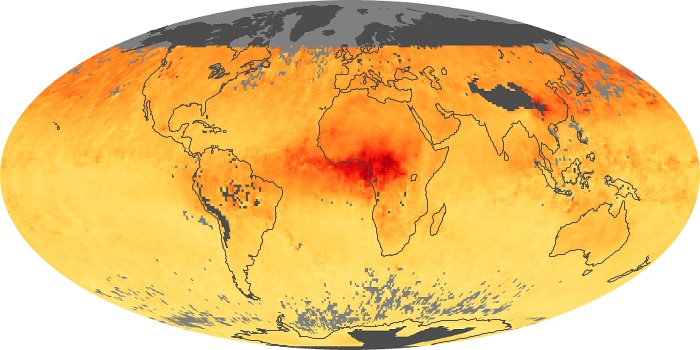
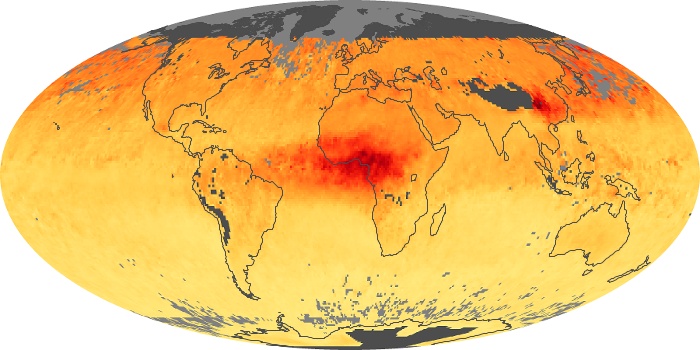
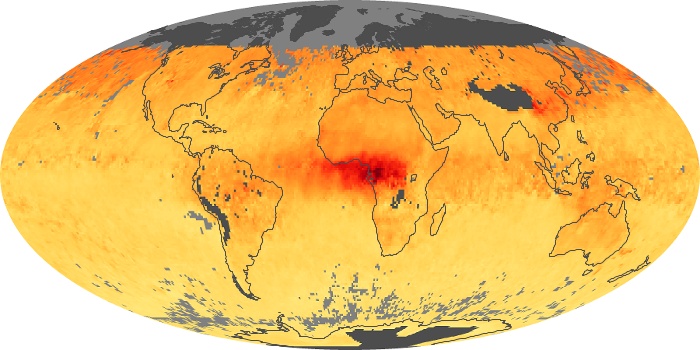
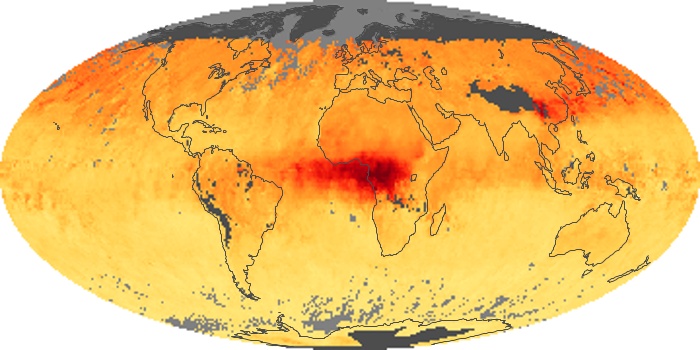
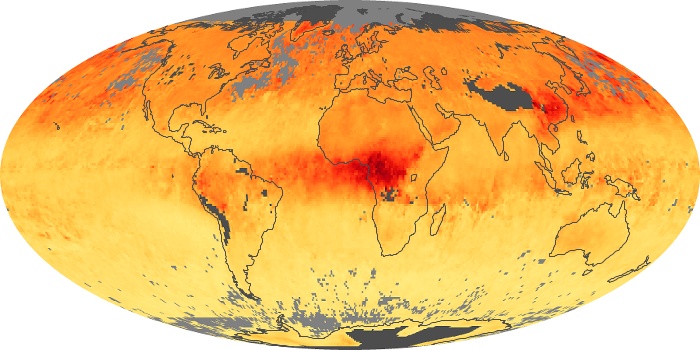
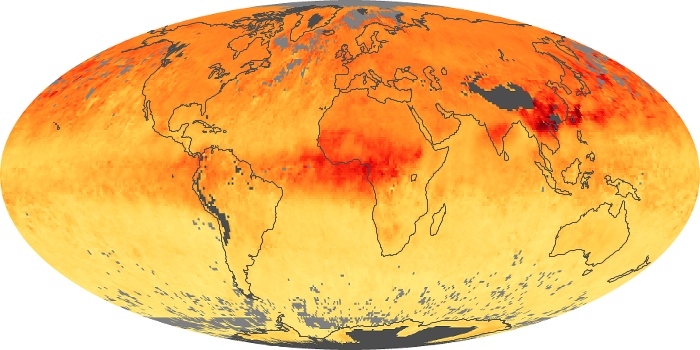
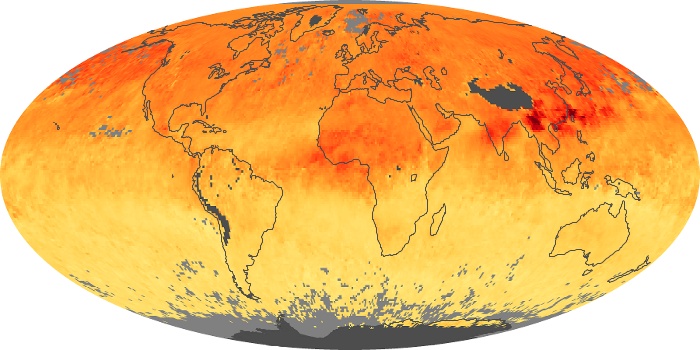
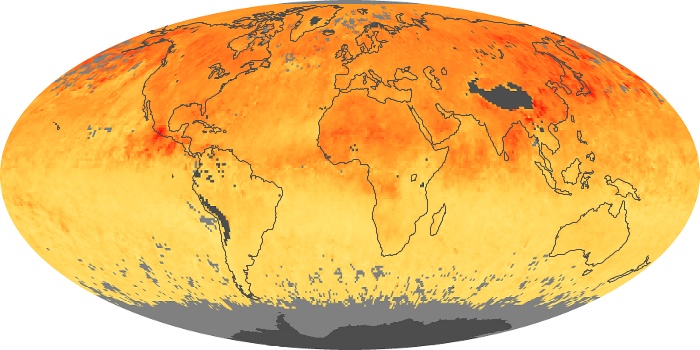
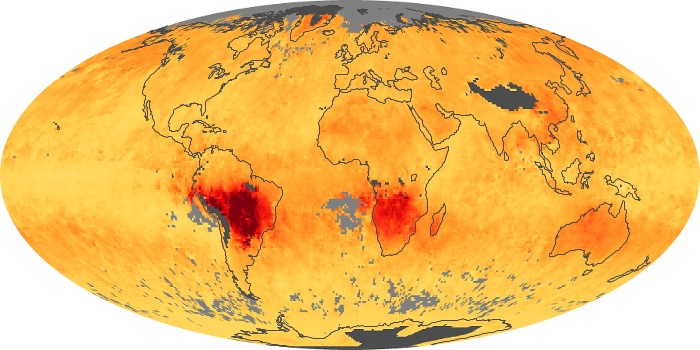
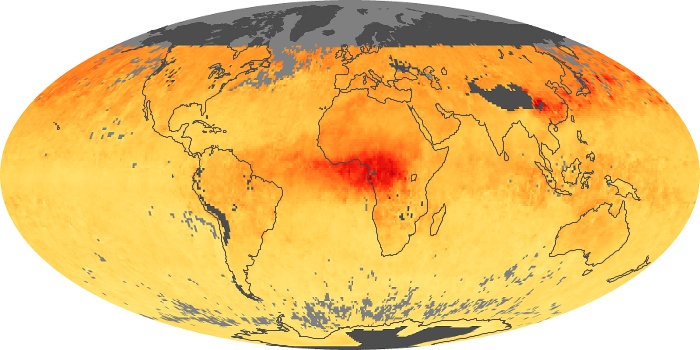
