

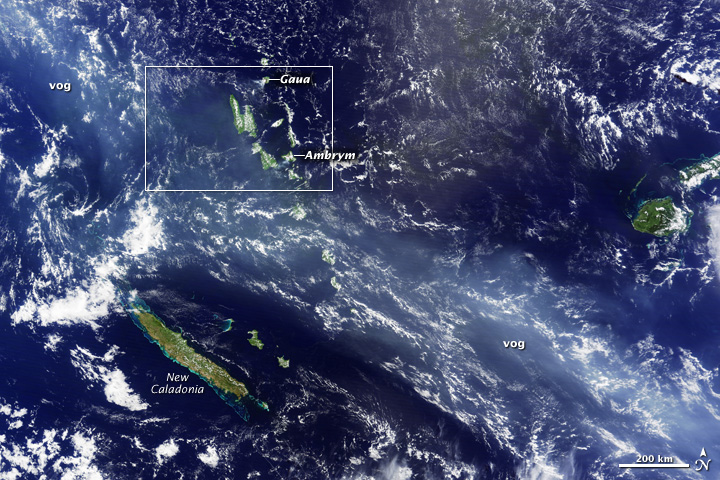
A thick blue haze stretched over the South Pacific archipelago of Vanuatu on the morning of April 12, 2010. The haze was volcanic fog—vog—emitted by Gaua and Ambrym Volcanoes. Both are known for producing volcanic plumes rich in sulfur dioxide. The sulfur dioxide gas emitted by the volcanoes reacts with moisture in the air to create small droplets (called aerosols) of sulfuric acid, which scatters blue light, coloring the plume. Although it is unclear which volcano is emitting more aerosols, the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) has reported daily ash plumes from Gaua since April 8th.
An overview image, top, shows the plume extending for thousands of kilometers to the northwest (upper left) and southeast (lower right) of the islands. The plume appears thicker and bluer in the corner of the image because the satellite is viewing the plume at an angle. The bottom image shows a higher-resolution view of the two volcanoes. This image was acquired by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Terra satellite.
NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team. Caption by Robert Simmon.