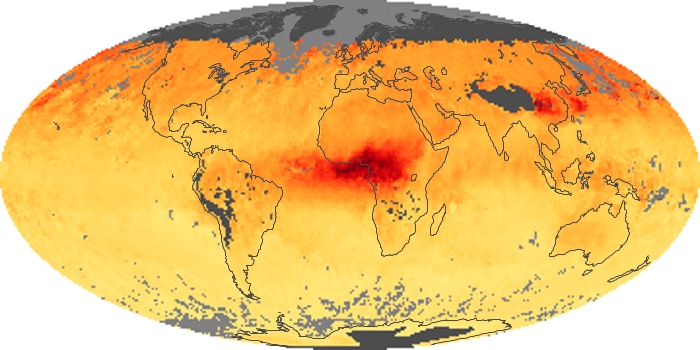
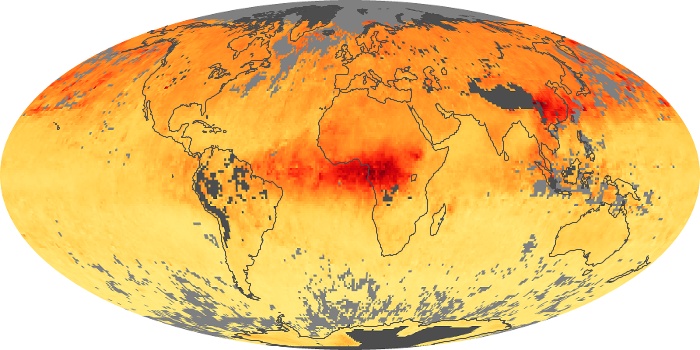
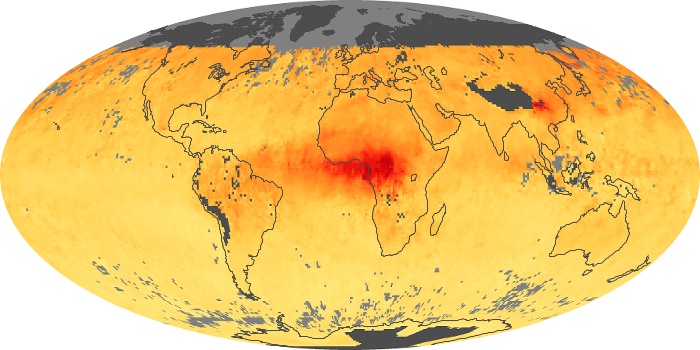
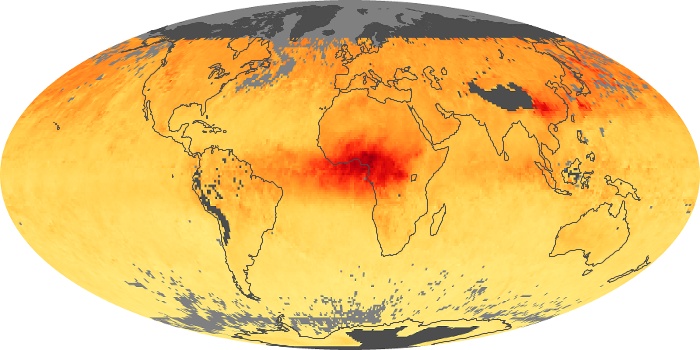
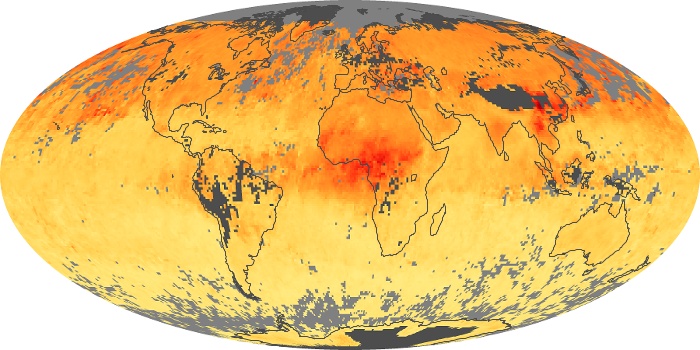
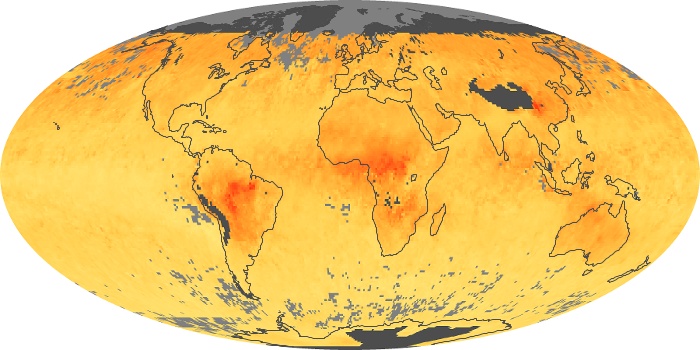
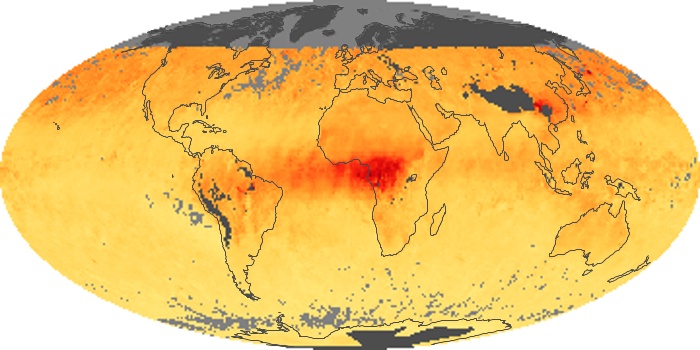
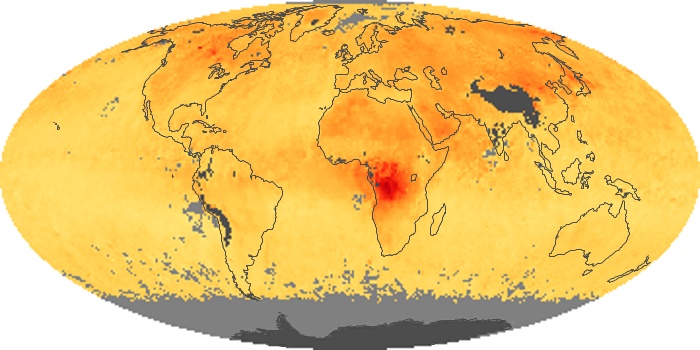
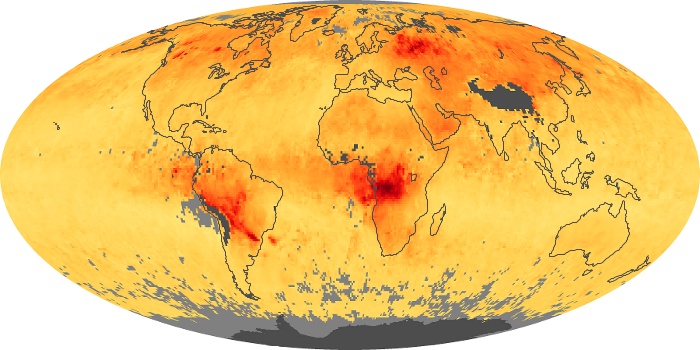
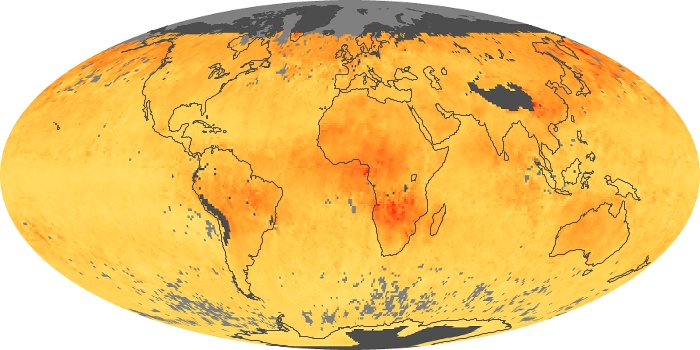
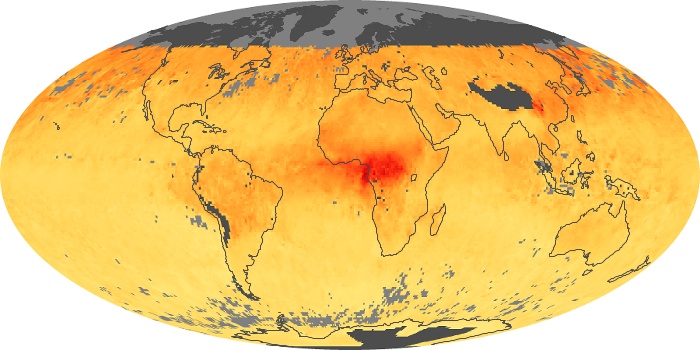
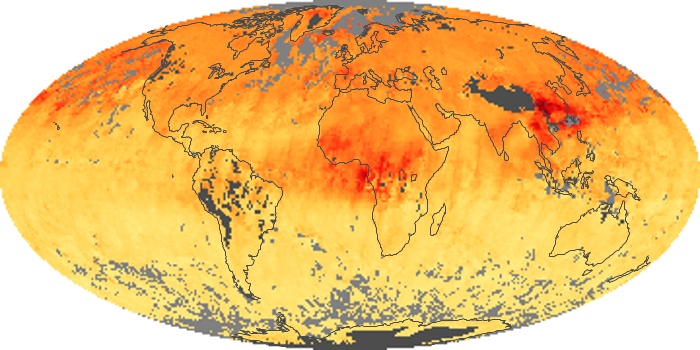
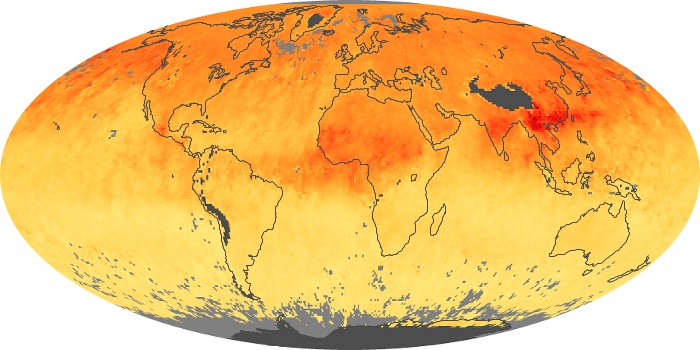
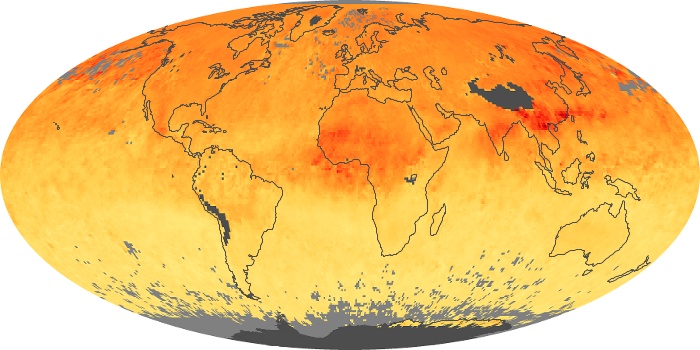
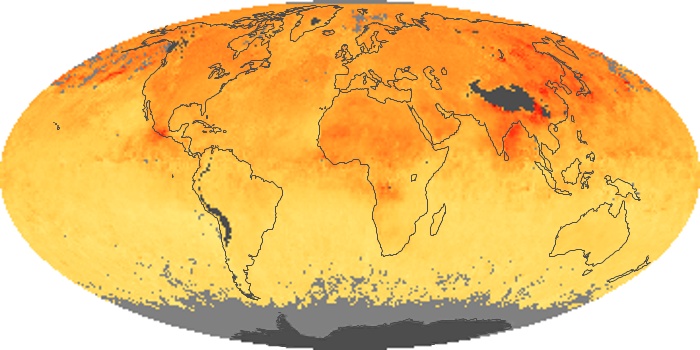
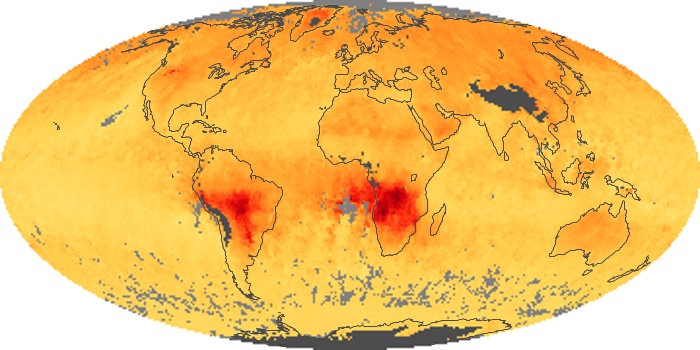
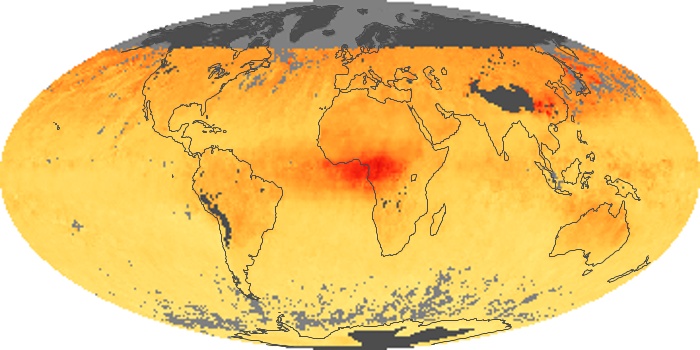
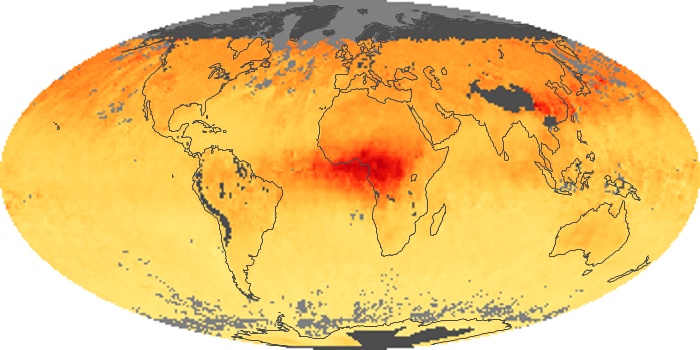
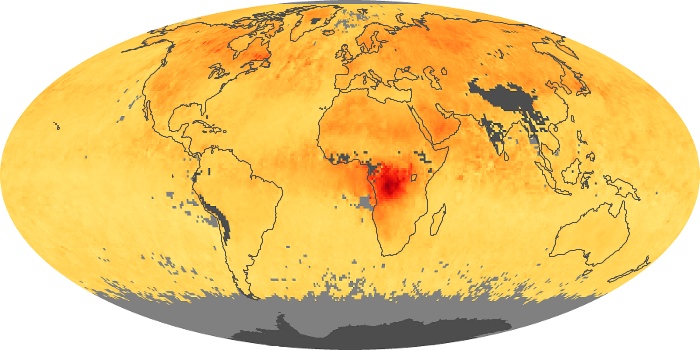
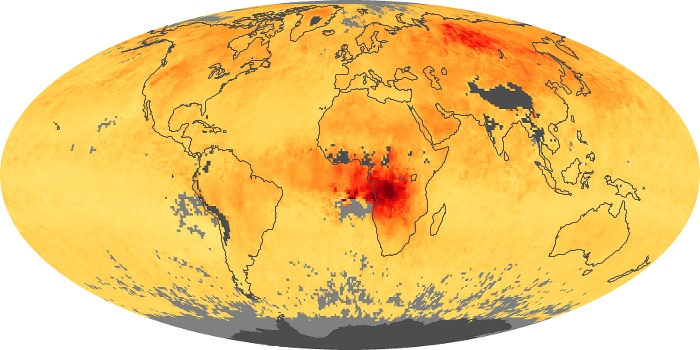
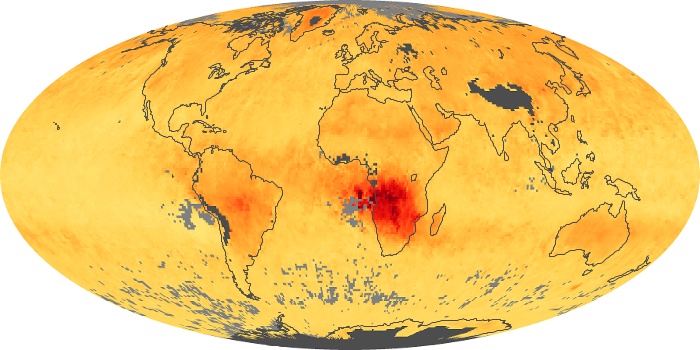
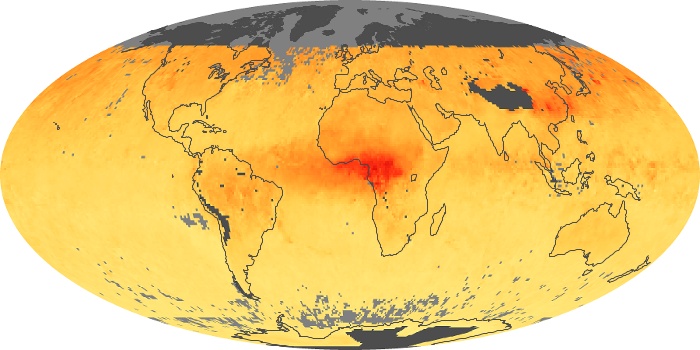
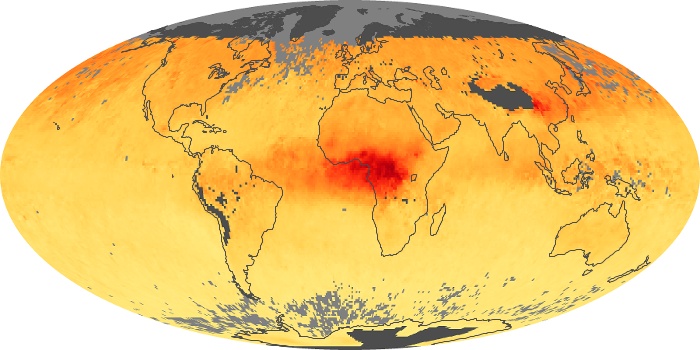
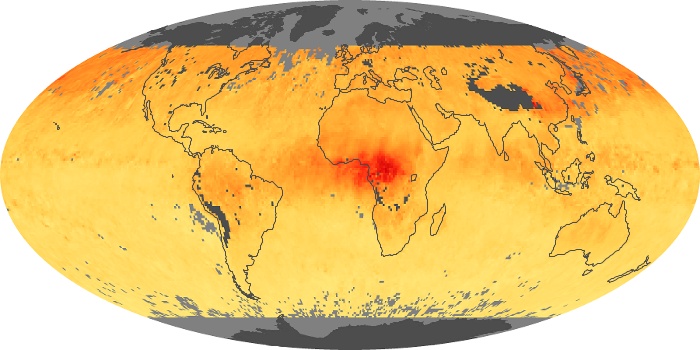
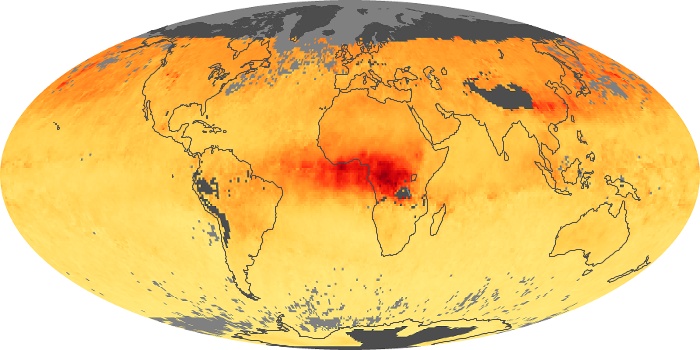
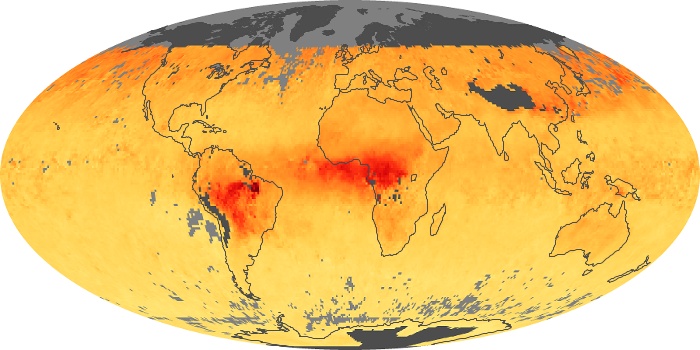
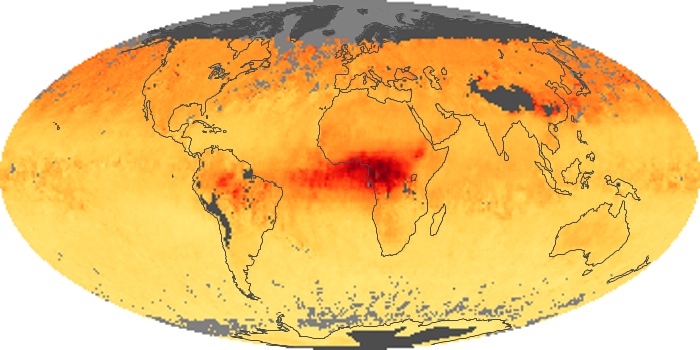
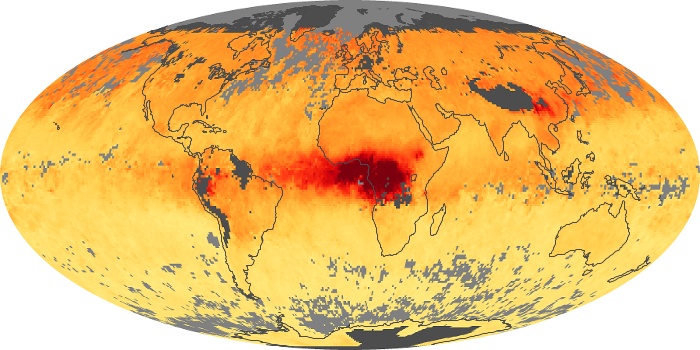
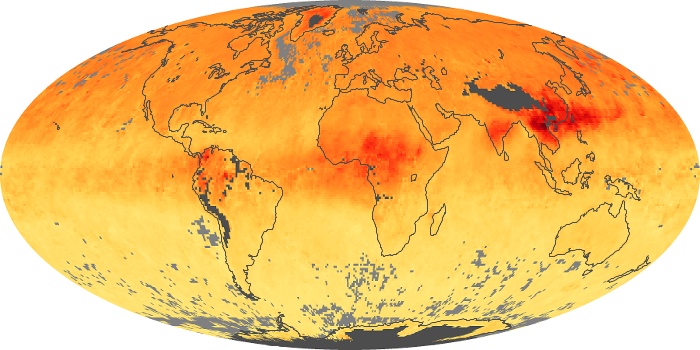
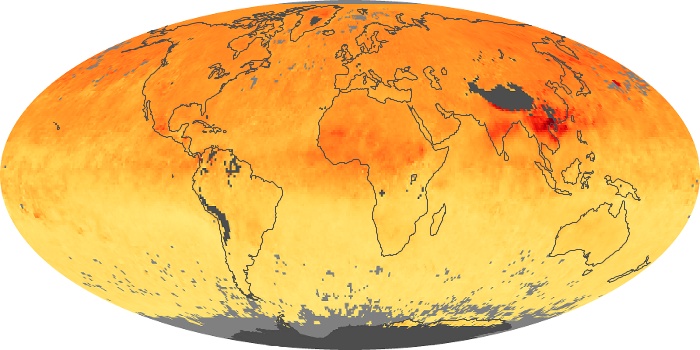
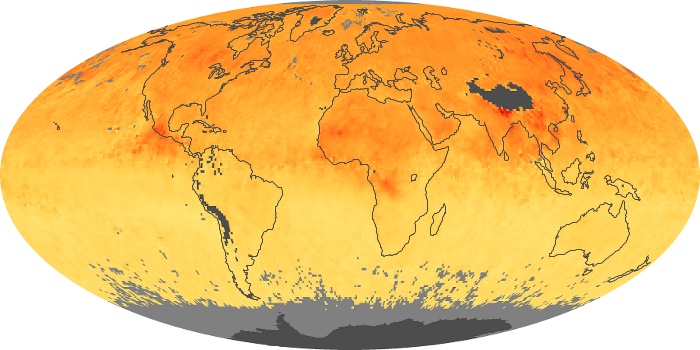
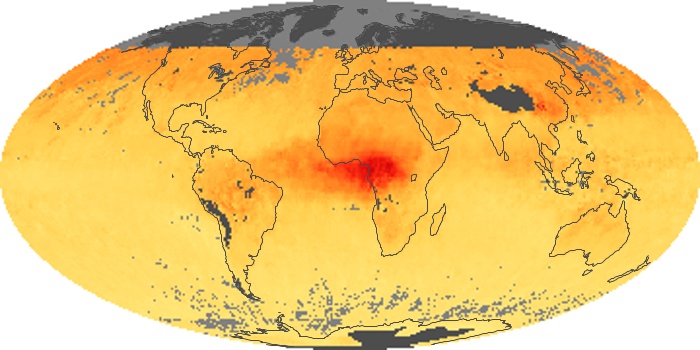
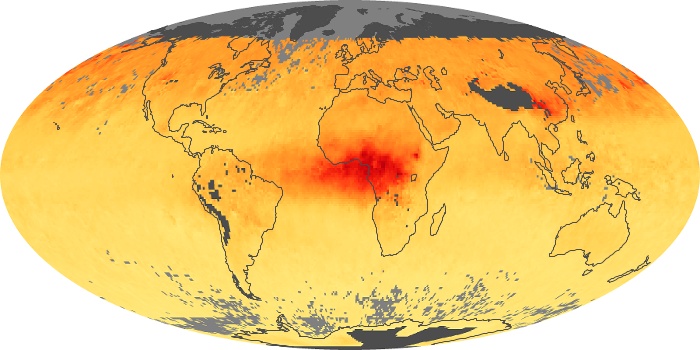
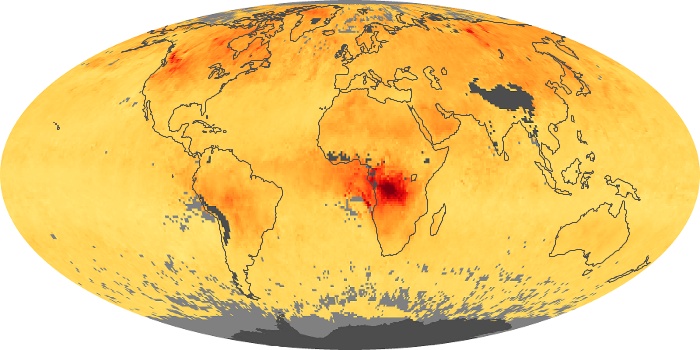
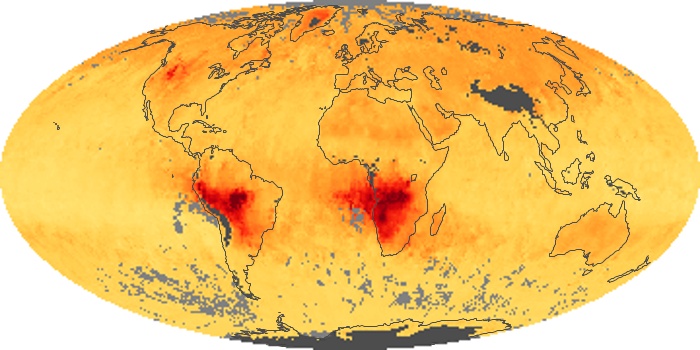
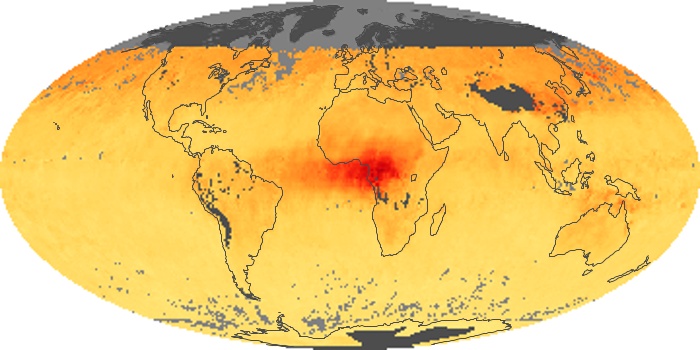
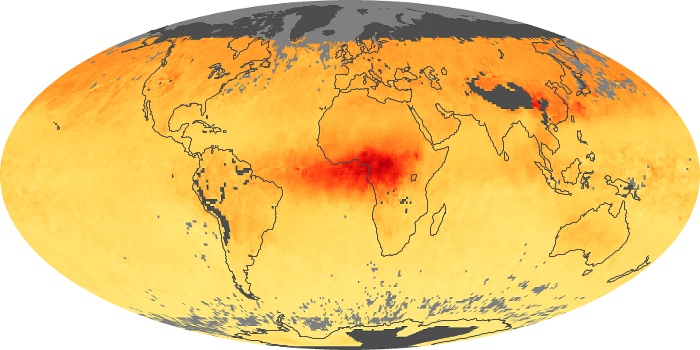
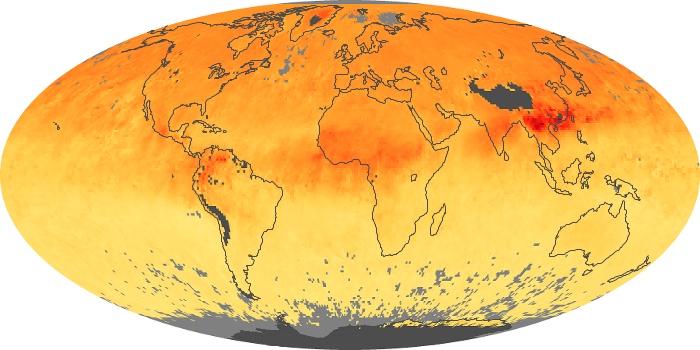
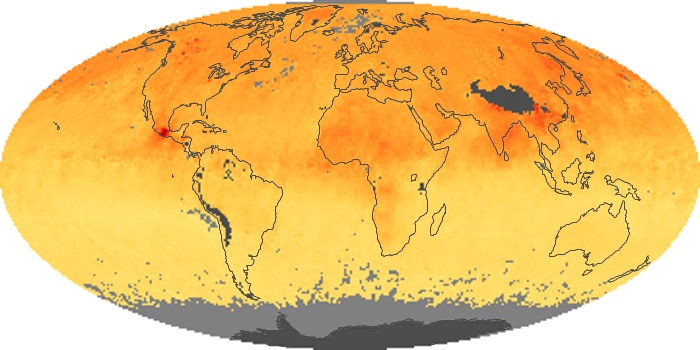
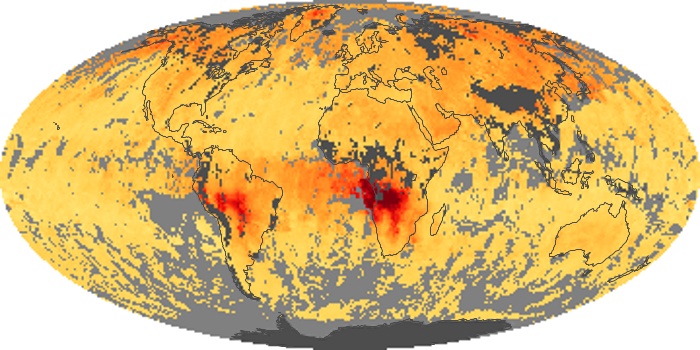
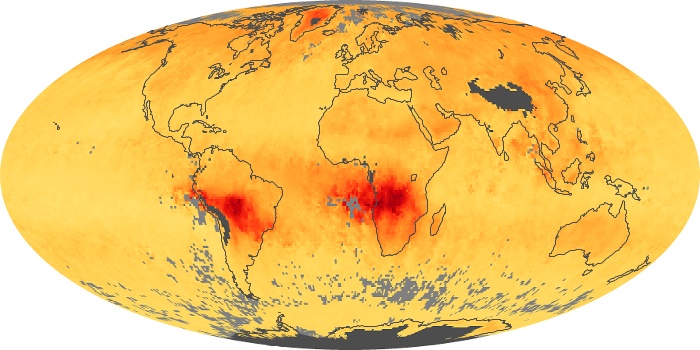
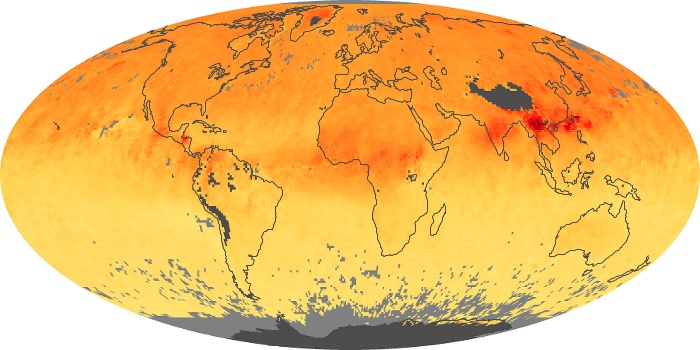
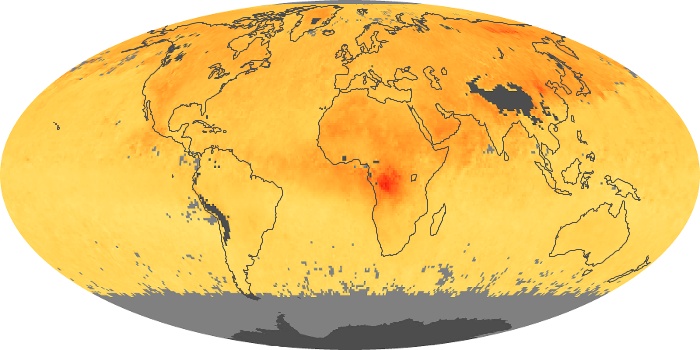
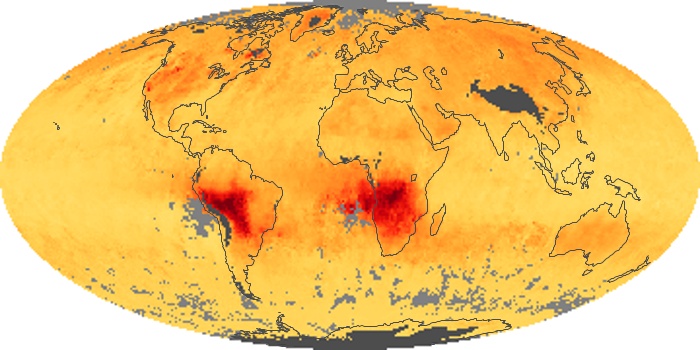
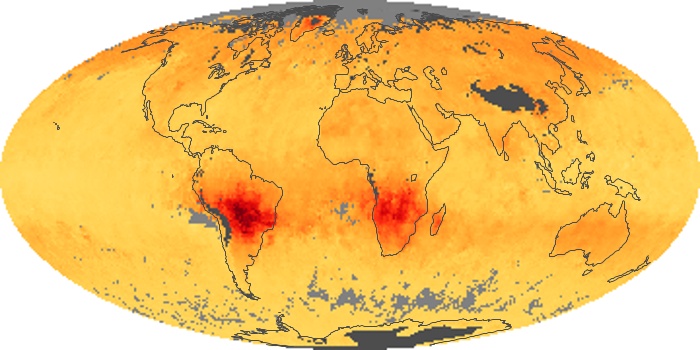
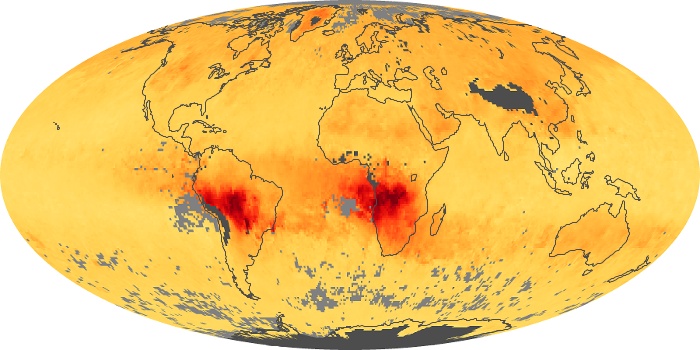
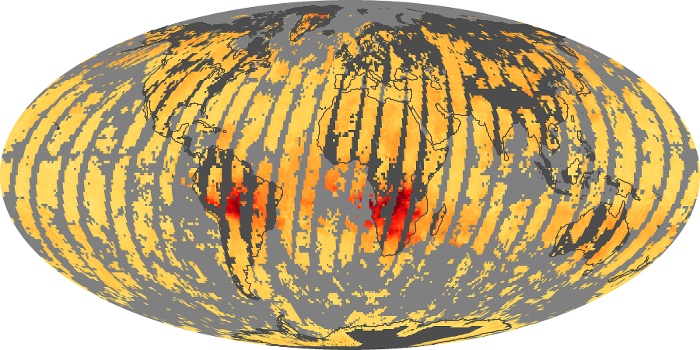
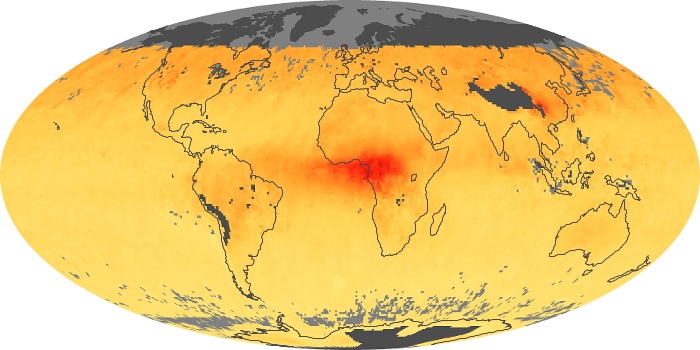
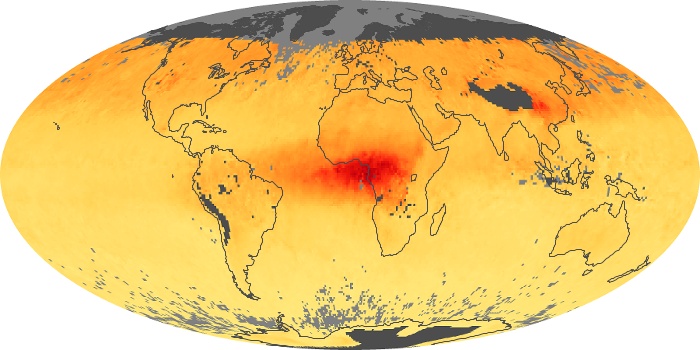
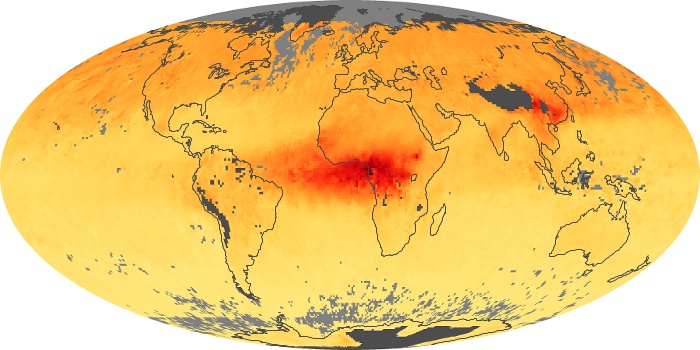
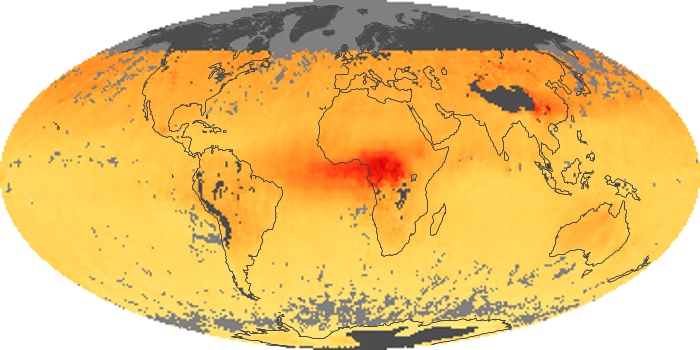
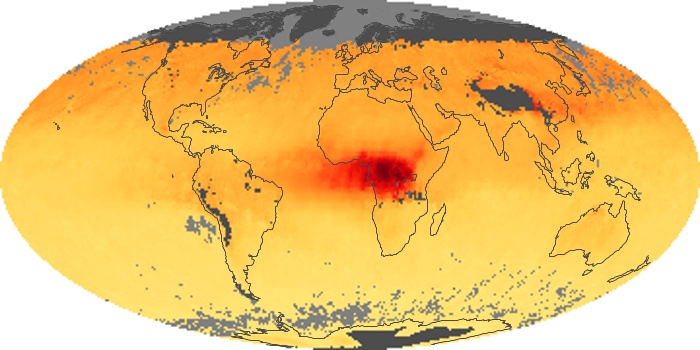
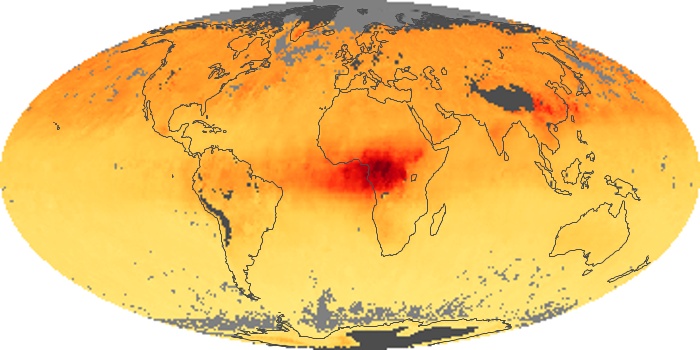
The carbon monoxide maps show the monthly averages of carbon monoxide at an altitude of about 12,000 feet, based on data from the MOPITT sensor on NASA’s Terra satellite. Concentrations of carbon monoxide are expressed in parts per billion by volume (ppbv). A concentration of 1 ppbv means that for every billion molecules of gas in the measured volume, one of them is a carbon monoxide molecule. Yellow areas have little or no carbon monoxide, while progressively higher concentrations are shown in orange and red.
View, download, or analyze more of these data from NASA Earth Observations (NEO):
Aerosol Optical Depth
Carbon Monoxide

alert message